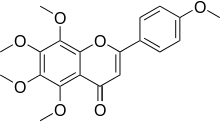
Tangeretin
Tangeretin is an O-polymethoxylated flavone that is found in tangerine and other citrus peels. Tangeretin strengthens the cell wall and acts as a plant's defensive mechanism against disease-causing pathogens.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-2- | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.883 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H20O7 | |
| Molar mass | 372.37 g/mol |
| Density | 1.244 ± 0.06 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 155 to 156 °C (311 to 313 °F; 428 to 429 K) |
| Boiling point | 565.3 ± 50.0 °C (1,049.5 ± 90.0 °F; 838.4 ± 50.0 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It has also been used as a marker compound to detect contamination in citrus juices.[2]
The following is a list of methods used to extract tangeretin from citrus peels:
- column chromatography
- preparative-high performance liquid chromatography
- super critical fluid chromatography
- high speed counter current chromatography
- a combination of vacuum flash silica gel chromatography and flash C8 column chromatography
- flash chromatography
However, methods for tangeretin extraction are currently being tested to maximize efficiency and percent yields as its uses in treatment of cancer and other diseases are becoming better understood.[2]
Tangeretin is commercially available as a dietary supplement.
References
- SciFinder.com (accessed Nov. 6, 2012). Tangeretin (481-53-8).
- Uckoo, RM; et al. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.