A* search algorithm
A* (pronounced "A-star") is a graph traversal and path search algorithm, which is often used in many fields of computer science due to its completeness, optimality, and optimal efficiency.[1] One major practical drawback is its space complexity, as it stores all generated nodes in memory. Thus, in practical travel-routing systems, it is generally outperformed by algorithms which can pre-process the graph to attain better performance,[2] as well as memory-bounded approaches; however, A* is still the best solution in many cases.[3]
| Class | Search algorithm |
|---|---|
| Data structure | Graph |
| Worst-case performance | |
| Worst-case space complexity |
| Graph and tree search algorithms |
|---|
| Listings |
|
| Related topics |
Peter Hart, Nils Nilsson and Bertram Raphael of Stanford Research Institute (now SRI International) first published the algorithm in 1968.[4] It can be seen as an extension of Edsger Dijkstra's 1959 algorithm. A* achieves better performance by using heuristics to guide its search.
History
A* was created as part of the Shakey project, which had the aim of building a mobile robot that could plan its own actions. Nils Nilsson originally proposed using the Graph Traverser algorithm[5] for Shakey's path planning.[6] Graph Traverser is guided by a heuristic function h(n), the estimated distance from node n to the goal node: it entirely ignores g(n), the distance from the start node to n. Bertram Raphael suggested using the sum, g(n) + h(n).[6] Peter Hart invented the concepts we now call admissibility and consistency of heuristic functions. A* was originally designed for finding least-cost paths when the cost of a path is the sum of its edge costs, but it has been shown that A* can be used to find optimal paths for any problem satisfying the conditions of a cost algebra.[7]
The original 1968 A* paper[4] contained a theorem that no A*-like algorithm[8] could expand fewer nodes than A* if the heuristic function is consistent and A*’s tie-breaking rule is suitably chosen. A ″correction″ was published a few years later[9] claiming that consistency was not required, but this was shown to be false in Dechter and Pearl's definitive study of A*'s optimality (now called optimal efficiency), which gave an example of A* with a heuristic that was admissible but not consistent expanding arbitrarily more nodes than an alternative A*-like algorithm.[10]
Description
A* is an informed search algorithm, or a best-first search, meaning that it is formulated in terms of weighted graphs: starting from a specific starting node of a graph, it aims to find a path to the given goal node having the smallest cost (least distance travelled, shortest time, etc.). It does this by maintaining a tree of paths originating at the start node and extending those paths one edge at a time until its termination criterion is satisfied.
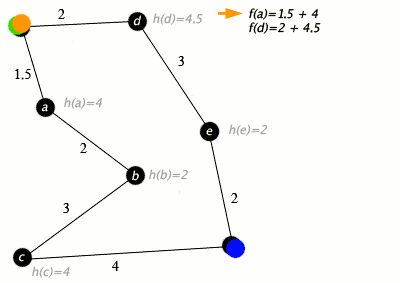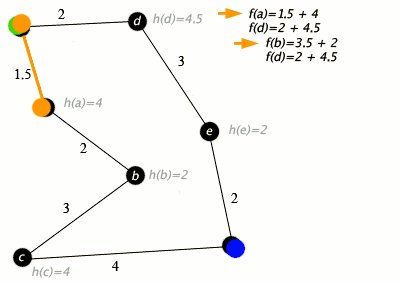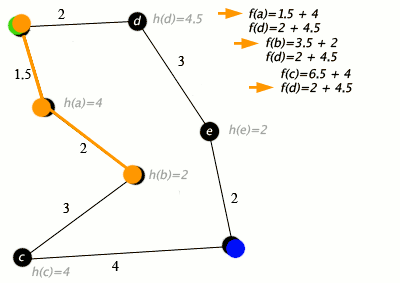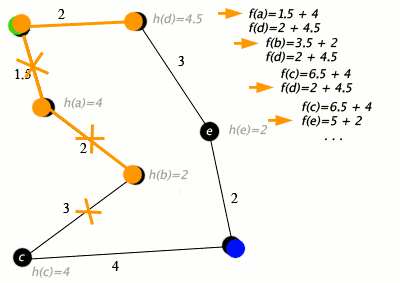
At each iteration of its main loop, A* needs to determine which of its paths to extend. It does so based on the cost of the path and an estimate of the cost required to extend the path all the way to the goal. Specifically, A* selects the path that minimizes
where n is the next node on the path, g(n) is the cost of the path from the start node to n, and h(n) is a heuristic function that estimates the cost of the cheapest path from n to the goal. A* terminates when the path it chooses to extend is a path from start to goal or if there are no paths eligible to be extended. The heuristic function is problem-specific. If the heuristic function is admissible, meaning that it never overestimates the actual cost to get to the goal, A* is guaranteed to return a least-cost path from start to goal.
Typical implementations of A* use a priority queue to perform the repeated selection of minimum (estimated) cost nodes to expand. This priority queue is known as the open set or fringe. At each step of the algorithm, the node with the lowest f(x) value is removed from the queue, the f and g values of its neighbors are updated accordingly, and these neighbors are added to the queue. The algorithm continues until a goal node has a lower f value than any node in the queue (or until the queue is empty).[lower-alpha 1] The f value of the goal is then the cost of the shortest path, since h at the goal is zero in an admissible heuristic.
The algorithm described so far gives us only the length of the shortest path. To find the actual sequence of steps, the algorithm can be easily revised so that each node on the path keeps track of its predecessor. After this algorithm is run, the ending node will point to its predecessor, and so on, until some node's predecessor is the start node.
As an example, when searching for the shortest route on a map, h(x) might represent the straight-line distance to the goal, since that is physically the smallest possible distance between any two points. For a grid map from a video game, using the Manhattan distance or the octile distance becomes better depending on the set of movements available (4-way or 8-way).
If the heuristic h satisfies the additional condition h(x) ≤ d(x, y) + h(y) for every edge (x, y) of the graph (where d denotes the length of that edge), then h is called monotone, or consistent. With a consistent heuristic, A* is guaranteed to find an optimal path without processing any node more than once and A* is equivalent to running Dijkstra's algorithm with the reduced cost d'(x, y) = d(x, y) + h(y) − h(x).
Pseudocode
The following pseudocode describes the algorithm:
function reconstruct_path(cameFrom, current)
total_path := {current}
while current in cameFrom.Keys:
current := cameFrom[current]
total_path.prepend(current)
return total_path
// A* finds a path from start to goal.
// h is the heuristic function. h(n) estimates the cost to reach goal from node n.
function A_Star(start, goal, h)
// The set of discovered nodes that may need to be (re-)expanded.
// Initially, only the start node is known.
// This is usually implemented as a min-heap or priority queue rather than a hash-set.
openSet := {start}
// For node n, cameFrom[n] is the node immediately preceding it on the cheapest path from start
// to n currently known.
cameFrom := an empty map
// For node n, gScore[n] is the cost of the cheapest path from start to n currently known.
gScore := map with default value of Infinity
gScore[start] := 0
// For node n, fScore[n] := gScore[n] + h(n). fScore[n] represents our current best guess as to
// how short a path from start to finish can be if it goes through n.
fScore := map with default value of Infinity
fScore[start] := h(start)
while openSet is not empty
// This operation can occur in O(1) time if openSet is a min-heap or a priority queue
current := the node in openSet having the lowest fScore[] value
if current = goal
return reconstruct_path(cameFrom, current)
openSet.Remove(current)
for each neighbor of current
// d(current,neighbor) is the weight of the edge from current to neighbor
// tentative_gScore is the distance from start to the neighbor through current
tentative_gScore := gScore[current] + d(current, neighbor)
if tentative_gScore < gScore[neighbor]
// This path to neighbor is better than any previous one. Record it!
cameFrom[neighbor] := current
gScore[neighbor] := tentative_gScore
fScore[neighbor] := gScore[neighbor] + h(neighbor)
if neighbor not in openSet
openSet.add(neighbor)
// Open set is empty but goal was never reached
return failure
Remark: In this pseudocode, if a node is reached by one path, removed from openSet, and subsequently reached by a cheaper path, it will be added to openSet again. This is essential to guarantee that the path returned is optimal if the heuristic function is admissible but not consistent. If the heuristic is consistent, when a node is removed from openSet the path to it is guaranteed to be optimal so the test ‘tentative_gScore < gScore[neighbor]’ will always fail if the node is reached again.
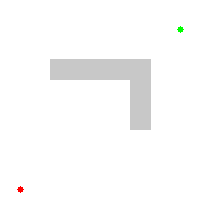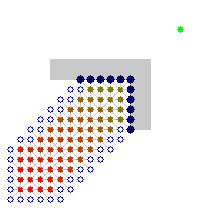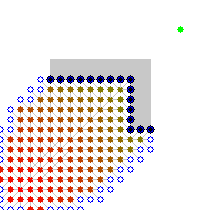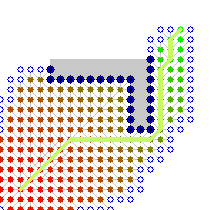
Example
An example of an A* algorithm in action where nodes are cities connected with roads and h(x) is the straight-line distance to target point:
Key: green: start; blue: goal; orange: visited
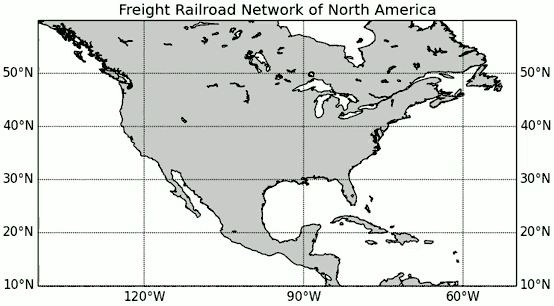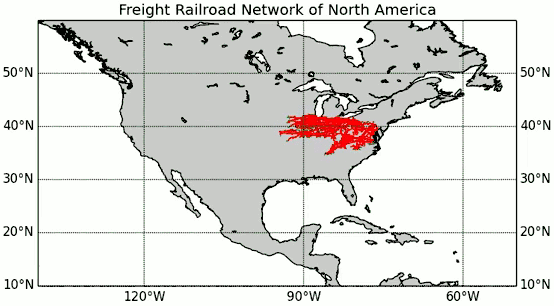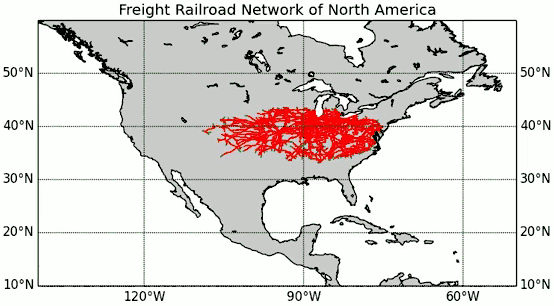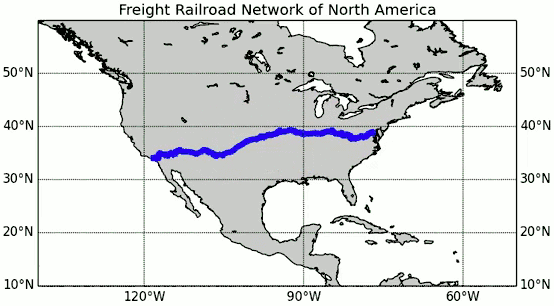
The A* algorithm also has real-world applications. In this example, edges are railroads and h(x) is the great-circle distance (the shortest possible distance on a sphere) to the target. The algorithm is searching for a path between Washington, D.C. and Los Angeles.
Implementation details
There are a number of simple optimizations or implementation details that can significantly affect the performance of an A* implementation. The first detail to note is that the way the priority queue handles ties can have a significant effect on performance in some situations. If ties are broken so the queue behaves in a LIFO manner, A* will behave like depth-first search among equal cost paths (avoiding exploring more than one equally optimal solution).
When a path is required at the end of the search, it is common to keep with each node a reference to that node's parent. At the end of the search these references can be used to recover the optimal path. If these references are being kept then it can be important that the same node doesn't appear in the priority queue more than once (each entry corresponding to a different path to the node, and each with a different cost). A standard approach here is to check if a node about to be added already appears in the priority queue. If it does, then the priority and parent pointers are changed to correspond to the lower cost path. A standard binary heap based priority queue does not directly support the operation of searching for one of its elements, but it can be augmented with a hash table that maps elements to their position in the heap, allowing this decrease-priority operation to be performed in logarithmic time. Alternatively, a Fibonacci heap can perform the same decrease-priority operations in constant amortized time.
Special cases
Dijkstra's algorithm, as another example of a uniform-cost search algorithm, can be viewed as a special case of A* where for all x.[11][12] General depth-first search can be implemented using A* by considering that there is a global counter C initialized with a very large value. Every time we process a node we assign C to all of its newly discovered neighbors. After each single assignment, we decrease the counter C by one. Thus the earlier a node is discovered, the higher its value. Both Dijkstra's algorithm and depth-first search can be implemented more efficiently without including an value at each node.
Properties
Termination and Completeness
On finite graphs with non-negative edge weights A* is guaranteed to terminate and is complete, i.e. it will always find a solution (a path from start to goal) if one exists. On infinite graphs with a finite branching factor and edge costs that are bounded away from zero ( for some fixed ), A* is guaranteed to terminate only if there exists a solution.
Admissibility
A search algorithm is said to be admissible if it is guaranteed to return an optimal solution. If the heuristic function used by A* is admissible, then A* is admissible. An intuitive ″proof″ of this is as follows:
When A* terminates its search, it has found a path from start to goal whose actual cost is lower than the estimated cost of any path from start to goal through any open node (the node's value). When the heuristic is admissible, those estimates are optimistic (not quite—see the next paragraph), so A* can safely ignore those nodes because they cannot possibly lead to a cheaper solution than the one it already has. In other words, A* will never overlook the possibility of a lower-cost path from start to goal and so it will continue to search until no such possibilities exist.
The actual proof is a bit more involved because the values of open nodes are not guaranteed to be optimistic even if the heuristic is admissible. This is because the values of open nodes are not guaranteed to be optimal, so the sum is not guaranteed to be optimistic.
Optimal efficiency
Algorithm A is optimally efficient with respect to a set of alternative algorithms Alts on a set of problems P if for every problem P in P and every algorithm A′ in Alts, the set of nodes expanded by A in solving P is a subset (possibly equal) of the set of nodes expanded by A′ in solving P. The definitive study of the optimal efficiency of A* is due to Rina Dechter and Judea Pearl.[10] They considered a variety of definitions of Alts and P in combination with A*'s heuristic being merely admissible or being both consistent and admissible. The most interesting positive result they proved is that A*, with a consistent heuristic, is optimally efficient with respect to all admissible A*-like search algorithms on all ″non-pathological″ search problems. Roughly speaking, their notion of non-pathological problem is what we now mean by ″up to tie-breaking″. This result does not hold if A*'s heuristic is admissible but not consistent. In that case, Dechter and Pearl showed there exist admissible A*-like algorithms that can expand arbitrarily fewer nodes than A* on some non-pathological problems.
Optimal efficiency is about the set of nodes expanded, not the number of node expansions (the number of iterations of A*'s main loop). When the heuristic being used is admissible but not consistent, it is possible for a node to be expanded by A* many times, an exponential number of times in the worst case.[13] In such circumstances Dijkstra's algorithm could outperform A* by a large margin.
Bounded relaxation
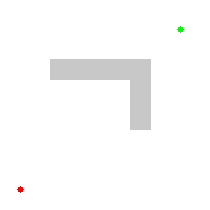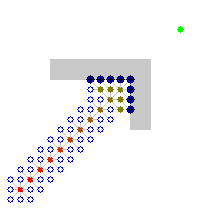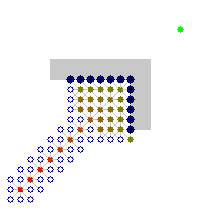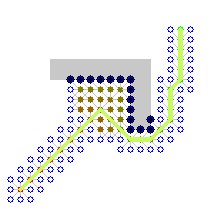
While the admissibility criterion guarantees an optimal solution path, it also means that A* must examine all equally meritorious paths to find the optimal path. To compute approximate shortest paths, it is possible to speed up the search at the expense of optimality by relaxing the admissibility criterion. Oftentimes we want to bound this relaxation, so that we can guarantee that the solution path is no worse than (1 + ε) times the optimal solution path. This new guarantee is referred to as ε-admissible.
There are a number of ε-admissible algorithms:
- Weighted A*/Static Weighting.[14] If ha(n) is an admissible heuristic function, in the weighted version of the A* search one uses hw(n) = ε ha(n), ε > 1 as the heuristic function, and perform the A* search as usual (which eventually happens faster than using ha since fewer nodes are expanded). The path hence found by the search algorithm can have a cost of at most ε times that of the least cost path in the graph.[15]
- Dynamic Weighting[16] uses the cost function , where , and where is the depth of the search and N is the anticipated length of the solution path.
- Sampled Dynamic Weighting[17] uses sampling of nodes to better estimate and debias the heuristic error.
- .[18] uses two heuristic functions. The first is the FOCAL list, which is used to select candidate nodes, and the second hF is used to select the most promising node from the FOCAL list.
- Aε[19] selects nodes with the function , where A and B are constants. If no nodes can be selected, the algorithm will backtrack with the function , where C and D are constants.
- AlphA*[20] attempts to promote depth-first exploitation by preferring recently expanded nodes. AlphA* uses the cost function , where , where λ and Λ are constants with , π(n) is the parent of n, and ñ is the most recently expanded node.
Complexity
The time complexity of A* depends on the heuristic. In the worst case of an unbounded search space, the number of nodes expanded is exponential in the depth of the solution (the shortest path) d: O(bd), where b is the branching factor (the average number of successors per state).[21] This assumes that a goal state exists at all, and is reachable from the start state; if it is not, and the state space is infinite, the algorithm will not terminate.
The heuristic function has a major effect on the practical performance of A* search, since a good heuristic allows A* to prune away many of the bd nodes that an uninformed search would expand. Its quality can be expressed in terms of the effective branching factor b*, which can be determined empirically for a problem instance by measuring the number of nodes expanded, N, and the depth of the solution, then solving[22]
Good heuristics are those with low effective branching factor (the optimal being b* = 1).
The time complexity is polynomial when the search space is a tree, there is a single goal state, and the heuristic function h meets the following condition:
where h* is the optimal heuristic, the exact cost to get from x to the goal. In other words, the error of h will not grow faster than the logarithm of the "perfect heuristic" h* that returns the true distance from x to the goal.[15][21]
The space complexity of A* is roughly the same as that of all other graph search algorithms, as it keeps all generated nodes in memory.[23] In practice, this turns out to be the biggest drawback of A* search, leading to the development of memory-bounded heuristic searches, such as Iterative deepening A*, memory bounded A*, and SMA*.
Applications
A* is often used for the common pathfinding problem in applications such as video games, but was originally designed as a general graph traversal algorithm.[4] It finds applications in diverse problems, including the problem of parsing using stochastic grammars in NLP.[24] Other cases include an Informational search with online learning.[25]
Relations to other algorithms
What sets A* apart from a greedy best-first search algorithm is that it takes the cost/distance already traveled, g(n), into account.
Some common variants of Dijkstra's algorithm can be viewed as a special case of A* where the heuristic for all nodes;[11][12] in turn, both Dijkstra and A* are special cases of dynamic programming.[26] A* itself is a special case of a generalization of branch and bound.[27]
Variants
- Anytime A*[28] or Anytime Repairing A* (ARA*)[29]
- Anytime Dynamic A*
- Block A*
- D*
- Field D*
- Fringe
- Fringe Saving A* (FSA*)
- Generalized Adaptive A* (GAA*)
- Incremental heuristic search
- Informational search[25]
- Iterative deepening A* (IDA*)
- Jump point search
- Lifelong Planning A* (LPA*)
- Multiplier-accelerated A* (MAA*) [30]
- New Bidirectional A* (NBA*)[31]
- Simplified Memory bounded A* (SMA*)
- Realtime A*[32]
- Theta*
- Time-Bounded A* (TBA*)[33]
A* can also be adapted to a bidirectional search algorithm. Special care needs to be taken for the stopping criterion.[34]
See also
- Breadth-first search
- Depth-first search
- Any-angle path planning, search for paths that are not limited to move along graph edges but rather can take on any angle
Notes
- Goal nodes may be passed over multiple times if there remain other nodes with lower f values, as they may lead to a shorter path to a goal.
References
- Russell, Stuart J. (2018). Artificial intelligence a modern approach. Norvig, Peter (4th ed.). Boston: Pearson. ISBN 978-0134610993. OCLC 1021874142.
- Delling, D.; Sanders, P.; Schultes, D.; Wagner, D. (2009). "Engineering Route Planning Algorithms". Algorithmics of Large and Complex Networks: Design, Analysis, and Simulation. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 5515. Springer. pp. 11个$7–139. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.164.8916. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-02094-0_7. ISBN 978-3-642-02093-3.
- Zeng, W.; Church, R. L. (2009). "Finding shortest paths on real road networks: the case for A*". International Journal of Geographical Information Science. 23 (4): 531–543. doi:10.1080/13658810801949850.
- Hart, P. E.; Nilsson, N. J.; Raphael, B. (1968). "A Formal Basis for the Heuristic Determination of Minimum Cost Paths". IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and Cybernetics. 4 (2): 100–107. doi:10.1109/TSSC.1968.300136.
- Doran, J. E.; Michie, D. (1966-09-20). "Experiments with the Graph Traverser program". Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. 294 (1437): 235–259. Bibcode:1966RSPSA.294..235D. doi:10.1098/rspa.1966.0205. ISSN 0080-4630.
- Nilsson, Nils J. (2009-10-30). The Quest for Artificial Intelligence (PDF). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521122931.
- Edelkamp, Stefan; Jabbar, Shahid; Lluch-Lafuente, Alberto (2005). "Cost-Algebraic Heuristic Search" (PDF). Proceedings of the Twentieth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI): 1362–1367.
- “A*-like” means the algorithm searches by extending paths originating at the start node one edge at a time, just as A* does. This excludes, for example, algorithms that search backward from the goal or in both directions simultaneously. In addition, the algorithms covered by this theorem must be admissible and “not more informed” than A*.
- Hart, Peter E.; Nilsson, Nils J.; Raphael, Bertram (1972-12-01). "Correction to 'A Formal Basis for the Heuristic Determination of Minimum Cost Paths'" (PDF). ACM SIGART Bulletin (37): 28–29. doi:10.1145/1056777.1056779. ISSN 0163-5719.
- Dechter, Rina; Judea Pearl (1985). "Generalized best-first search strategies and the optimality of A*". Journal of the ACM. 32 (3): 505–536. doi:10.1145/3828.3830.
- De Smith, Michael John; Goodchild, Michael F.; Longley, Paul (2007), Geospatial Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Principles, Techniques and Software Tools, Troubadour Publishing Ltd, p. 344, ISBN 9781905886609.
- Hetland, Magnus Lie (2010), Python Algorithms: Mastering Basic Algorithms in the Python Language, Apress, p. 214, ISBN 9781430232377.
- Martelli, Alberto (1977). "On the Complexity of Admissible Search Algorithms". Artificial Intelligence. 8 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1016/0004-3702(77)90002-9.
- Pohl, Ira (1970). "First results on the effect of error in heuristic search". Machine Intelligence. 5: 219–236.
- Pearl, Judea (1984). Heuristics: Intelligent Search Strategies for Computer Problem Solving. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-05594-8.
- Pohl, Ira (August 1973). "The avoidance of (relative) catastrophe, heuristic competence, genuine dynamic weighting and computational issues in heuristic problem solving" (PDF). Proceedings of the Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-73). 3. California, USA. pp. 11–17.
- Köll, Andreas; Hermann Kaindl (August 1992). "A new approach to dynamic weighting". Proceedings of the Tenth European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI-92). Vienna, Austria. pp. 16–17.
- Pearl, Judea; Jin H. Kim (1982). "Studies in semi-admissible heuristics". IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 4 (4): 392–399. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.1982.4767270.
- Ghallab, Malik; Dennis Allard (August 1983). "Aε – an efficient near admissible heuristic search algorithm" (PDF). Proceedings of the Eighth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-83). 2. Karlsruhe, Germany. pp. 789–791. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-06.
- Reese, Bjørn (1999). "AlphA*: An ε-admissible heuristic search algorithm". Archived from the original on 2016-01-31. Retrieved 2014-11-05. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Russell, Stuart; Norvig, Peter (2003) [1995]. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall. pp. 97–104. ISBN 978-0137903955.
- Russell, Stuart; Norvig, Peter (2009) [1995]. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (3rd ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-13-604259-4.
- Russell, Stuart J. (2018). Artificial intelligence a modern approach. Norvig, Peter (4th ed.). Boston: Pearson. ISBN 978-0134610993. OCLC 1021874142.
- Klein, Dan; Manning, Christopher D. (2003). A* parsing: fast exact Viterbi parse selection. Proc. NAACL-HLT.
- Kagan E. and Ben-Gal I. (2014). "A Group-Testing Algorithm with Online Informational Learning" (PDF). IIE Transactions, 46:2, 164-184. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Ferguson, Dave; Likhachev, Maxim; Stentz, Anthony (2005). A Guide to Heuristic-based Path Planning (PDF). Proc. ICAPS Workshop on Planning under Uncertainty for Autonomous Systems.
- Nau, Dana S.; Kumar, Vipin; Kanal, Laveen (1984). "General branch and bound, and its relation to A∗ and AO∗" (PDF). Artificial Intelligence. 23 (1): 29–58. doi:10.1016/0004-3702(84)90004-3.
- Hansen, Eric A., and Rong Zhou. "Anytime Heuristic Search." J. Artif. Intell. Res.(JAIR) 28 (2007): 267-297.
- Likhachev, Maxim; Gordon, Geoff; Thrun, Sebastian. "ARA*: Anytime A* search with provable bounds on sub-optimality". In S. Thrun, L. Saul, and B. Schölkopf, editors, Proceedings of Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Cambridge, MA, 2003. MIT Press.
- Li, Jerry and Zimmerle, Daniel (2019), "Designing Optimal Network for Rural Electrification using Multiplier-accelerated A* Algorithm", 2019 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Macao, Macao, 2019, pp. 1-5. Accepted version of this paper is available at Researchgate or the author's personal page
- Pijls, Wim; Post, Henk "Yet another bidirectional algorithm for shortest paths" In Econometric Institute Report EI 2009-10/Econometric Institute, Erasmus University Rotterdam. Erasmus School of Economics.
- Korf, Richard E. "Real-time heuristic search." Artificial intelligence 42.2-3 (1990): 189-211.
- Björnsson, Yngvi; Bulitko, Vadim; Sturtevant, Nathan (July 11–17, 2009). TBA*: time-bounded A* (PDF). IJCAI 2009, Proceedings of the 21st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Pasadena, California, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc. pp. 431–436.
- "Efficient Point-to-Point Shortest Path Algorithms" (PDF). Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) from Princeton University
Further reading
- Nilsson, N. J. (1980). Principles of Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, California: Tioga Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-935382-01-3.