Stinstedt
Stinstedt is a municipality in the district of Cuxhaven, in Lower Saxony, Germany.
Stinstedt | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Stinstedt within Cuxhaven district 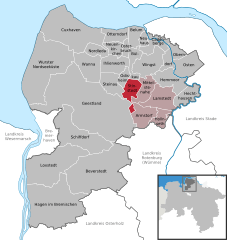  | |
 Stinstedt  Stinstedt | |
| Coordinates: 53°39′41″N 08°58′16″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Lower Saxony |
| District | Cuxhaven |
| Municipal assoc. | Börde Lamstedt |
| Subdivisions | 4 Ortsteile |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Herbert Pape |
| Area | |
| • Total | 30.1 km2 (11.6 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 7 m (23 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 551 |
| • Density | 18/km2 (47/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 21772 |
| Dialling codes | 04756 |
| Vehicle registration | CUX |
| Website | www.stinstedt.de |
History
Stinstedt belonged to the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen, established in 1180. The farmers were subject with their small tithe[2] to the Himmelpforten Convent,[3] secularised in 1647. In 1648 the Prince-Archbishopric was transformed into the Duchy of Bremen, which was first ruled in personal union by the Swedish Crown[4] - interrupted by a Danish occupation (1712-1715) - and from 1715 on by the Hanoverian Crown.[5]
After a Prussian and then French occupation from 1806 to 1810, the ephemeric Kingdom of Westphalia annexed the Duchy, before France annexed it with effect of 1 January 1811.[6] In 1813 the Duchy was restored to the Electorate of Hanover, which - after its upgrade to the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814 - incorporated the Duchy in a real union and the Ducal territory, including Stinstedt, became part of the new Stade Region, established in 1823.
References
- Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen, LSN-Online Regionaldatenbank, Tabelle 12411: Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes, Stand 31. Dezember 2018.
- The great tithe comprised 10% of the field crops, whereas the small tithe amounted to 10% of the livestock and its products. Cf. Silvia Schulz-Hauschildt, Himmelpforten – Eine Chronik, Gemeinde Himmelpforten municipality (ed.), Stade: Hansa-Druck Stelzer, 1990, p. 45. No ISBN.
- Georg von Issendorff, Kloster und Amt Himmelpforten. Nach Akten und Urkunden dargestellt, reprint of the edition by "Stader Archiv", 1911/1913, extended by Clemens Förster, Stade and Buxtehude: Krause, 1979, p. 8. No ISBN.
- Silvia Schulz-Hauschildt, Himmelpforten – Eine Chronik, Gemeinde Himmelpforten municipality (ed.), Stade: Hansa-Druck Stelzer, 1990, p. 57. No ISBN.
- Georg von Issendorff, Kloster und Amt Himmelpforten. Nach Akten und Urkunden dargestellt, reprint of the edition by "Stader Archiv", 1911/1913, extended by Clemens Förster, Stade and Buxtehude: Krause, 1979, p. 56. No ISBN.
- Klaus Isensee, Die Region Stade in westfälisch-französischer Zeit 1810–1813: Studien zum napoleonischen Herrschaftssystem unter besonderer Berücksichtigung des Stadt Stade und des Fleckens Harsefeld, Stade: Stader Geschichts- und Heimatverein, 2003, simultaneously: Hanover, Univ., Diss., 1991, (=Einzelschriften des Stader Geschichts- und Heimatvereins; vol. 33), p. 100. No ISBN.