Symmetric hydrogen bond
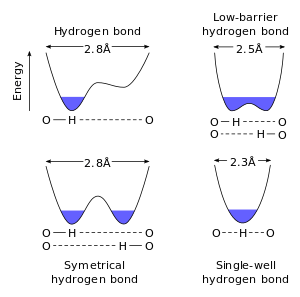
A symmetric hydrogen bond is a special type of hydrogen bond in which the proton is spaced exactly halfway between two identical atoms. The strength of the bond to each of those atoms is equal. It is an example of a 3-center 4-electron bond. This type of bond is much stronger than "normal" hydrogen bonds, in fact, its strength is comparable to a covalent bond. It is seen in ice at high pressure (Ice X), and also in the solid phase of many anhydrous acids such as hydrofluoric acid and formic acid at high pressure. It is also seen in the bifluoride ion [F−H−F]−. Much has been done to explain the symmetric hydrogen bond quantum-mechanically, as it seems to violate the duet rule for the first shell: The proton is effectively surrounded by four electrons. Because of this problem, some consider it to be an ionic bond.
References
- Steiner, Thomas (2002). "The Hydrogen Bond in the Solid State". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 41: 48. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20020104)41:1<48::AID-ANIE48>3.0.CO;2-U.