Tissue factor pathway inhibitor
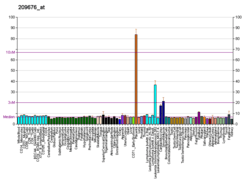
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (or TFPI) is a single-chain polypeptide which can reversibly inhibit Factor Xa (Xa). While Xa is inhibited, the Xa-TFPI complex can subsequently also inhibit the FVIIa-tissue factor complex. TFPI contributes significantly to the inhibition of Xa in vivo, despite being present at concentrations of only 2.5 nM.
Genetics
The gene for TFPI is located on chromosome 2q31-q32.1, and has nine exons which span 70 kb. The gene has not been completely sequenced yet. A similar gene, termed TFPI2, has been identified on chromosome 7q22; in addition to TFPI activity, its product also has retinal pigment epithelial cell growth-promoting properties.
Protein structure
TFPI has a relative molecular mass of 34,000 to 40,000 depending on the degree of proteolysis of the C-terminal region.
TFPI consists of a highly negatively charged amino-terminus, three tandemly linked Kunitz domains, and a highly positively charged carboxy-terminus. With its Kunitz domains, TFPI exhibits significant homology with human inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor and bovine basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor.
Interactions
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor has been shown to interact with Factor X.[5]
See also
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000003436 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027082 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Broze, G J; Warren L A; Novotny W F; Higuchi D A; Girard J J; Miletich J P (Feb 1988). "The lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor that inhibits the factor VII-tissue factor complex also inhibits factor Xa: insight into its possible mechanism of action". Blood. UNITED STATES. 71 (2): 335–43. doi:10.1182/blood.V71.2.335.335. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 3422166.
External links
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 152310 (TFPI1), Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 600033 (TFPI2)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P10646 (Tissue factor pathway inhibitor) at the PDBe-KB.
Further reading
- Broze GJ, Girard TJ, Novotny WF (1991). "Regulation of coagulation by a multivalent Kunitz-type inhibitor". Biochemistry. 29 (33): 7539–46. doi:10.1021/bi00485a001. PMID 2271516.
- McVey JH (2000). "Tissue factor pathway". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Haematology. 12 (3): 361–72. doi:10.1053/beha.1999.0030. PMID 10856975.
- Bajaj MS, Birktoft JJ, Steer SA, Bajaj SP (2002). "Structure and biology of tissue factor pathway inhibitor". Thromb. Haemost. 86 (4): 959–72. PMID 11686353.
- Witt I (2002). "[Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: biochemistry, molecular biology, physiology and physiopathology]". Hamostaseologie. 22 (2): 30–5. doi:10.1267/Hamo02020071. PMID 12193974.
- Lwaleed BA, Bass PS (2006). "Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: structure, biology and involvement in disease". J. Pathol. 208 (3): 327–39. doi:10.1002/path.1871. PMID 16261634.
- Van der Logt CP, Kluck PM, Wiegant J, et al. (1992). "Refined regional assignment of the human tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) gene to chromosome band 2q32 by non-isotopic in situ hybridization". Hum. Genet. 89 (5): 577–8. doi:10.1007/bf00219189. PMID 1353057.
- Higuchi DA, Wun TC, Likert KM, Broze GJ (1992). "The effect of leukocyte elastase on tissue factor pathway inhibitor". Blood. 79 (7): 1712–9. PMID 1558967.
- van der Logt CP, Reitsma PH, Bertina RM (1991). "Intron-exon organization of the human gene coding for the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor: the factor Xa dependent inhibitor of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation". Biochemistry. 30 (6): 1571–7. doi:10.1021/bi00220a018. PMID 1993173.
- Girard TJ, Eddy R, Wesselschmidt RL, et al. (1991). "Structure of the human lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor gene. Intro/exon gene organization and localization of the gene to chromosome 2". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (8): 5036–41. PMID 2002045.
- Wun TC, Kretzmer KK, Girard TJ, et al. (1988). "Cloning and characterization of a cDNA coding for the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor shows that it consists of three tandem Kunitz-type inhibitory domains". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (13): 6001–4. PMID 2452157.
- Novotny WF, Girard TJ, Miletich JP, Broze GJ (1989). "Purification and characterization of the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor from human plasma". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (31): 18832–7. PMID 2553722.
- Girard TJ, Warren LA, Novotny WF, et al. (1989). "Identification of the 1.4 kb and 4.0 kb messages for the lipoprotein associated coagulation inhibitor and expression of the encoded protein". Thromb. Res. 55 (1): 37–50. doi:10.1016/0049-3848(89)90454-4. PMID 2781520.
- Girard TJ, Warren LA, Novotny WF, et al. (1989). "Functional significance of the Kunitz-type inhibitory domains of lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor". Nature. 338 (6215): 518–20. Bibcode:1989Natur.338..518G. doi:10.1038/338518a0. PMID 2927510.
- Broze GJ, Miletich JP (1987). "Characterization of the inhibition of tissue factor in serum". Blood. 69 (1): 150–5. PMID 3024756.
- Broze GJ, Warren LA, Novotny WF, et al. (1988). "The lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor that inhibits the factor VII-tissue factor complex also inhibits factor Xa: insight into its possible mechanism of action". Blood. 71 (2): 335–43. doi:10.1182/blood.V71.2.335.335. PMID 3422166.
- Rao LV, Rapaport SI (1987). "Studies of a mechanism inhibiting the initiation of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation". Blood. 69 (2): 645–51. PMID 3492226.
- Stubbs MT, Huber R, Bode W (1996). "Crystal structures of factor Xa specific inhibitors in complex with trypsin: structural grounds for inhibition of factor Xa and selectivity against thrombin". FEBS Lett. 375 (1–2): 103–7. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(95)01190-P. PMID 7498454.
- Warshawsky I, Bu G, Mast A, et al. (1995). "The carboxy terminus of tissue factor pathway inhibitor is required for interacting with hepatoma cells in vitro and in vivo". J. Clin. Invest. 95 (4): 1773–81. doi:10.1172/JCI117855. PMC 295702. PMID 7706485.
- Broze GJ, Lange GW, Duffin KL, MacPhail L (1995). "Heterogeneity of plasma tissue factor pathway inhibitor". Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis. 5 (4): 551–9. PMID 7841311.