Santo Tomas, Davao del Norte
Santo Tomas, officially the Municipality of Santo Tomas (Cebuano: Lungsod sa Santo Tomas; Tagalog: Bayan ng Santo Tomas), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Davao del Norte, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 118,750 people.[3]
Santo Tomas | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Santo Tomas | |
 Municipal Hall | |
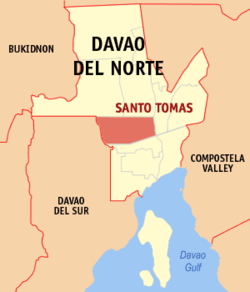 Map of Davao del Norte with Santo Tomas highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 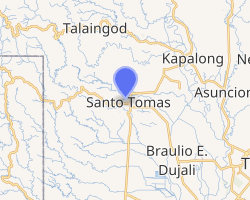
| |
.svg.png) Santo Tomas Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 7°32′N 125°37′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Davao Region (Region XI) |
| Province | Davao del Norte |
| District | 2nd District |
| Founded | August 14, 1959 |
| Barangays | 19 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Ernesto T. Evangelista |
| • Vice Mayor | Gabriel Eric L. Estela |
| • Congressman | Alan R. Dujali |
| • Electorate | 64,276 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 221.8 km2 (85.6 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 118,750 |
| • Density | 540/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| • Households | 26,041 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 1st municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 23.26% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 296,102,536.71 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 8112 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)84 |
| Climate type | tropical rainforest climate |
| Native languages | Davawenyo Cebuano Ata Manobo Kalagan language Tagalog |
| Website | www |
Etymology
Santo Tomas was so named after Saint Thomas, the patron saint of Danao which is the hometown of then Governor of undivided Davao Province Vicente Duterte, father of the 16th Philippine president Rodrigo Duterte.
History
What is now Santo Tomas, initially called Tibal-og, was once part of the jurisdiction of nearby town of Kapalong. Before the 1950s. the place used to be a lush forest inhabited by the indigenous Ata-Manobo people.
According to the town's pioneering residents, the area of what is now Kapalong (in which what is now Santo Tomas was still part of) and Panabo City were planted for abaca during the pre-war years.
After the founding of Santo Tomas as a municipality, it continued to grow and prosper, even as it went several successions of mayoralty governance throughout its history.
Geography
Santo Tomas is located on the island of Mindanao, and it is in the province's second political district. It is bounded in the north by the Municipalities of Kapalong and Talaingod, in the east by the Municipality of Asuncion, in the west by Davao City, and in the south by the Municipality of Braulio E. Dujali.
Barangays
Santo Tomas is politically subdivided into 19 barangays.
- Balagunan
- Bobongon
- Casig-Ang
- Esperanza
- Kimamon
- Kinamayan
- La Libertad
- Lungaog
- Magwawa
- New Katipunan
- New Visayas
- Pantaron
- Salvacion
- San Jose
- San Miguel
- San Vicente
- Talomo
- Tibal-og
- Tulalian
Climate
Rainfall in Santo Tomas is evenly distributed throughout the year. Being a nearly typhoon-free municipality, the production of high-value crops is favorable all year round and makes a profitable investment.
| Climate data for Santo Tomas, Davao del Norte | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22 (72) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 63 (2.5) |
50 (2.0) |
35 (1.4) |
22 (0.9) |
47 (1.9) |
68 (2.7) |
51 (2.0) |
53 (2.1) |
49 (1.9) |
47 (1.9) |
39 (1.5) |
38 (1.5) |
562 (22.3) |
| Average rainy days | 15.0 | 12.6 | 10.4 | 8.2 | 18.8 | 22.5 | 21.2 | 20.5 | 20.3 | 20.3 | 14.4 | 11.7 | 195.9 |
| Source: Meteoblue [5] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 16,687 | — |
| 1970 | 21,241 | +2.44% |
| 1975 | 31,584 | +8.28% |
| 1980 | 44,512 | +7.10% |
| 1990 | 67,916 | +4.32% |
| 1995 | 77,182 | +2.43% |
| 2000 | 84,367 | +1.93% |
| 2007 | 97,210 | +1.97% |
| 2010 | 109,269 | +4.35% |
| 2015 | 118,750 | +1.60% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3][6][7][8] | ||
Santo Tomas is home to a diverse culture inter-mingling with Mandaya and Ata-Manobo. The people are predominantly Cebuano.
Economy

Significant to the economic development of Santo Tomas is a number of multi-national corporations and cooperatives engaged in banana based commercial production successfully operating in the municipality. Rice production also contributes to the economic development of the municipality. SantoTomas was part of the lists for the top 15 richest municipality in Davao Region which was listed as the second place.
Transportation

Santo Tomas sits astride the Davao del Norte Provincial Circumferential Road. It is more or less 30 kilometres (19 mi) or about an hour ride from Tagum City by any land vehicle, and the town offers a wide choice of public utility jeepneys via Kinamayan route or bus liners via Carmen route. Davao City is approximately 63 kilometres (39 mi) or an hour and a half ride by bus or private car.
Santo Tomas is accessible by land through any type of vehicle. There are tricycle units serving the different routes within the municipality. Most tricycles are color-coded red, with a capacity of 6 passengers per tricycle.
Education
Santo Tomas have several public and private institutions.
Elementary schools:
- Apitong Elementary School (Public)
- Balagunan Elementary School (Public)
- Balisong Elementary School (Public)
- Bobongon Elementary School (Public)
- Casig-ang Elementary School (Public)
- Davao Winchester Colleges Inc. (Private)
- Esperanza Elementary School (Public)
- Holy Infant School of Santo Tomas, Inc. (Private)
- Jireh School of Tomorrow (Private)
- Jesus Lumain Elementary School (Public)
- Kimamon Elementary School (Public)
- Kinamayan Integrated School (Public)
- La Libertad Elementary School (Public)
- Lunga-og Elementary School (Public)
- Magwawa Elementary School (Public)
- Marsman Elementary School (Public)
- Maryknoll High School of Santo Tomas (Private)
- Mustard Seed Christian School, Inc. (Private)
- Nafco Central Elementary School (Public)
- New Katipunan Elementary School (Public)
- New Visayas Elementary School (Public)
- Pantaron Elementary School (Public)
- Philippine Baptist Christian College of Mindanao, Inc. (Private)
- Salvacion Elementary School (Public)
- San Isidro Elementary School (Public)
- San Jose Elementary School (Public)
- San Vincenzo Learning Center (Private)
- Santo Tomas Central Elementary School - Sped Center (Public)
- Talomo Elementary School (Public)
- Talos Elementary School (Public)
- Temple Christian School, Inc. (Private)
- Tulalian Elementary School (Public)
High schools:
- Balagunan National High School (Public)
- Davao Winchester Colleges Inc. (Private)
- Kimamon National High School (Public)
- La Libertad National High School (Public)
- Marsman National High School (Public)
- Maryknoll High School of Santo Tomas (Private)
- Mustard Seed Christian School, Inc. (Private)
- Philippine Baptist Christian College of Mindanao, Inc. (Private)
- Salvacion National High School (Public)
- Santo Tomas National High School (Public)
- Temple Christian School Inc. (Private)
- Tulalian National High School (Public)
Tertiary education:
- Bukidnon State University (discontinued)
- Davao Winchester Colleges Inc. (Private)
- University of Southeastern Philippines
- Santo Tomas College of Agriculture Science and Technology (STCAST)
Technical/vocational schools:
- ABA Technical School of Santo Tomas, Inc.
- Davao Winchester Colleges Inc. (Private)
Celebrations
Araw ng Santo Tomas (lit. Day of Santo Tomas) is a celebration held every 14 August annually. Events include drum and lyre competitions; parades, fireworks display, and many more.
Recently Winners (by ranking secondary level)
- Tulalian National High School
- Balagunan National High School
- La Libertad National High School
- Santo Tomas National High School
- Marsman National High School
- Kimamon National High School
- Magwawa Intigrated School
Gallery
 Row of parked tricycles outside the Santo Tomas Central Elem. School SPED Center campus.
Row of parked tricycles outside the Santo Tomas Central Elem. School SPED Center campus. Santo Tomas Cultural Gymnasium
Santo Tomas Cultural Gymnasium San Miguel Parish Church
San Miguel Parish Church Sito's Santo Tomas branch
Sito's Santo Tomas branch
References
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- "Province: Davao del Norte". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region XI (Davao Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- "Santo Tomas: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 29 February 2020.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region XI (Davao Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region XI (Davao Region)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Davao del Norte". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Santo Tomas, Davao del Norte. |