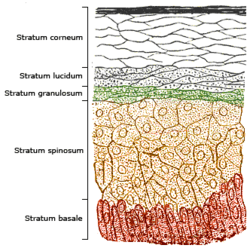
Stratum spinosum
The stratum spinosum (or spinous layer/prickle cell layer)[1] is a layer of the epidermis found between the stratum granulosum and stratum basale.[2] Their spiny (Latin, spinosum) appearance is due to shrinking of the microfilaments between desmosomes that occurs when stained with H&E. Keratinization begins in the stratum spinosum.[3] This layer is composed of polyhedral keratinocytes. They have large pale-staining nuclei as they are active in synthesizing fibrilar proteins, known as cytokeratin, which build up within the cells aggregating together forming tonofibrils. The tonofibrils go on to form the desmosomes, which allow for strong connections to form between adjacent keratinocytes.
Diffuse hyperplasia of the stratum spinosum is termed acanthosis.
Additional images
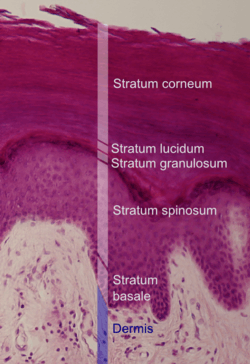
- Epidermis and dermis of human skin
 Section of epidermis
Section of epidermis
See also
References
- McGrath, J.A.; Eady, R.A.; Pope, F.M. (2004). Rook's Textbook of Dermatology (Seventh Edition). Blackwell Publishing. Pages 3.7-3.8. ISBN 978-0-632-06429-8.
- James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005) Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (10th ed.). Saunders. Page 2. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 6. ISBN 1-4160-3185-5.