Staufen im Breisgau
Staufen im Breisgau (High Alemannic: Staufe im Brisgau) is a German town in the Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald district of Baden-Württemberg. It had a population of approximately 7,600 in 2013.
Staufen im Breisgau | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Staufen im Breisgau within Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald district 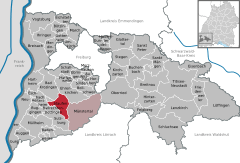  | |
 Staufen im Breisgau  Staufen im Breisgau | |
| Coordinates: 47°52′53″N 7°43′53″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Baden-Württemberg |
| Admin. region | Freiburg |
| District | Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald |
| Subdivisions | 3 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Michael Benitz |
| Area | |
| • Total | 23.26 km2 (8.98 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 284 m (932 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 8,209 |
| • Density | 350/km2 (910/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 79219 |
| Dialling codes | 07633 |
| Vehicle registration | FR |
| Website | www |
General
The city of Staufen im Breisgau lies in the Land district of Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald (Breisgau-Upper Black Forest) in the German State of Baden-Württemberg. The City of Staufen has approximately 7,700 inhabitants and forms, together with the community of Münstertal, Black Forest, a community administrative unit.
It is noted in history and culture for its association with Dr Faustus who, according to one source,[2] died in or near Staufen around 1540.
Geography
Staufen lies at the foot of the Black Forest at the exit from the Münstertal. The Black Forest valley of Neumagen goes here directly over into the Rhine plain. The piedmont of the Black Forest is less distinct. North of the valley exit, the steeply rising old castle ruins dominates; to the southwest begins the hilly landscape of the Markgräflerland. Staufen lies on the border between two natural and economic areas: the Rhine plain up to the piedmont with its cultivation of grain, vineyards and vegetables; and the Black Forest, with its cattle and wood, and, until the 19th century, silver mines.
Geothermal drilling controversy

Since 2008, the centre of the city has reported to have risen some 12 centimetres (4.7 in),[4] after initially sinking a few millimeters.[5] This has caused considerable damage to buildings in the city centre, including the historical town hall.
The cause for this geological change has been identified as a drilling operation conducted in the summer and autumn of 2007 to provide geothermal heating to the city hall. The drilling perforated an anhydrite layer and caused high-pressure groundwater to come into contact with the anhydrite, which then began to expand.
By 2010, some sections of town had risen by 30 centimetres (12 in).[6] In July 2013, no end to the rising process was in sight.[7]
Data from the TerraSAR-X radar satellite before and after the changes have confirmed the localised nature of the situation. "A geochemical process called anhydrite swelling has been confirmed as the cause of these uplifts. This is a transformation of the mineral anhydrite (anhydrous calcium sulphate) into gypsum (hydrous calcium sulphate). A pre-condition for this transformation is that the anhydrite is in contact with water, which is then stored in its crystalline structure".[8]
Infrastructure
Staufen is located next to the Münstertal railway which runs from Bad Krozingen to Münstertal, Black Forest. The railway was electrified in 2013 and is operated by the Südwestdeutsche Verkehrs-Aktiengesellschaft (SWEG).
References
- "Bevölkerung nach Nationalität und Geschlecht am 31. Dezember 2018". Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemberg (in German). July 2019.
- The Zimmern Chronicle, ca. 1565
- Tom Scott - The German Town That's Literally Breaking Apart, Youtube
- Jens Lubbadeh, Spiegel.de "Eine Stadt zerreißt", Der Spiegel, 15 November 2008 (in German). (Partial translation)
- Bojan Pancevski, "Geothermal probe sinks German city", The Daily Telegraph, 31 March 2008.
- Hans Christof Wagner, "Risse in Staufen: Pumpen, reparieren und hoffen", Badische-Zeitung, 17 October 2010 (in German)
- Franz Schmider, "Kein Ende der Hebungen in Staufen in Sicht", Badische-Zeitung, 13 July 2013 (in German)
- Formacije, A (2010). "Damage to the historic town of Staufen (Germany) caused by geothermal drillings through anhydrite-bearing formations" (PDF). Acta Carsologica. 39 (2): 233. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-26.
- Butscher, Christoph; Huggenberger, Peter; Auckenthaler, Adrian; Bänninger, Dominik (2010). "Risikoorientierte Bewilligung von Erdwärmesonden" (PDF). Grundwasser. 16: 13–24. doi:10.1007/s00767-010-0154-5.
- Goldscheider, Nico; Bechtel, Timothy D. (2009). "Editors' message: The housing crisis from underground—damage to a historic town by geothermal drillings through anhydrite, Staufen, Germany". Hydrogeology Journal. 17 (3): 491. doi:10.1007/s10040-009-0458-7. - "TerraSAR-X Image Of The Month: Ground Uplift Under Staufen's Old Town". Spacemart. 22 October 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2009 – via TerraSAR-X radar satellite.
External links
- Official website

- (in German) Staufen:images