SFRS9
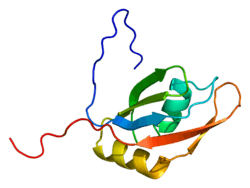
Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 9, also known as SFRS9, is a human gene encoding an SR protein involved in splice site selection in alternative splicing.[5]
Interactions
SFRS9 has been shown to interact with Y box binding protein 1[6] and NOL3.[7]
gollark: We could use this; it seems a cool idea.
gollark: WOW¡
gollark: !esowiki esowiki
gollark: !wiki Folders
gollark: <@435756251205468160> esowiki folders
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000111786 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029538 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: SFRS9 splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 9".
- Raffetseder, Ute; Frye Björn; Rauen Thomas; Jürchott Karsten; Royer Hans-Dieter; Jansen Petra Lynen; Mertens Peter R (May 2003). "Splicing factor SRp30c interaction with Y-box protein-1 confers nuclear YB-1 shuttling and alternative splice site selection". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (20): 18241–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212518200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12604611.
- Stoss, O; Schwaiger F W; Cooper T A; Stamm S (Apr 1999). "Alternative splicing determines the intracellular localization of the novel nuclear protein Nop30 and its interaction with the splicing factor SRp30c". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (16): 10951–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.16.10951. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10196175.
Further reading
- Screaton GR, Cáceres JF, Mayeda A, et al. (1995). "Identification and characterization of three members of the human SR family of pre-mRNA splicing factors". EMBO J. 14 (17): 4336–49. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00108.x. PMC 394518. PMID 7556075.
- Nayler O, Strätling W, Bourquin JP, et al. (1998). "SAF-B protein couples transcription and pre-mRNA splicing to SAR/MAR elements". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (15): 3542–9. doi:10.1093/nar/26.15.3542. PMC 147731. PMID 9671816.
- Yuan Y; Li DM; Sun H (1998). "PIR1, a novel phosphatase that exhibits high affinity to RNA . ribonucleoprotein complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (32): 20347–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.32.20347. PMID 9685386.
- Petersen-Mahrt SK, Estmer C, Ohrmalm C, et al. (1999). "The splicing factor-associated protein, p32, regulates RNA splicing by inhibiting ASF/SF2 RNA binding and phosphorylation". EMBO J. 18 (4): 1014–24. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.4.1014. PMC 1171193. PMID 10022843.
- Stoss O; Schwaiger FW; Cooper TA; Stamm S (1999). "Alternative splicing determines the intracellular localization of the novel nuclear protein Nop30 and its interaction with the splicing factor SRp30c". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (16): 10951–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.16.10951. PMID 10196175.
- Elliott DJ, Bourgeois CF, Klink A, et al. (2000). "A mammalian germ cell-specific RNA-binding protein interacts with ubiquitously expressed proteins involved in splice site selection". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (11): 5717–22. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.5717E. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.11.5717. PMC 18499. PMID 10823932.
- Stoss O, Olbrich M, Hartmann AM, et al. (2001). "The STAR/GSG family protein rSLM-2 regulates the selection of alternative splice sites". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (12): 8665–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006851200. PMID 11118435.
- Denegri M, Chiodi I, Corioni M, et al. (2002). "Stress-induced nuclear bodies are sites of accumulation of pre-mRNA processing factors". Mol. Biol. Cell. 12 (11): 3502–14. doi:10.1091/mbc.12.11.3502. PMC 60271. PMID 11694584.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, et al. (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
- Young PJ, DiDonato CJ, Hu D, et al. (2002). "SRp30c-dependent stimulation of survival motor neuron (SMN) exon 7 inclusion is facilitated by a direct interaction with hTra2 beta 1". Hum. Mol. Genet. 11 (5): 577–87. doi:10.1093/hmg/11.5.577. PMID 11875052.
- Simard MJ; Chabot B (2002). "SRp30c is a repressor of 3' splice site utilization". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (12): 4001–10. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.12.4001-4010.2002. PMC 133842. PMID 12024014.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Raffetseder U, Frye B, Rauen T, et al. (2003). "Splicing factor SRp30c interaction with Y-box protein-1 confers nuclear YB-1 shuttling and alternative splice site selection". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (20): 18241–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212518200. PMID 12604611.
- Xu Q; Leung DY; Kisich KO (2003). "Serine-arginine-rich protein p30 directs alternative splicing of glucocorticoid receptor pre-mRNA to glucocorticoid receptor beta in neutrophils". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (29): 27112–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300824200. PMID 12738786.
- Li J, Hawkins IC, Harvey CD, et al. (2003). "Regulation of alternative splicing by SRrp86 and its interacting proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (21): 7437–47. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.21.7437-7447.2003. PMC 207616. PMID 14559993.
- Kondo S, Yamamoto N, Murakami T, et al. (2004). "Tra2 beta, SF2/ASF and SRp30c modulate the function of an exonic splicing enhancer in exon 10 of tau pre-mRNA". Genes Cells. 9 (2): 121–30. doi:10.1111/j.1356-9597.2004.00709.x. PMID 15009090.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Wang Y, Wang J, Gao L, et al. (2005). "Tau exons 2 and 10, which are misregulated in neurodegenerative diseases, are partly regulated by silencers which bind a SRp30c.SRp55 complex that either recruits or antagonizes htra2beta1". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (14): 14230–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413846200. PMID 15695522.
- Scherer SE, Muzny DM, Buhay CJ, et al. (2006). "The finished DNA sequence of human chromosome 12". Nature. 440 (7082): 346–51. Bibcode:2006Natur.440..346S. doi:10.1038/nature04569. PMID 16541075.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.