Sukhoi Su-12
The Sukhoi Su-12 (Aircraft RK) was a prototype Soviet reconnaissance and artillery spotter aircraft developed during World War II.
| Su-12 | |
|---|---|
| Role | Reconnaissance aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Sukhoi |
| Designer | Pavel Sukhoi |
| First flight | 26 August 1947 |
| Status | Prototype |
| Primary user | Soviet Air Forces |
| Number built | 1 |
Development
In November 1943, the Sukhoi OKB designed an artillery spotter aircraft based on the German Focke-Wulf Fw 189.[1] As designed, the aircraft had a crew of three and was powered by a pair of Shvetsov M-62 engines. The aircraft was initially denied funding but was eventually approved thanks to an intervention by the Soviet Chief Marshal of Artillery N.N. Voronov.[1] As a result of evolving specifications, the crew was increased to four and the engines were changed to more powerful Shvetsov ASh-82M with 1,640 kW (2,200 hp).
The Su-12 prototype flew on 26 August 1947 with N.D. Fikson at the controls. The test flight program was completed by 30 October. Due to problems with the ASh-82M engines, the powerplant was changed to ASh-82FN making 1,380 kW (1,850 hp), but while reliable, the less-powerful engines caused the Su-12 to miss its top speed and service ceiling specifications.[1] The Su-12 successfully completed government testing in September 1949 and was recommended for production. Due to lack of production capacity in the USSR, in October 1949 it was proposed to build the airplane in Czechoslovakia. However, the application for production was denied, citing failure to meet performance specifications.[1] Subsequent efforts by the Sukhoi Design Bureau to secure funding and continue work on the Su-12 were denied.
Specifications (Su-12)
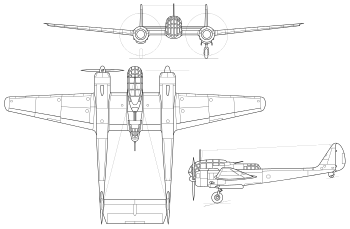
Data from Shavrov[2], OKB Sukhoi[3]
General characteristics
- Crew: 3
- Length: 11.92 m (39 ft 1 in)
- Wingspan: 21.57 m (70 ft 9 in)
- Height: 5.54 m (18 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 52 m2 (560 sq ft)
- Airfoil: root: NACA 23014; tip: NACA 23009.25[4]
- Empty weight: 6,970 kg (15,366 lb)
- Gross weight: 9,610 kg (21,186 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 620 l (160 US gal; 140 imp gal) in two wing tanks and two engine nacelle tanks
- Powerplant: 2 × Shvetsov ASh-82FN 14-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 1,380 kW (1,850 hp) each
- Propellers: 4-bladed AV-9VF21K, 3.6 m (11 ft 10 in) diameter feathering constant-speed propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 531 km/h (330 mph, 287 kn) at 5,600 m (18,373 ft)
- Range: 1,140 km (710 mi, 620 nmi) at 1,000 m (3,281 ft)
- Endurance: >4 hours at 1,000 m (3,281 ft)
- Service ceiling: 11,000 m (36,000 ft)
- Time to altitude: 5,000 m (16,404 ft) in 7 minutes 30 seconds
- Take-off run: 230 m (755 ft)
- Landing run: 320 m (1,050 ft)
Armament
- Guns: 4 × 20 mm Berezin B-20 autocannon (1 fixed forward-firing, 2 in the upper turret, 1 in the tail turret)
- Bombs: Up to 800 kg (1,765 lb) of bombs
References
- Antonov,Vladimir & Gordon, Yefim & others. OKB Sukhoi”. Leicester. Midland. 1996. ISBN 1-85780-012-5
External links
- "Sukhoi Su-12". Sukhoi Company Museum. Archived from the original on 2011-09-29. Retrieved 2011-07-12.
Notes
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sukhoi Su-12. |
- "Sukhoi Su-12". Sukhoi Company Museum. Archived from the original on 2011-09-29. Retrieved 2007-01-14.
- Shavrov V.B. (1994). Istoriia konstruktskii samoletov v SSSR, 1938-1950 gg. (3 izd.). Mashinostroenie. ISBN 5217004770.
- Antonov, Vladimir; Gordon, Yefim; Gordyukov, Nikolai; Yakovlev, Vladimir; Zenkin, Vyacheslav; Carruth, Lenox; Miller, Jay (1996). OKB Sukhoi : a history of the design bureau and its aircraft (1st ed.). Earl Shilton: Midland Publishing. pp. 73–75. ISBN 9781857800128.
- Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.