Prevertebral fascia
The prevertebral fascia (or prevertebral layer of cervical fascia) is a fascia in the neck.
| Prevertebral fascia | |
|---|---|
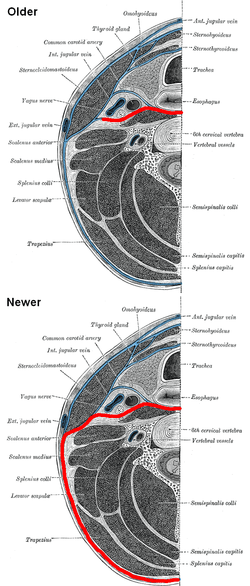 Prevertebral fascia labeled in red, both according to older literature (e.g. Gray's) and newer literature
.[1] Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the fascia coli. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lamina prevertebralis fasciae cervicalis |
| TA | A04.2.05.006 |
| FMA | 46560 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Variations
In some literature, the prevertebral fascia also includes the other fascial layers extending around the vertebral column and enclosing all muscles laterally and posteriorly to it.[1] However, in this article, it is assumed to be as marked in the corresponding picture.
Location
The prevertebral fascia extends medially behind the carotid vessels, where it assists in forming their sheath, and passes in front of the prevertebral muscles.
The prevertebral fascia is fixed above to the base of the skull, and below it extends behind the esophagus into the posterior mediastinal cavity of the thorax. It descends in front of the longus colli muscles.
The prevertebral fascia is prolonged downward and laterally behind the carotid vessels and in front of the scalene muscles. It forms a sheath for the brachial nerves, subclavian artery, and subclavian vein in the posterior triangle of the neck; it is continued under the clavicle as the axillary sheath and is attached to the deep surface of the coracoclavicular fascia.
Surrounding structures
It forms the posterior limit of a fibrous compartment, which contains the larynx and trachea, the thyroid gland, and the pharynx and esophagus.
Parallel to the carotid sheath and along its medial aspect the prevertebral fascia gives off a thin lamina, the buccopharyngeal fascia, which closely invests the constrictor muscles of the pharynx, and is continued forward from the constrictor pharyngis superior on to the buccinator.
Anterior to it, the alar (retrovisceral) fascia is attached to it by loose connective tissue only, and thus an easily distended space, the retropharyngeal space, is found between them.
Immediately above and behind the clavicle an areolar space exists between the investing layer and the sheath of the subclavian vessels, and in this space are found the lower part of the external jugular vein, the descending clavicular nerves, the transverse scapular and transverse cervical vessels, and the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle.
This space is limited below by the fusion of the coracoclavicular fascia with the anterior wall of the axillary sheath.
Inferiorly, the prevertebral layer blends with the endothoracic fascia peripherally and fuses with the anterior longitudinal ligament centrally at approximately the level of the T3 vertebra. Due to this, the superior extent of the retropharyngeal space is essentially continuous with the root of the neck, and is termed the danger space. It extends laterally as the axillary sheath.[2]
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 389 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Essential Clinical Anatomy. K.L. Moore & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002.
- Clinically Oriented Anatomy. K.L. Moore, A.F. Dalley, & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 6 ed. 2010.