Surface force
Surface force denoted fs is the force that acts across an internal or external surface element in a material body. Surface force can be decomposed into two perpendicular components: normal forces and shear forces. A normal force acts normally over an area and a shear force acts tangentially over an area.
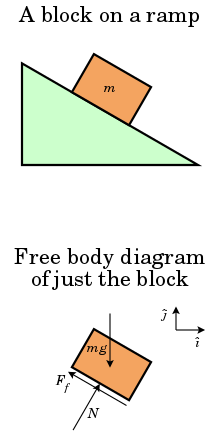
Block on a ramp and corresponding free body diagram of the block showing the surface force from the ramp onto the bottom of the block and separated into two components, a normal force N and a frictional shear force f, along with the body force of gravity mg acting at the center of mass.
Equations for surface force
Surface force due to pressure
- , where f = force, p = pressure, and A = area on which a uniform pressure acts
Examples
Pressure related surface force
Since pressure is , and area is a ,
- a pressure of over an area of will produce a surface force of .
gollark: I vaguely understand them after looking at the kinds of various things.
gollark: Fallacy no longer sounds like a real word.
gollark: Muahahaha semantic satiation.
gollark: Actually, fallacy fallacy is a fallacious fallacy.
gollark: Initiating orbital concept transduction array.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.