Salpingopharyngeus muscle
The salpingopharyngeus muscle arises from the superior border of the medial cartilage of the pharyngotympanic tube (Eustachian tube), in the nasal cavity, making the posterior welt of the torus tubarius;[1] it passes downward and blends with the posterior fasciculus of the palatopharyngeus muscle.
| Salpingopharyngeus muscle | |
|---|---|
 Dissection of the muscles of the palate from behind. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Lower part of the cartilage of the auditory tube |
| Insertion | Fibers pass downward and blend with the palatopharyngeus muscle to the upper border thyroid cartilage, blending with constrictor fibers |
| Nerve | Vagus nerve (CN X) |
| Actions | Assists in elevating the pharynx, pulls on torus tubarius to pressure equalize middle ear |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus salpingopharyngeus |
| TA | A05.3.01.115 |
| FMA | 46665 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The salpingopharyngeus is known to raise the pharynx and larynx during deglutition (swallowing) and laterally draws the pharyngeal walls up. In addition, it opens the pharyngeal orifice of the pharyngotympanic tube during swallowing. This allows for the equalization of pressure between the auditory canal and the pharynx. As the salpingopharyngeus is used to open the eustachian tubes to equalize pressure in the middle ear, the muscle can easily be stimulated by swallowing.
The salpingopharyngeus is innervated by the vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus, and irrigated by the ascending pharyngeal artery.
See also
Additional images
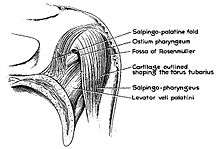 Torus tubarius dissection show salpingopharyngeus muscle
Torus tubarius dissection show salpingopharyngeus muscle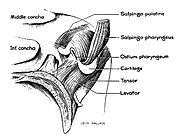 salpingopharyngeus muscle dissection
salpingopharyngeus muscle dissection
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1143 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Simkins, Cleveland S. (1943). "Functional Anatomy of the Eustachian Tube". Archives of Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery. 38 (5): 476–84. doi:10.1001/archotol.1943.00670040495009.