Sorption
Sorption is a physical and chemical process by which one substance becomes attached to another. Specific cases of sorption are treated in the following articles:
- Absorption – "the incorporation of a substance in one state into another of a different state"[1] (e.g., liquids being absorbed by a solid or gases being absorbed by a liquid);
- Adsorption – the physical adherence or bonding of ions and molecules onto the surface of another phase (e.g., reagents adsorbed to a solid catalyst surface);
- Ion exchange – an exchange of ions between two electrolytes or between an electrolyte solution and a complex.
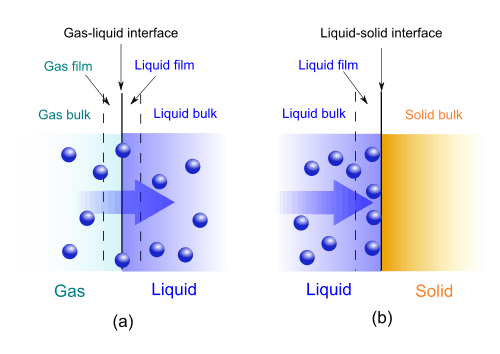
Gas–liquid absorption (a) and liquid–solid adsorption (b) mechanism. Blue spheres are solute molecules.
The reverse of sorption is desorption.
Sorption rate
The adsorption and absorption rate of a diluted solute in gas or liquid solution to a surface or interface can be calculated using Fick's laws of diffusion.
gollark: >and really no decent program would rely on it
gollark: >that shouldn't be needed
gollark: That seems arbitrary and prone to issues.
gollark: Whynot™?
gollark: I think they mean the mouse cursor.
See also
- Sorption isotherm
References
- Crini, edited by Grégorio; Badot, Pierre-Marie (2010). Sorption processes and pollution : conventional and non-conventional sorbents for pollutant removal from wastewaters. Besançon: Presses universitaires de Franche-Comté. p. 43. ISBN 2848673044.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
| Look up sorption in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.