Shichinohe Domain
Shichinohe Domain (七戸藩, Shichinohe-han) was a tozama feudal domain of Edo period Japan, located in Mutsu Province, Honshū. It was centered at Shichinohe Castle in what is now the modern town of Shichinohe, Aomori in the Kamikita District of Aomori Prefecture, in the Tōhoku region of far northern Japan.
| Shichinohe Domain 七戸藩 | |
|---|---|
| under Tokugawa shogunate Japan | |
| 1819–1871 | |
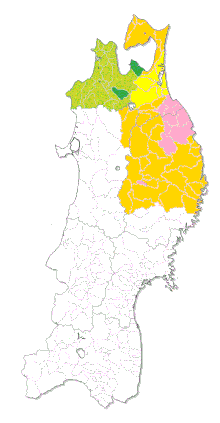 Map of Nanbu and Tsugaru clan holdings in the late Edo period. Morioka Domain in orange, Hachinohe Domain in pink and Shichinohe Domain in yellow; lands of the rival Tsugaru Domain are in green | |
| Capital | Shichinohe Castle |
| Area | |
| • Coordinates | 40°41′53″N 141°08′56″E |
| • Type | Daimyō |
| Historical era | Edo period |
• Split from Morioka Domain | 1819 |
• Disestablished | 1871 |
| Today part of | part of Aomori Prefecture |
History
The Nanbu clan controlled this region of northern Japan from the Muromachi period, and Shichinohe Castle was occupied by a branch of the clan on this site until the end of the Sengoku period. However, in 1591 the Shichinohe-branch of the Nanbu clan opposed the forces of clan chieftain Nanbu Nobunao and Toyotomi Hideyoshi during the Kunohe Rebellion and were defeated. The castle was abandoned in 1592 and allowed to fall into ruins.[1] The Shichinohe Nanbu clan was allowed to survive as 2300 koku hatamoto serving Morioka Domain under the Tokugawa shogunate. Their revenues were increased to 5000 koku in 1694, and they were given charge of a daikansho erected on the site of their old castle in 1804. With a raise in revenues to 11,000 koku in 1819, Shichinohe Domain was created.
The 11,000 koku domain existed largely on paper, as its daimyō lived in Edo permanently, and ruled the domain via a karō, who resided at a jin'ya erected on the site of the old castle.
In 1858, the daimyō of Shichinohe, Nanbu Nobuchika was raised to the status of castellan and granted formal permission to rebuild Shichinohe Castle as part of Japan’s increased defensive preparations again possible foreign incursions in light of the recent Perry Expedition. However, the Meiji restoration occurred before any construction could begin.
During the Boshin War of the Meiji Restoration, Nanbu Nobutami, the 3rd daimyō, supported the Ōuetsu Reppan Dōmei and fought against the pro-imperial forces of Hirosaki Domain in the Battle of Noheji. Consequently, he was forced into retirement by the new Meiji government and the revenues of Shichinohe Domain were decreased by 1,000 koku. His successor, Nanbu Nobukata became domain governor in 1869, and in October of that same year, the peasants in the domain rose up in a revolt. In July 1871, with the abolition of the han system, Shichinohe Domain became Shichinohe Prefecture, and was merged into the newly created Aomori Prefecture in September 1871. Nanbu Nobukata was later granted the title of viscount (shishaku) under the kazoku peerage.
List of daimyōs

| Name | Tenure | Courtesy title | Court Rank | kokudaka | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nanbu Nobuchika (南部信鄰) | 1819–1821 | Harima-no-kami (播磨守) | Junior 5th Rank, Lower Grade (従五位下) | 11,000 koku |
| 2 | Nanbu Nobunori (南部信誉) | 1822–1862 | Tamba-no-kami (丹波守) | Junior 4th Rank, Lower Grade (従四位下) | 11,000 koku |
| 3 | Nanbu Nobutami (南部信民) | 1862–1868 | Mimasaku-no-kami (美作守) | Junior 5th Rank, Lower Grade (従五位下) | 11,000 koku |
| 4 | Nanbu Nobukata (南部信方) | 1868–1871 | -none- | Junior 5th Rank (従五位下) | 10,000 koku |
Nanbu Nobuchika
Nanbu Nobuchika (南部信鄰, December 11, 1776 – December 19, 1821) was the 1st daimyō of Shichinohe Domain. He was the eldest son of Nanbu Nobuyoshi, a 5000 koku hatamoto of Morioka Domain. In December 1819, he received additional territories from his uncle, Nanbu Toshitaka, bringing his total past 10,000 koku and received elevation to the rank of daimyō. His courtesy title was Harima-no-kami, and his Court rank was Junior Fifth Rank, Lower Grade. Due to the death of the first Nanbu Toshimochi in 1820, he was called upon to assist in the governing of Morioka Domain. He was received in formal audience by shōgun Tokugawa Ienari on November 15, 1821 and confirmed in his title, but died only a few days later.
Nanbu Nobunori
Nanbu Nobunori (南部信誉, November 1805 – September 5, 1862) was the 2nd daimyō of Shichinohe Domain. He was the eldest son of Nanbu Nobuchika, and became daimyō at the age of 16 upon the death of his father. His courtesy title was Tamba-no-kami, and his Court rank was Junior Fifth Rank, Lower Grade. During his tenure, Shichinohe was awarded an increase in status to that of a “castle-holding domain” in 1858. His wife was the daughter of Mori Nagayoshi, daimyō of Mikazuki Domain. Although he had a son, he adopted the 4th son of Nanbu Toshitada from Morioka Domain to be his heir, but then set him aside in favour of an even more distant relative, Nanbu Nobutami, in 1849.[2]
Nanbu Nobutami
Nanbu Nobutami (南部信民, May 1833 – March 15, 1900) was the 3rd daimyō of Shichinohe Domain. He was the cousin of the karō of Morioka Domain, Sannohe Shikibu and great-grandson of Nanbu Toshimi). He was adopted by Nanbu Nobunori as his heir in 1849. is courtesy title was Mimasaka-no-kami, and his Court rank was Junior Fifth Rank, Lower Grade.On becoming daimyō in 1862, he closely aligned his policies with Morioka Domain. During the Boshin War of the Meiji restoration, he joined the Ōuetsu Reppan Dōmei to fight against the Nanbu clan’s hereditary enemies, the Tsugaru clan of Hirosaki Domain. After the war, his holdings were reduced by 1000 koku and he was ordered to retire by the Meiji government. However, as his successor Nanbu Nobukata was still underage, he continued to rule the domain, and sponsored sericulture and livestock raising in his final years.[3]
Nanbu Nobukata
Nanbu Nobukata (南部信方, June 22, 1858 – July 29, 1923) was the 4th and final daimyō of Shichinohe Domain. He was the third son of the daimyō of Morioka, Nanbu Toshihisa, and was adopted as heir to Nanbu Nobutami in December 1868 when Nobutami was ordered by the new Meiji government to retire for his role in leading the domain during the Boshin War. He became domain governor in June 1869 and had to suppress a peasant’s uprising in October of the same year. He was sent to America to study for a three year period from February 1876. In 1884 he was elevated to the kazoku peerage title of viscount (shishaku) [4] His wife was the daughter of Inoue Toshiyoshi, the daimyō of Kariya Domain, and he had only one daughter, who married into the Shimazu clan.
 Nanbu Nobutami
Nanbu Nobutami Nanbu Nobutaka
Nanbu Nobutaka
Bakumatsu period holdings
As with most domains in the han system, Shichinohe Domain consisted of several discontinuous territories calculated to provide the assigned kokudaka, based on periodic cadastral surveys and projected agricultural yields.[5][6]
- Mutsu Province
- 35 villages in Kita District
See also
- List of Han
References
- Papinot, E. (1910). Historical and Geographic Dictionary of Japan. Tuttle (reprint) 1972.
External links
- Shichinohe on "Edo 300 HTML" (19 Oct. 2007) (in Japanese)
Notes
- 七戸城跡. 記念物(史跡) (in Japanese). Aomori Prefectural Government. March 31, 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
- Ueda, Masaaki; Nishizawa, Jun'ichi; Hirayama, Ikuo (2001). 日本人名大辞典 (in Japanese). Kodansha. ISBN 9784062108003.
- 岩手県姓氏歴史人物大辞典 (in Japanese). Kadokawa. 1998. ISBN 4040020308.
- Shichinohe town official home page
- Mass, Jeffrey P. and William B. Hauser. (1987). The Bakufu in Japanese History, p. 150.
- Elison, George and Bardwell L. Smith (1987). Warlords, Artists, & Commoners: Japan in the Sixteenth Century, p. 18.