Serianthes nelsonii
Serianthes nelsonii is a large tree endemic to Guam and Rota of the Mariana Islands. Only one mature tree exists on Guam, while 121 mature trees have been identified on Rota since 1984.[2]
| Serianthes nelsonii | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | S. nelsonii |
| Binomial name | |
| Serianthes nelsonii | |
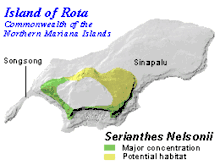 | |
The tree is found in limestone forests in Rota and Guam. It has bipinnately compound leaves and brush-like flowers with long pinkish filaments. Seedpods contain one to seven smooth brown seeds.[2]
Name
There are three local names for S. nelsonii. On Guam, it is known as hayun lågu, meaning "northern tree" or "foreign tree", referring to Rota, which is located north of Guam. The common name on Rota is trongkon guåfi, meaning "fire tree". Another name on Rota is trongkon fi'a may have originated in a region on Rota called Fia. Alternatively, "fi'a" may have derived from the Chamorro pronunciation of "fire", from "guåfi". The species was named "nelsonii" by E.D. Merrill in 1919 to honor Peter Nelson of the Guam Department of Agriculture, the discoverer of the plant.[2]
Conservation
S. nelsonii was declared an endangered plant in 1987[2] and was assessed as critically endangered in 1998 and again in 2017.[1] The University of Guam began a program to save the plant in 1998 with the help of numerous other agencies. S. nelsonii seedlings are being raised on protected lands for transplantation back into the wilds of Guam. On Rota, the Department of Lands and Natural Resource is monitoring the plant population and growing seedlings in a plant nursery.[2] In 2019, the single remaining mature tree on Guam was diagnosed with heart rot, raising concerns about if it could survive the next tropical storms. A total of 18 trees exist on Guam. In June 2019, the Legislature of Guam passed a resolution to urging a halt to planned military buildup and construction until the impact to S. nelsonii could be investigated.[3]
Insufficient regeneration is blamed for the decline of the population. Possible causes include insect predation on seeds and predation on seedlings by invasive ungulates and mealybugs. The subpopulation on Rota is expected to decline as older trees die.[1]
References
- Wiles, G.; Williams, E. (2017). "Serianthes nelsonii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T30437A98715973. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T30437A98715973.en.
- Serianthes nelsonii, poster by Agricultural Experiment Station, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, University of Guam
- Ngirairikl, Oyaol (25 June 2019). "Guam has 18 rare tree survivors". The Guam Daily Post. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Serianthes nelsonii. |
- "Species Profile for Hayun Iagu (Serianthes nelsonii)". Environmental Conservation Online System. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
