Sàbat Hill
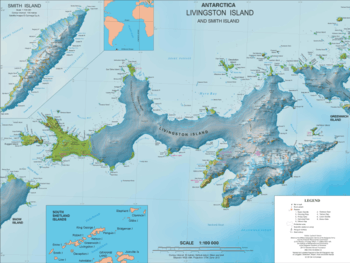
Sàbat Hill (Bulgarian: хълм Сабат, ‘Halm Sàbat’ \'h&lm 'sa-bat\) is the ice-free hill rising to 151 m in Dospey Heights on the Ray Promontory of Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Surmounting Richards Cove to the west-northwest and Barclay Bay to the east.
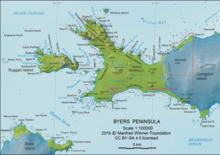
The feature is part of the Antarctic Specially Protected Area ASPA 126 Byers Peninsula, situated in one of its restricted zones.[1]
The hill is named after the Catalan Francesc Sàbat who, together with Jorge Enrique, made the first ascent of the island's summit Mount Friesland (1700 m) on 30 December 1991.
Location
Sàbat Hill is located at 62°34′59.8″S 61°08′18.0″W, which is 1.36 km north of Battenberg Hill, and 560 m southeast of Voyteh Point that is formed by an offshoot of the hill. Spanish mapping in 1992, and Bulgarian in 2010.
Maps
- Península Byers, Isla Livingston. Mapa topográfico a escala 1:25000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1992.
- L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005.
- L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. ISBN 978-954-92032-6-4
- L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Smith Island. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2017. ISBN 978-619-90008-3-0
Notes
- Management Plan for Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 126 Byers Peninsula. Measure 4 (2016), ATCM XXXIX Final Report. Santiago, 2016
References
- Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer. Antarctic Place-names Commission. (details in Bulgarian, basic data in English)
- Sàbat Hill. SCAR Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica
External links
- Sàbat Hill. Copernix satellite image
This article includes information from the Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria which is used with permission.