SFCA Lignel 10
The SFCA Lignel 10 was a French single seat aircraft designed to bridge a training gap between basic trainers and front-line fighters. The military requirement was soon dropped and only one was built.
| Lignel 10 | |
|---|---|
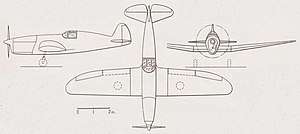 | |
| 3-views of the Lignel 10 | |
| Role | Fighter trainer |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Société Française de Construction Aéronautique (SFCA]) |
| First flight | February 1938 |
| Number built | 1 |
Design and development
The Lignel 10 of 1938 was a wooden low wing cantilever monoplane, one in the series of Société Française de Construction Aéronautique designs stretching back to the 1935 SFCA Maillet 20. It was a single-seater, intended to meet a military requirement for a trainer that would assist the pupil's transition from simple two seat trainers to faster and more complex fighters with flaps and retractable undercarriages. The wings of the Lignel 10, like those of the rest of the series were in three parts, with a rectangular plan centre section without diheral and outer panels which, on the Lignel 10, had about 6° of dihedral. The leading edges of these outer panels were straight and only slightly swept but the trailing edges were increasingly curved towards the wing tips. Inset ailerons and the split flaps were both on the outer panels.[1]
The Lignel 10 was powered by a 160 kW (220 hp) Renault 6Q-03[2] air-cooled, supercharged, inverted 6 cylinder inline engine. The cockpit, enclosed under multi-part glazing, placed the pilot over the wing trailing edge. The rear fuselage was raised to continue the canopy line, dropping gently away to the tail. Its fin and tailplane, the latter mounted at mid-fuselage, had straight, swept edges but rounded tips and carried round-edged, unbalanced control surfaces. The rudder extended down to the keel and worked in a small elevator cut-out.[1]
Its tailwheel landing gear had its main legs mounted at the outer ends of the wing centre section at about 40% chord, retracting outwards into the outer wing panels, Each leg carried a single landing wheel.[1]
The Lignel 10 first flew in February 1938.[3] It was undergoing tests at Villacoublay in July,[4] completing them by December 1938.[2] Only one was built as the military requirement was soon abandoned.[1]
Specifications (Lignel 10)
Data from L'Aéronautique December 1938[1]
General characteristics
- Crew: One
- Length: 7.85 m (25 ft 9 in) [Notes 1]
- Wingspan: 10.26 m (33 ft 8 in) [5]
- Height: 2.65 m (8 ft 8 in) [3]
- Wing area: 15 m2 (160 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 800 kg (1,764 lb) [3]
- Gross weight: 1,200 kg (2,646 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Renault 6Q-03[2] air-cooled, supercharged, inverted 6 cylinder inline, 160 kW (220 hp) at 2,000 m (6,560 ft)
- Propellers: 2-bladed
Performance
Notes
- from 3-view in ref1
References
- "Société française Constructions aéronautique (S.F.C.A.)". L'Aéronautique (235): 318. December 1938.
- "A la S.F.C.A." Les Ailes (912): 3–4. 11 December 1938.
- Bruno Parmentier (1 December 1998). "S.F.C.A. Lignel 10". Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- "Les Avions en Essai ." Les Ailes (892): 9. 21 July 1938.
- "Military Aircraft of the World". Flight. XXV (1579): 316. 30 March 1939.