Soloviev D-20
The Soloviev D-20P was a low-bypass turbofan engine rated at 52.9 kN (11,900 lbf) thrust. It was built by the Soloviev Design Bureau. The engine was used on the Tupolev Tu-124. A later derivative with increased bypass ratio, the D-20P-125, was developed into the Soloviev D-30 family of low and medium bypass engines.[1]
| D-20 | |
|---|---|
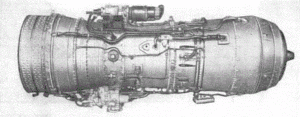 | |
| Left side view of the Soloviev D-20 engine | |
| Type | Turbofan |
| Manufacturer | Soloviev Design Bureau |
| Major applications | Tupolev Tu-124 |
Specifications
Data from Aircraft engines of the World 1970[2]
General characteristics
- Type: Twin-spool turbofan engine
- Length: 3,304 mm (130.1 in)
- Diameter: 976 mm (38.4 in)
- Frontal area: 0.74 m2 (8 sq ft)
- Dry weight: 1,450 kg (3,200 lb)
Components
- Compressor: Three-stage LP, eight-stage HP, axial flow
- Combustors: Cannular with 12 flame tubes
- Turbine: Two-stage LP turbine, single-stage HP turbine
- Fuel type: Aviation Kerosene, Jet A, Jet A-1, JP-1
- Oil system: Pressure spray at 3.9 bar (57 psi)
Performance
- Maximum thrust: 53 kN (11,900 lbf) at 11,700 HP rpm
- Overall pressure ratio: 13:1 overall
- Fan pressure ratio: 2.6:1
- HP pressure ratio: 13.6:1
- Fan pressure ratio: 2.6:1
- Bypass ratio: 1:1
- Air mass flow:
- Fan mass airflow: 113 kg/s (250 lb/s) at 8,550 LP rpm
- HP mass airflow: 56.5 kg/s (125 lb/s) at 11,7000 HP rpm
- Fan mass airflow: 113 kg/s (250 lb/s) at 8,550 LP rpm
- Turbine inlet temperature: JPT 923 K (650 °C)
- Specific fuel consumption:
- S.f.c. cruise: 73 kg/kN/h (0.72 lb/lbf/h)
- S.f.c. take-off: 92 kg/kN/h (0.9 lb/lbf/h)
- S.f.c. cruise: 73 kg/kN/h (0.72 lb/lbf/h)
- Thrust-to-weight ratio: 3.73
gollark: Random data would be better than the same distinct data, though?
gollark: I wonder if you could randomize the data it uses to fingerprint without breaking anything too badly. Though I guess "this is random" would be a strong signal itself.
gollark: Would it not show those as different OSes?
gollark: I should add this to my website.
gollark: And so can some governments.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Soloviev D-20. |
- Gunston, Bill (1989). World Encyclopaedia of Aero Engines (2nd ed.). Cambridge, England: Patrick Stephens Limited. p. 164. ISBN 978-1-85260-163-8.
- Wilkinson, Paul H. (1970). Aircraft engines of the World 1970 (22nd ed.). London: Paul H. Wilkinson. p. 223.
Further reading
- Taylor, John W.R., ed. (1972). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1972–73. London: Sampson Low, Marston & Co. Ltd. p. 751. ISBN 978-0354001090.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.