Schoenus compar
Schoenus compar (ivory veldrush) is a species of sedge endemic to southern South Africa.
| Schoenus compar | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Ivory veldrush | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Schoenus |
| Species: | S. compar |
| Binomial name | |
| Schoenus compar L. | |
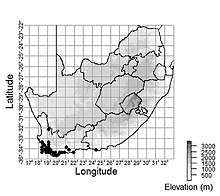 | |
| Documented collection localities in South Africa | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Diagnostic characters
Similar to other sedges, plants in this group are very difficult to identify. It appears that part of this problem is caused by the tendency of the southern African Schoenus to form hybrids with each other.[2] However, hybridization is yet to be observed in S. compar.[1]
This species is one of the more conspicuous Southern African Schoenus species.[1] Key diagnostic characters include papery, ivory leaf sheaths, as well as compact and thick inflorescences.[1] The spikelet glumes are relatively firm and viscous, and range in colour from gold when young to reddish-brown when mature.[1] Part of the plant is viscous, especially the culm bases and inflorescences.[1]
 Inflorescence
Inflorescence Inflorescences
Inflorescences Spikelet (black scale bar represents 1 mm)
Spikelet (black scale bar represents 1 mm)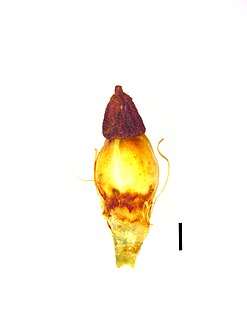 Nutlet (black scale bar represents 1 mm)
Nutlet (black scale bar represents 1 mm)
Taxonomy
Schoenus compar is a species in family Cyperaceae, tribe Schoeneae.[3] Other notable genera in tribe Schoeneae include Lepidosperma, Oreobolus, Costularia, Tetraria and Gahnia.[3][4][5] The most closely related species to S. compar are other southern African Schoenus species, specifically, species in the Schoenus compar - Schoenus pictus group.[1]
Southern African Schoenus were once classified as Tetraria; however, based on molecular and morphological differences, we now know that the two groups are evolutionary distinct.[6] To ensure that this group of sedges is monophyletic (i.e. the genus only has closely related species), the southern African Tetraria were transferred into Schoenus.[6] In the field, the southern African Schoenus can be distinguished from Tetraria species by their lack of stem leaves and the absence of reticulate sheaths at the bases of the flowering stems.[6]
Distribution and ecology
Schoenus compar mostly occurs in southwestern South Africa, although it reaches Humansdorp in the East and the Cederberg mountains in the north.[1] It is a species that grows on coarser growing substrates (e.g. sand or rocks) at lower elevations (20 m to over 800 m) than other Southern African Schoenus species.[1] This species mostly grows on dry sites among fynbos vegetation.[1]
Images
 Growth form of Schoenus compar
Growth form of Schoenus compar Growth form of Schoenus compar
Growth form of Schoenus compar
References
- Elliott, T.L.; Muasya, A.M. (2018). "A taxonomic revision of Schoenus compar - Schoenus pictus and allies (Cyperaceae, tribe Schoeneae) with three new species described from South Africa". South African Journal of Botany. 114: 303–315. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2017.11.020.
- Levyns, M. (1947). "Tetraria and related genera, with special reference to the flora of the Cape Peninsula". Journal of South African Botany. 13: 73–93.
- Elliott, T.L.; Barrett, R.L.; Muasya, A.M. (2019). "A taxonomic revision of Schoenus cuspidatus and allies (Cyperaceae, tribe Schoeneae)—Part 1". South African Journal of Botany. 121: 519–535. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2018.11.021.
- Viljoen, J.-A.; Muasya, A.M.; Barrett, R.L.; Bruhl, J.J.; Gibbs, A.K.; Slingsby, J.A.; Wilson, K. L.; Verboom, G.A. (2013). "Radiation and repeated transoceanic dispersal of Schoeneae (Cyperaceae) through the southern hemisphere". American Journal of Botany. 100 (12): 2494–2508. doi:10.3732/ajb.1300105.
- Larridon, I.; Bauters, K.; Semmouri, I.; Viljoen, J.-A.; Prychid, C.J.; Muasya, A.M.; Bruhl, J.J.; Wilson, K.L.; Senterre, B.; Goetghebeur, P. (2018). "Molecular phylogenetics of the genus Costularia (Schoeneae, Cyperaceae) reveals multiple distinct evolutionary lineages". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 126: 196–209. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2018.04.016.
- Elliott, T.L.; Muasya, A.M. (2017). "Taxonomic realignment in the southern African Tetraria (Cyperaceae, tribe Schoeneae; Schoenus clade)". South African Journal of Botany. 112: 354–360. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2017.06.011.