Syntelog
Syntelog: a special case of gene homology where sets of genes are derived from the same ancestral genomic region. This may arise from speciation events, or through whole or partial genome duplication events (e.g. polyploidy). This term is distinct from ortholog, paralog, in-paralog, out-paralog, and xenolog because it refers only to genes' evolutionary history evidenced by sequence similarity and relative genomic position.
Example
Comparison between two genomic regions of Arabidopsis thaliana derived from its most recent genome duplication event. Syntelogs are indicated by red lines connecting regions of sequence similarly (red boxes):
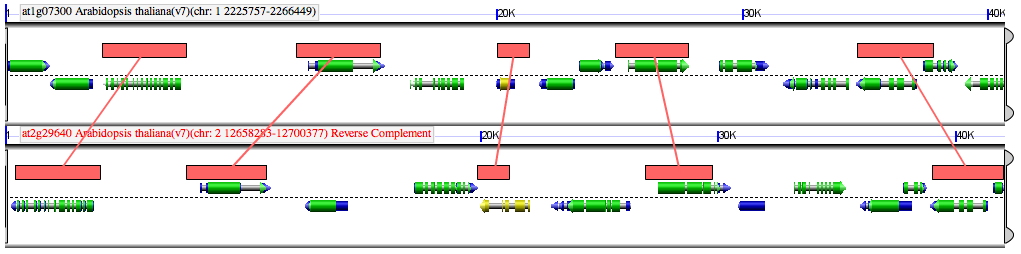
Sequence analysis and visualization of syntelogs performed by GEvo.[1] Sequences were compared using the BlastZ algorithm.