Stomatella stellata
Stomatella stellata is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.[1]
| Stomatella stellata | |
|---|---|
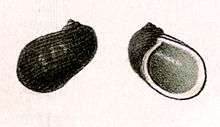 | |
| Drawing with two views of a shell of Stomatella stellata | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| (unranked): | clade Vetigastropoda |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | S. stellata |
| Binomial name | |
| Stomatella stellata Souverbie, 1863 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
This species has become a "species inquirenda", meaning of doubtful identity.
Description
The heigfht of the shell attains 7½ mm, its diameter 5¼ mm. The shell is ear-shaped, with a minute spire and a very large, convex body whorl. Its surface is somewhat shining, black with scattered whitish dots, spots or zigzag lines. The shell is sculptured by numerous close microscopic spiral striae, several smaller alternating with larger ones, and somewhat decussated by impressed growth lines. The spire is very short with a minute whitish nucleus. The three whorls are convex. The body whorl is very large. The ovate aperture is angled above, polished, and bright inside, and of a blue color. The columella is arched. A slight chink is at the place of the umbilicus.[2]
Distribution
This marine species occurs off Madagascar and in the Indo-Pacific; off Queensland, Australia.
References
- Stomatella stellata Souverbie, 1863. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 13 August 2012.
- G.W. Tryon (1890) Manual of Conchology XII; Academy of Natural Sciences, Philadelphia, 1890
- Souverbie, M. & Montrouzier, R.P. 1863. Descriptions d'espèces nouvelles de l'Archipel Calédonien et des îles Salomon et Woodlark. Journal de Conchyliologie 11(2): 161-176
- Brazier, J. 1877 [imprint 1878]. Continuation of the Mollusca collected during the Chevert Expedition. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales 2(1): 41-53
- Pilsbry, H.A. 1890. Manual of Conchology. Philadelphia : Academy of Natural Sciences Philadelphia Vol. 12 323 pp., 65 pls.
- Hedley, C. 1901. A revision of the types of the marine shells of the "Chevert" Expedition. Records of the Australian Museum 4: 121-130
- Dautzenberg, Ph. (1929). Contribution à l'étude de la faune de Madagascar: Mollusca marina testacea. Faune des colonies françaises, III (fasc. 4). Société d'Editions géographiques, maritimes et coloniales: Paris. 321–636, plates IV-VII pp.
- Cernohorsky, W.O. 1978. Tropical Pacific marine shells. Sydney : Pacific Publications 352 pp., 68 pls
- Wilson, B. 1993. Australian Marine Shells. Prosobranch Gastropods. Kallaroo, Western Australia : Odyssey Publishing Vol. 1 408 pp.
- Herbert D.G. (1996) A critical review of the trochoidean types in the Muséum d'Histoire naturelle, Bordeaux (Mollusca, Gastropoda). Bulletin du Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle, Paris, ser. 4, 18 (A, 3-4): 409–445.