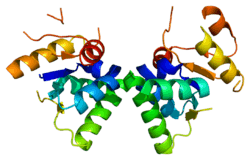SMG5
Protein SMG5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMG5 gene.[5][6][7] This protein contains a PIN domain that appears to have mutated the residues in the active site.[8]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000198952 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000001415 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Reichenbach P, Hoss M, Azzalin CM, Nabholz M, Bucher P, Lingner J (Apr 2003). "A human homolog of yeast Est1 associates with telomerase and uncaps chromosome ends when overexpressed". Curr Biol. 13 (7): 568–74. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00173-8. PMID 12676087.
- Snow BE, Erdmann N, Cruickshank J, Goldman H, Gill RM, Robinson MO, Harrington L (Apr 2003). "Functional conservation of the telomerase protein Est1p in humans". Curr Biol. 13 (8): 698–704. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00210-0. PMID 12699629.
- "Entrez Gene: SMG5 Smg-5 homolog, nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor (C. elegans)".
- Glavan F, Behm-Ansmant I, Izaurralde E, Conti E (November 2006). "Structures of the PIN domains of SMG6 and SMG5 reveal a nuclease within the mRNA surveillance complex". EMBO J. 25 (21): 5117–25. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601377. PMC 1630413. PMID 17053788.
Further reading
- Nakajima D, Okazaki N, Yamakawa H, et al. (2003). "Construction of expression-ready cDNA clones for KIAA genes: manual curation of 330 KIAA cDNA clones". DNA Res. 9 (3): 99–106. doi:10.1093/dnares/9.3.99. PMID 12168954.
- Kikuno R, Nagase T, Ishikawa K, et al. (1999). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XIV. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 6 (3): 197–205. doi:10.1093/dnares/6.3.197. PMID 10470851.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ohnishi T, Yamashita A, Kashima I, et al. (2004). "Phosphorylation of hUPF1 induces formation of mRNA surveillance complexes containing hSMG-5 and hSMG-7". Mol. Cell. 12 (5): 1187–200. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00443-X. PMID 14636577.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Unterholzner L, Izaurralde E (2005). "SMG7 acts as a molecular link between mRNA surveillance and mRNA decay". Mol. Cell. 16 (4): 587–96. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.10.013. PMID 15546618.
- Fukuhara N, Ebert J, Unterholzner L, et al. (2005). "SMG7 is a 14-3-3-like adaptor in the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway". Mol. Cell. 17 (4): 537–47. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.01.010. PMID 15721257.
- Azzalin CM, Lingner J (2006). "The human RNA surveillance factor UPF1 is required for S phase progression and genome stability". Curr. Biol. 16 (4): 433–9. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.01.018. PMID 16488880.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
- Lee H, Sengupta N, Villagra A, et al. (2006). "Histone deacetylase 8 safeguards the human ever-shorter telomeres 1B (hEST1B) protein from ubiquitin-mediated degradation". Mol. Cell. Biol. 26 (14): 5259–69. doi:10.1128/MCB.01971-05. PMC 1592721. PMID 16809764.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.