Taphophobia
Fear of being buried alive is the fear of being placed in a grave while still alive as a result of being incorrectly pronounced dead. The abnormal, psychopathological version of this fear is referred to as taphophobia (from Greek τάφος - taphos, "grave, tomb"[1] and φόβος - phobos, "fear"[2]), which is translated as "fear of graves".[3]
Before the era of modern medicine, the fear was not entirely irrational. Throughout history, there have been numerous cases of people being buried alive by accident. In 1905, the English reformer William Tebb collected accounts of premature burial. He found 219 cases of near live burial, 149 actual live burials, 10 cases of live dissection and 2 cases of awakening while being embalmed.[4]
The 18th century had seen the development of mouth-to-mouth resuscitation and crude defibrillation techniques to revive persons considered dead, and the Royal Humane Society had been formed as the Society for the Recovery of Persons Apparently Drowned.[5] In 1896, an American funeral director, T. M. Montgomery, reported that "nearly 2% of those exhumed were no doubt victims of suspended animation",[6] although folklorist Paul Barber has argued that the incidence of burial alive has been overestimated, and that the normal effects of decomposition are mistaken for signs of life.[7]
There have been many urban legends of people being accidentally buried alive. Legends included elements such as someone entering into the state of sopor or coma, only to wake up years later and die a horrible death. Other legends tell of coffins opened to find a corpse with a long beard or corpses with the hands raised and palms turned upward. Of note is a legend about the premature burial of Ann Hill Carter Lee, the wife of Henry Lee III.[8]
Several notable historical figures are thought to have been afraid of live burial, including Frédéric Chopin (who requested that his heart be cut out to ensure his death), George Washington (who requested that his body be laid out for three days), and Hans Christian Andersen and Alfred Nobel (who both asked to have their arteries cut open).[9]
Literature found fertile ground in exploring the natural fear of being buried alive. One of Edgar Allan Poe's horror stories, "The Premature Burial", is about a person suffering from taphophobia. Other Poe stories about premature burial are "The Fall of the House of Usher" and "The Cask of Amontillado"—and to a lesser extent, "The Black Cat".
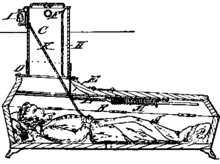
Fear of being buried alive was elaborated to the extent that those who could afford it would make all sorts of arrangements for the construction of a safety coffin[10] to ensure this would be avoided (e.g., glass lids for observation, ropes to bells for signaling, and breathing pipes for survival until rescued).[11]
An urban legend states that the sayings "Saved by the bell" and "Dead ringer" are both derived from the notion of having a rope attached to a bell outside the coffin that could alert people that the recently buried person is not yet deceased; these theories have been proven a hoax.[12][13]
Although greater public confidence in the medical profession and its ability to diagnose death accurately has seen a reduction in fear of premature burial after the early 20th century there have been periods of public alarm in recent decades after medical errors in diagnosing death were reported.[14] Taphophobia may remain common in some parts of the world. For example, a study of Pakistani women found severe taphophobia in one third of subjects with mental illness and a mild degree of this fear in half of the controls.[15] Although rare in the developed world, a recent study reported three cases of taphophobia among older people in the west of Ireland.[16]
See also
References
- τάφος, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- φόβος, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- Dietrich, H (1977). "Taphophobia and resurrection mania". Schweizer Arkiv für Neurologie, Neurochirurgie und Psychiatrie. 120 (2): 195–203. PMID 905788.
- Quigley, Christine. The Corpse: A History
- Steven B. Harris, M.D. (September 1990). "The Society for the Recovery of Persons Apparently Dead". Cryonics. Retrieved 2006-12-06.
- "Just Dying to Get Out", from Snopes.com
- Barber, Paul. Vampires, Burial and Death: Folklore and Reality. Yale University Press, 1988.
- Robert E. Lee's Mother
- Little, Becky. "Why Many Famous Figures Feared They'd Be Buried Alive". History. A&E Television Networks. Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- A Short History of Security Coffins Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine
- Improved burial case
- Wilton, David (2009). Word Myths: Debunking Linguistic Urban Legends. Oxford University Press. pp. 75–77. ISBN 978-0-19-537557-2.
- Mikkelson, Barbara. "snopes.com: Life in the 1500s". snopes.com. Retrieved 2012-08-23.
- Bondeson, Jan (17 March 2002). Buried Alive: The Terrifying History of Our Most Primal Fear. London: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0393322224.
- Bajwa, Munaza (2014). "Prevalence and factors associated with phobias among women". Asean Journal of Psychiatry. 15 (2): 140–145.
- Fanous, S.; O’Keeffe, S.T. (June 2015). "Not yet dead and buried! Three cases of taphophobia in older people". European Geriatric Medicine. 6 (3): 274–275. doi:10.1016/j.eurger.2015.01.011.