Southern Area Command (RAAF)
Southern Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in March 1940, and initially controlled units located in Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia and southern New South Wales. Headquartered in Melbourne, Southern Area Command was responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. From 1942 its operational responsibilities excluded New South Wales.
| Southern Area Command | |
|---|---|
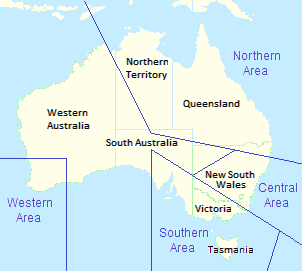 Provisional RAAF area command boundaries, February 1940 | |
| Active | 1940–53 |
| Allegiance | Australia |
| Branch | Royal Australian Air Force |
| Role | Air defence Aerial reconnaissance Protection of adjacent sea lanes |
| Garrison/HQ | Melbourne |
| Engagements | World War II |
| Commanders | |
| Notable commanders | Henry Wrigley (1940) Adrian Cole (1940–41) Frank Bladin (1941) Ian McLachlan (1944–45) Charles Eaton (1945) Allan Walters (1948–50) Alan Charlesworth (1951–53) |
The area command continued to operate following the end of the war, becoming the hub of Air Force training services. In October 1953, the RAAF began reorganising its command-and-control system from one based on geography to one based on function; Southern Area was re-formed as Training Command, which in 2006 became Air Force Training Group, a component of RAAF Air Command.
History
World War II
Prior to World War II, the Royal Australian Air Force was small enough for all its elements to be directly controlled by RAAF Headquarters in Melbourne. After war broke out in September 1939, the RAAF began to decentralise its command structure, commensurate with expected increases in manpower and units.[1][2] Its initial move in this direction was to create Nos. 1 and 2 Groups to control units in Victoria and New South Wales, respectively.[3] Then, between March 1940 and May 1941, the RAAF divided Australia and New Guinea into four geographically based command-and-control zones: Central Area, Southern Area, Western Area, and Northern Area.[4] The roles of these area commands were air defence, protection of adjacent sea lanes, and aerial reconnaissance. Each was led by an Air Officer Commanding (AOC) responsible for the administration and operations of all air bases and units within his boundary.[2][4]
No. 1 Group, which had been established on 20 November 1939, was re-formed as one of the first two area commands, Southern Area, on 7 March 1940. Headquartered in Melbourne, Southern Area Command was given control of all Air Force units in Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia and the southern Riverina district of New South Wales.[5] Its inaugural AOC was Air Commodore Henry Wrigley, who had also led No. 1 Group.[6] His senior administrative staff officer was Group Captain Joe Hewitt.[7] Wrigley handed over command to Air Commodore Adrian "King" Cole, formerly AOC Central Area, in November 1940.[6]
By mid-1941, the RAAF's expanding instructional program necessitated the establishment of overarching training organisations on a semi-functional, semi-geographical basis. Accordingly, on 2 August, No. 1 (Training) Group was formed in Melbourne to assume responsibility for training units within Southern Area's boundaries, and No. 2 (Training) Group in Sydney took over training units then under Central Area, which was disbanded; control of other Central Area units was "divided as convenient", according to the official history of the war, between Southern and Northern Area Commands.[8][9] Air Commodore Frank Bladin held command of Southern Area from September to December 1941.[6]

As of 20 April 1942, operational authority over all RAAF combat infrastructure, including area commands, was invested in the newly established Allied Air Forces Headquarters under South West Pacific Area Command (SWPA).[10][11] On 15 May, Southern Area, which by then was considered too large, yielded responsibility for operational and maintenance units within New South Wales to a new area command, Eastern Area. Control of maintenance units under Southern Area was transferred to the newly established No. 4 (Maintenance) Group in Melbourne on 14 September.[12] September also saw the formation of RAAF Command, led by Air Vice Marshal Bill Bostock, to oversee the majority of Australian flying units in the SWPA.[13][14] Bostock exercised control of air operations through the area commands, although RAAF Headquarters continued to hold overarching administrative authority over Australian units.[15]
Of geographical necessity, the operational responsibilities of the RAAF's southerly areas centred on maritime patrol and anti-submarine warfare, while the northern commands concentrated on air defence and offensive bombing.[15] In February 1943, Southern Area Command began incorporating convoy escorts into the training program of the Beauforts of No. 1 Operational Training Unit at Bairnsdale, Victoria.[16] As of April, the area was operating two squadrons: No. 67, flying maritime reconnaissance and anti-submarine missions with Avro Ansons out of RAAF Station Laverton, Victoria; and No. 86, flying P-40 Kittyhawk fighters from Gawler, South Australia.[17] No. 67 Squadron was one of several RAAF reserve formations hastily raised to augment the anti-submarine effort, crewed by staff and students from operational training units.[18][19] Group Captain Ian McLachlan commanded the area from March 1944 until January 1945, when he handed over to Group Captain Charles Eaton.[6]
The German submarine U-862 operated off southern Australia in December 1944 and January 1945, and the few combat units in Southern Area were heavily engaged in the search—ultimately unsuccessful—for this submarine and any others in the vicinity.[20] The Ansons were found wanting when it came to night operations, and Southern Area had to call in aircraft from Eastern Area and from training and maintenance units to buttress its patrol effort.[21] In April, Eaton complained to Bostock that intelligence from British Pacific Fleet concerning its ships' movements eastwards out of Western Area was hours out of date by the time it was received at Southern Area Command, leading to RAAF aircraft missing their rendezvous and wasting valuable flying hours searching empty ocean. There had been no U-boat strikes since February, and by June the naval authorities indicated that there was no pressing need for air cover except for the most important vessels.[20] Eaton led the command through to the surrender of Japan in September, and into December 1945.[6][22]
Post-war reorganisation
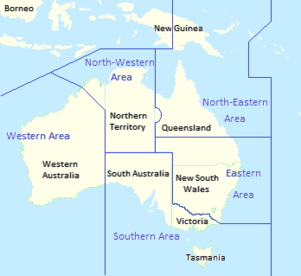
On 2 September 1945, following the end of the Pacific War, South West Pacific Area was dissolved and the RAAF again assumed full control of all its operational elements.[23] The Air Force shrank dramatically as personnel were demobilised and units disbanded; most of the RAAF's bases and aircraft employed in operations after the war were situated within Eastern Area's sphere of control in New South Wales and southern Queensland.[24] In September 1946, the Chief of the Air Staff, Air Vice Marshal George Jones, proposed reducing the five extant mainland area commands (North-Western, North-Eastern, Eastern, Southern, and Western Areas) to three: Northern Area, covering Queensland and the Northern Territory; Eastern Area, covering New South Wales; and Southern Area, covering Western Australia, South Australia, Victoria and Tasmania. The proposal was part of a much larger plan to restructure the post-war RAAF; the Federal government rejected the plan and the wartime area command boundaries essentially remained in place.[25][26] RAAF College (which became RAAF Academy in 1961) was established at RAAF Station Point Cook, Victoria, under Southern Area Command in August 1947.[27] The area's later AOCs included Air Commodores Allan Walters, from 1948 to 1950, and Alan Charlesworth, the last officer to command the area, from 1951 to 1953.[28][29]
The Federal government retired Jones in 1952 and replaced him with Air Marshal Donald Hardman, RAF, who proceeded to re-organise the RAAF command-and-control system along functional lines, establishing Home (operational), Training, and Maintenance Commands in October 1953. The first was re-formed from the existing Eastern Area Command, which was considered a de facto operational organisation owing to the preponderance of such forces within its boundaries. The second was re-formed from Southern Area Command, as it was already the hub of training services, controlling those in New South Wales and Queensland as well as Victoria and South Australia. The third and final functional command was formed from the extant Maintenance Group headquarters in Melbourne. The transition to a functional system was completed in February 1954, when the three new commands assumed control of all operations, training and maintenance from Western, North-Western, and North-Eastern Area Commands.[30][31]
Aftermath
The functional commands established in 1953–54 were revised in 1959. Home Command was renamed Operational Command, and Training and Maintenance Commands merged to become Support Command.[32] Operational Command was renamed Air Command in 1987, and three years later Support Command split into Logistics Command and Training Command.[33] Training Command was re-formed as Air Force Training Group, a force element group under Air Command, in 2006.[34]
Order of battle
As at 30 April 1942, Southern Area's order of battle comprised:[35]
- RAAF Station Laverton
- General Reconnaissance School, Cressy
- No. 7 (General Reconnaissance) Squadron, Bairnsdale
- No. 7 Fighter Sector Headquarters, Melbourne
- RAAF Station Richmond
- RAAF Station Canberra
- No. 4 (Army Cooperation) Squadron
- No. 18 (Heavy Bomber) Squadron
- Survey Flight
- RAAF Station Rathmines
- No. 2 Fighter Sector Headquarters, Newcastle
Notes
- Stephens, The Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 111–112
- "Organising for war: The RAAF air campaigns in the Pacific" (PDF). Pathfinder. No. 121. Air Power Development Centre. October 2009. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 66–67
- Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 91–92
- Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force, pp. xix–xx, 27–29
- Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force, pp. 302–304
- "Many Air Force promotions appointments". The Courier-Mail. Brisbane: National Library of Australia. 25 April 1940. p. 2. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, p. 112
- Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force, pp. xx, 38
- Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, p. 473
- Odgers, Air War Against Japan, pp. 15–16
- Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force, pp. xxi, 134–135
- Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 585–588
- Odgers, Air War Against Japan, pp. 4–6
- Stephens, The Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 144–145
- Wilson, The Eagle and the Albatross, pp. 79–80
- Odgers, Air War Against Japan, p. 141
- Odgers, Air War Against Japan, p. 140
- Wilson, The Eagle and the Albatross, pp. 73–74
- Odgers, Air War Against Japan, pp. 351–354
- Stevens, A Critical Vulnerability, p. 269
- "Eaton, Charles". World War 2 Nominal Roll. Department of Veterans' Affairs. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force!, p. 262
- Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 11–12, 72–73
- Helson, The Private Air Marshal, pp. 321–325
- Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 68, 462
- Frost, RAAF College & Academy, pp. 6, 45
- "Air Vice-Marshals (L–Z)". Air Marshals of the RAAF. Air Power Development Centre. Archived from the original on 1 June 2011. Retrieved 20 July 2015.
- "Honorary Air Vice-Marshals". Air Marshals of the RAAF. Air Power Development Centre. Archived from the original on 1 June 2011. Retrieved 20 July 2015.
- "Sir Donald Hardman's reorganisation of the RAAF" (PDF). Pathfinder. No. 106. Air Power Development Centre. March 2009. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 73–76, 462–463
- Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 76–77
- Dennis et al, The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History, pp. 150–151
- "Air Force Training Group". Royal Australian Air Force. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force, pp. 299–300
References
- Ashworth, Norman (2000). How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume One – Narrative (PDF). Canberra: RAAF Air Power Studies Centre. ISBN 0-642-26550-X.
- Dennis, Peter; Grey, Jeffrey; Morris, Ewan; Prior, Robin (2008) [1995]. The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History. South Melbourne: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-551784-2.
- Frost, R.E. (1991). RAAF College & Academy 1947–86 (PDF). Canberra: Royal Australian Air Force. ISBN 978-0-646-08518-0.
- Gillison, Douglas (1962). Australia in the War of 1939–1945: Series Three (Air) Volume I – Royal Australian Air Force 1939–1942. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 2000369.
- Helson, Peter (2010). The Private Air Marshal: A Biography of Air Marshal Sir George Jones, KBE, CB, DFC (PDF). Canberra: Air Power Development Centre. ISBN 978-1-920800-50-5.
- Odgers, George (1968) [1957]. Australia in the War of 1939–1945: Series Three (Air) Volume II – Air War Against Japan 1943–1945. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 246580191.
- Stephens, Alan (1995). Going Solo: The Royal Australian Air Force 1946–1971 (PDF). Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service. ISBN 978-0-644-42803-3.
- Stephens, Alan (2006) [2001]. The Royal Australian Air Force: A History. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19555-541-7.
- Stevens, David (2005). A Critical Vulnerability: The Impact of the Submarine Threat on Australia's Maritime Defence 1915–1954 (PDF). Canberra: Sea Power Centre – Australia. ISBN 0-642-29625-1.
- Wilson, David (2003). The Eagle and the Albatross: Australian Aerial Maritime Operations 1921–1971 (Ph. D thesis). Sydney: University of New South Wales.