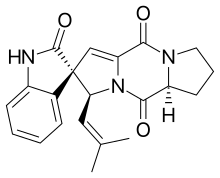
Spirotryprostatin B
Spirotryprostatin B is an indolic alkaloid found in the Aspergillus fumigatus fungus that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. Spirotryprostatin B and several other indolic alkaloids (including Spirotryprostatin A, as well as other tryprostatins and cyclotryprostatins) have been found to have anti-mitotic properties, and as such they have become of great interest as anti-cancer drugs. Because of this, the total syntheses of these compounds is a major pursuit of organic chemists, and a number of different syntheses have been published in the chemical literature.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H21N3O3 | |
| Molar mass | 363.41 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Total synthesis
The first total synthesis was accomplished in 2000 by the Danishefsky group at Columbia University, with a number of other syntheses following shortly thereafter by Williams, Ganesan, Fuji, Carreira, Horne, Overman, and most recently Trost.
From a synthetic point of view, the most challenging structural features of the molecule are the C3 spirocyclic ring juncture and the adjacent prenyl-substituted carbon. Approaches toward preparing the skeleton of spirotryprostatin B have varied considerably.
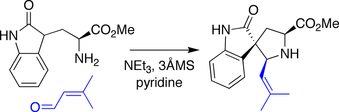
Danishefsky spirotryprostatin B synthesis
In the Danishefsky synthesis, an amine derived from tryptophan was condensed with an aldehyde, triggering a Mannich-type reaction wherein the pendant oxindole acted as a nucleophile toward the intermediate iminium species.
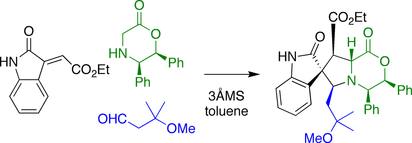
Williams spirotryprostatin B synthesis
The synthesis by the Williams group utilized a 3-component coupling reaction. A secondary amine was combined with an aldehyde to form an intermediate azomethine ylide, which underwent a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition with an unsaturated oxindole also present in the reaction mixture.
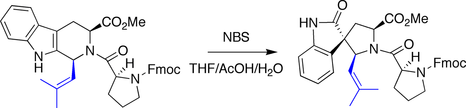
Ganesan spirotryprostatin B synthesis
Ganesan made use of a biomimetic strategy in his synthesis of spirotryprostatin B. An indole was treated with N-bromosuccinimide to trigger an oxidative rearrangement, forming the quaternary stereocenter in a diastereoselective manner.
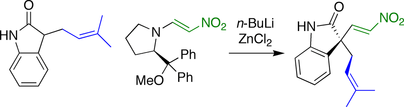
Fuji spirotryprostatin B synthesis
In the synthesis developed by the Fuji group, the stereochemistry at the spirocyclic carbon was established by a nitroolefination reaction. An oxindole with pendant prenyl group was reacted with a nitroolefin bearing a chiral leaving group.
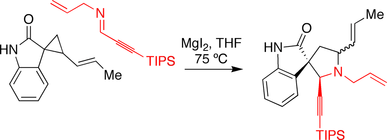
Carreira spirotryprostatin B synthesis
The Carreira group made use of a magnesium iodide promoted annulation reaction in their approach toward spirotryprostatin B. An oxindole bearing a cyclopropane was reacted with an imine in the presence of the magnesium iodide, triggering the ring-expansion reaction.
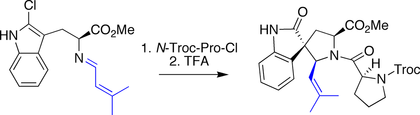
Horne spirotryprostatin B synthesis
Horne's synthesis of spirotryprostatin B also made use of a Mannich-type process, wherein a chloro-indole served as the pro-nucleophile. The cyclization was triggered by treating the pendant imine with the acyl chloride derived from proline. The resulting iminium species was attacked by the chloro-indole, forming the spirocyclic bond.
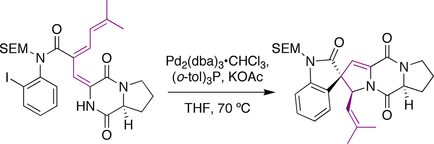
Overman spirotryprostatin B synthesis
The Overman group utilized a Heck reaction to prepare the molecule. An iodo-aniline with a tethered alkene was subjected to palladium catalysis. The intermediate palladium-allyl species was intercepted by the pendant amide nitrogen to generate the prenyl stereocenter in the same reaction.
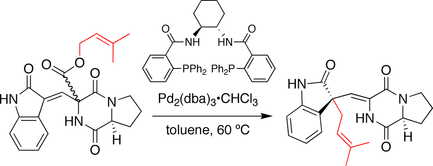
Trost spirotryprostatin B synthesis
In the synthesis developed by the Trost group, the stereochemistry at the spirocyclic ring juncture is established by a decarboxylation-prenylation sequence, reminiscent of the Carroll reaction. Here, a prenyl ester serves as both the nucleophile and electrophile precursor. Upon treatment with a chiral palladium catalyst the prenyl group ionizes and decarboxylates. The resulting ion pair subsequently recombines to generate the prenylated product. Notably, double bond migration occurs and the prenyl group is attacked at the oxindole carbon.
References
- ^ Borthwick AD; et al. (2012). "2,5-Diketopiperazines: Synthesis, Reactions, Medicinal Chemistry, and Bioactive Natural Products". Chemical Reviews. 112 (7): 3641–3716. doi:10.1021/cr200398y. PMID 22575049.
- ^ Cui, CB (1996). "Spirotryprostatin B, a novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitor produced by Aspergillus fumigatus". J. Antibiot. 49 (8): 832–835. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.49.832. PMID 8823522.
- ^ von Nussbaum, F; Danishefsky, SJ (2000). "A Rapid Total Synthesis of Spirotryprostatin B: Proof of Its Relative and Absolute Stereochemistry". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39 (12): 2175–2178. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20000616)39:12<2175::AID-ANIE2175>3.0.CO;2-J. PMID 10941053.
- ^ Sebahar, PR; Williams, RM (2000). "The Asymmetric Total Synthesis of (+)- and (−)-Spirotryprostatin B". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122 (23): 5666–5667. doi:10.1021/ja001133n.
- ^ Wang, H; Ganesan, A (2000). "A Biomimetic Total Synthesis of (−)-Spirotryprostatin B and Related Studies". J. Org. Chem. 65 (15): 4685–4693. doi:10.1021/jo000306o. PMID 10959875.
- ^ Bagul, TD; et al. (2002). "Total Synthesis of Spirotryprostatin B via Asymmetric Nitroolefination". Org. Lett. 4 (2): 249–251. doi:10.1021/ol016999s. PMID 11796062.
- ^ Meyers, C; Carreira, EM (2003). "Total Synthesis of (−)-Spirotryprostatin B". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42 (6): 694–696. doi:10.1002/anie.200390192. PMID 12575009.
- ^ Miyake, FY; et al. (2004). "Preparation and Synthetic Applications of 2-Halotryptophan Methyl Esters: Synthesis of Spirotryprostatin B". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43 (40): 5357–5360. doi:10.1002/anie.200460419. PMID 15468070.
- ^ Overman, LE; Rosen, MD (2000). "Total Synthesis of (−)-Spirotryprostatin B and Three Stereoisomers". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39 (24): 4596–4599. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20001215)39:24<4596::AID-ANIE4596>3.0.CO;2-F.
- ^ Trost, BM; Stiles, DT (2007). "Total Synthesis of Spirotryprostatin B via Diastereoselective Prenylation". Org. Lett. 9 (15): 2763–2766. doi:10.1021/ol070971k. PMID 17592853.