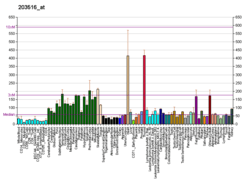
Syntrophin, alpha 1
Alpha-1-syntrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNTA1 gene[5][6][7]. Alpha-1 syntrophin is a signal transducing adaptor protein and serves as a scaffold for various signaling molecules. Alpha-1 syntrophin contains a PDZ domain, two Pleckstrin homology domain and a 'syntrophin unique' domain.
Function
Dystrophin is a large, rod-like cytoskeletal protein found at the inner surface of muscle fibers. Dystrophin is missing in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patients and is present in reduced amounts in Becker Muscular Dystrophy patients. The protein encoded by this gene is a peripheral membrane protein found associated with dystrophin and dystrophin-related proteins. This gene is a member of the syntrophin gene family, which contains at least two other structurally related genes.[7] The PDZ domain of syntrophin-α1(SNTA1), the most abundant isoform in the heart, has been reported to bind to the C-terminal domain of murine cardiac voltage-gated sodium channels (SkM2) causing altering ion channel activity leading to Long QT syndrome.[8][9]
Interactions
Syntrophin, alpha 1 has been shown to interact with Dystrophin,[5][10][11] Nav1.1[11] and Nav1.5[11], and Aquaporin 4.[12]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000101400 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027488 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Ahn AH, Freener CA, Gussoni E, Yoshida M, Ozawa E, Kunkel LM (Mar 1996). "The three human syntrophin genes are expressed in diverse tissues, have distinct chromosomal locations, and each bind to dystrophin and its relatives". J Biol Chem. 271 (5): 2724–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.5.2724. PMID 8576247.
- Castelló A, Brochériou V, Chafey P, Kahn A, Gilgenkrantz H (Jun 1996). "Characterization of the dystrophin-syntrophin interaction using the two-hybrid system in yeast". FEBS Lett. 383 (1–2): 124–8. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)00214-1. PMID 8612778.
- "Entrez Gene: SNTA1 syntrophin, alpha 1 (dystrophin-associated protein A1, 59kDa, acidic component)".
- Wu G, Ai T, Kim JJ, Mohapatra B, Xi Y, Li Z, Abbasi S, Purevjav E, Samani K, Ackerman MJ, Qi M, Moss AJ, Shimizu W, Towbin JA, Cheng J, Vatta M (Aug 2008). "Alpha-1-syntrophin mutation and the long-QT syndrome: a disease of sodium channel disruption". Circ Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 1 (3): 193–201. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.108.769224. PMC 2726717. PMID 19684871.
- Hedley PL, Jørgensen P, Schlamowitz S, Wangari R, Moolman-Smook J, Brink PA, Kanters JK, Corfield VA, Christiansen M (2009). "The genetic basis of long QT and short QT syndromes: a mutation update". Human Mutation. 30 (11): 1486–511. doi:10.1002/humu.21106. PMID 19862833.
- Yang B, Jung D, Rafael JA, Chamberlain JS, Campbell KP (Mar 1995). "Identification of alpha-syntrophin binding to syntrophin triplet, dystrophin, and utrophin". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (10): 4975–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.10.4975. PMID 7890602.
- Gee SH, Madhavan R, Levinson SR, Caldwell JH, Sealock R, Froehner SC (Jan 1998). "Interaction of muscle and brain sodium channels with multiple members of the syntrophin family of dystrophin-associated proteins". J. Neurosci. 18 (1): 128–37. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.18-01-00128.1998. PMID 9412493.
- Neely JD, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP, Froehner SC, Agre P, Adams ME (November 2001). "Syntrophin-dependent expression and localization of Aquaporin-4 water channel protein". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (24): 14108–13. doi:10.1073/pnas.241508198. PMC 61176. PMID 11717465.
Further reading
- Miyagoe-Suzuki Y, Takeda SI (2002). "Association of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) with alpha1-syntrophin at the sarcolemma". Microsc. Res. Tech. 55 (3): 164–70. doi:10.1002/jemt.1167. PMID 11747091.
- Blake DJ (2002). "Dystrobrevin dynamics in muscle-cell signalling: a possible target for therapeutic intervention in Duchenne muscular dystrophy?". Neuromuscul. Disord. 12 Suppl 1: S110–7. doi:10.1016/S0960-8966(02)00091-3. PMID 12206805.
- Yang B, Jung D, Rafael JA, Chamberlain JS, Campbell KP (1995). "Identification of alpha-syntrophin binding to syntrophin triplet, dystrophin, and utrophin". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (10): 4975–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.10.4975. PMID 7890602.
- Gee SH, Madhavan R, Levinson SR, Caldwell JH, Sealock R, Froehner SC (1998). "Interaction of muscle and brain sodium channels with multiple members of the syntrophin family of dystrophin-associated proteins". J. Neurosci. 18 (1): 128–37. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.18-01-00128.1998. PMID 9412493.
- Iwata Y, Pan Y, Yoshida T, Hanada H, Shigekawa M (1998). "Alpha1-syntrophin has distinct binding sites for actin and calmodulin". FEBS Lett. 423 (2): 173–7. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00085-4. PMID 9512352.
- Hasegawa M, Cuenda A, Spillantini MG, Thomas GM, Buée-Scherrer V, Cohen P, Goedert M (1999). "Stress-activated protein kinase-3 interacts with the PDZ domain of alpha1-syntrophin. A mechanism for specific substrate recognition". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (18): 12626–31. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.18.12626. PMID 10212242.
- Hillier BJ, Christopherson KS, Prehoda KE, Bredt DS, Lim WA (1999). "Unexpected modes of PDZ domain scaffolding revealed by structure of nNOS-syntrophin complex". Science. 284 (5415): 812–5. doi:10.1126/science.284.5415.812. PMID 10221915.
- Fernández-Larrea J, Merlos-Suárez A, Ureña JM, Baselga J, Arribas J (1999). "A role for a PDZ protein in the early secretory pathway for the targeting of proTGF-alpha to the cell surface". Mol. Cell. 3 (4): 423–33. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80470-0. PMID 10230395.
- Lumeng C, Phelps S, Crawford GE, Walden PD, Barald K, Chamberlain JS (1999). "Interactions between beta 2-syntrophin and a family of microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinases". Nat. Neurosci. 2 (7): 611–7. doi:10.1038/10165. PMID 10404183.
- Adams ME, Kramarcy N, Krall SP, Rossi SG, Rotundo RL, Sealock R, Froehner SC (2000). "Absence of alpha-syntrophin leads to structurally aberrant neuromuscular synapses deficient in utrophin". J. Cell Biol. 150 (6): 1385–98. doi:10.1083/jcb.150.6.1385. PMC 2150701. PMID 10995443.
- Newey SE, Benson MA, Ponting CP, Davies KE, Blake DJ (2001). "Alternative splicing of dystrobrevin regulates the stoichiometry of syntrophin binding to the dystrophin protein complex". Curr. Biol. 10 (20): 1295–8. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00760-0. PMID 11069112.
- Olalla L, Aledo JC, Bannenberg G, Márquez J (2001). "The C-terminus of human glutaminase L mediates association with PDZ domain-containing proteins". FEBS Lett. 488 (3): 116–22. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02373-5. PMID 11163757.
- Marchand S, Stetzkowski-Marden F, Cartaud J (2001). "Differential targeting of components of the dystrophin complex to the postsynaptic membrane". Eur. J. Neurosci. 13 (2): 221–9. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2001.01373.x. PMID 11168526.
- Xu H, Goldfarb M (2001). "Multiple effector domains within SNT1 coordinate ERK activation and neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (16): 13049–56. doi:10.1074/jbc.M009925200. PMID 11278583.
- Hogan A, Shepherd L, Chabot J, Quenneville S, Prescott SM, Topham MK, Gee SH (2001). "Interaction of gamma 1-syntrophin with diacylglycerol kinase-zeta. Regulation of nuclear localization by PDZ interactions". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (28): 26526–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104156200. PMID 11352924.
- Oak SA, Russo K, Petrucci TC, Jarrett HW (2001). "Mouse alpha1-syntrophin binding to Grb2: further evidence of a role for syntrophin in cell signaling". Biochemistry. 40 (37): 11270–8. doi:10.1021/bi010490n. PMID 11551227.
- Adams ME, Mueller HA, Froehner SC (2001). "In vivo requirement of the alpha-syntrophin PDZ domain for the sarcolemmal localization of nNOS and aquaporin-4". J. Cell Biol. 155 (1): 113–22. doi:10.1083/jcb.200106158. PMC 2150783. PMID 11571312.
- Neely JD, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP, Froehner SC, Agre P, Adams ME (2002). "Syntrophin-dependent expression and localization of Aquaporin-4 water channel protein". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (24): 14108–13. doi:10.1073/pnas.241508198. PMC 61176. PMID 11717465.