Roman Catholic Diocese of Lavant
The Diocese of Lavant(tal) (Latin: Lavantina) was a suffragan bishopric of the Archdiocese of Salzburg, established 1228 in the Lavant Valley of Carinthia.

In 1859 the episcopal see was re-assigned to Maribor (Marburg an der Drau) in present-day Slovenia, while the Carinthian parishes passed to the Diocese of Gurk. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Maribor (Marburg, in Slovenia) was later separated from the Salzburg ecclesiastical province and became a suffragan of the Archbishop of Ljubljana on 5 March 1962, with which the title of Bishop of Lavant was united. On 7 April 2006 the diocese was elevated to the Archdiocese of Maribor.
While the bishops of Lavant bore the title of prince-bishops (German:Fürstbischof), this was purely honorary and they never became full-fledged prince-bishops with secular power over a self-ruling prince-bishopric (Hochstift), unlike the majority of the bishops in the Holy Roman Empire. They only exercised pastoral authority over their diocese like other ordinary bishops and for that reason, they did not have seat and vote in the Imperial Diet.
History
The original seat of the bishopric lay in the eastern part of Carinthia in the valley of the Lavant River. It was here, in the parish of Sankt Andrä, that Archbishop Eberhard II of Salzburg had established, on 20 August 1212, with the consent of Pope Innocent III and Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, a collegiate chapter, the regular canons of which followed the Rule of St. Augustine; its members were chosen from the cathedral chapter of Salzburg. On account of the great remoteness and the difficulty of travelling, the Salzburg Archbishop, about the year 1223, asked Pope Honorius III to allow him to found a bishopric at Sankt Andrä. After the pope had had the archbishop's request examined by commissioners, and had given his consent, Eberhard drew up the deed of foundation, on 10 May 1228, wherein he secured the possession of the episcopal chair for himself and his successors in perpetuity. He named as first suffragan bishop his court chaplain Ulrich (died 1257), who had formerly been priest of Haus im Ennstal, in the Duchy of Styria.
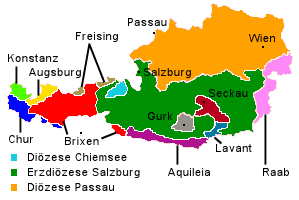
In the deed of foundation of the new bishopric, no exact boundaries were defined. In a deed of Archbishop Frederick II of Salzburg of 1280, seventeen parishes, situated partly in Carinthia and partly in Styria, were described as belonging to Lavant; the extent of the diocese was rather small, but the bishops also attended to the office of vicar-general (diocesan deputy) of the Archbishops of Salzburg for some scattered districts; they also frequently attended to the office of Vicedominus (bishop's feudal deputy in secular affairs) at Friesach.
The tenth bishop, Dietrich von Wolfsau (1318–32), is mentioned in deeds as the first (honorific) prince-bishop; he was also secretary of the Habsburg duke Frederick the Handsome, and was present at the Battle of Mühldorf in 1322. Since the twenty-second bishop, Theobald Schweinbeck (1446–63), the bishops have borne without intermission the title of Fürst (prince).
The following prominent bishops deserve special mention: the humanist Johann I von Rott (1468–82), died as Prince-Bishop of Breslau; Georg II Agrikola (1570–84), who after 1572 was also at the same time Bishop of Seckau; Georg III Stobäus von Palmburg (1584–1618), a worthy promotor of the Counter-Reformation; Maximilian Gandolph Freiherr von Kienburg (1654–65), did much towards increasing the financial resources of the diocese.
By the new regulations under Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II, several territories were added to the Diocese of Lavant. Prince-Archbishop Michael Brigido of Laibach in 1788 ceded a number of parishes in the southern part of what is now the Diocese of Lavant the Diocese of Gurk; and the district of Völkermarkt, which was afterwards again detached, was added to the bishopric at that time.
The extent of the diocese was changed by the circumscription of 1 June 1859. The valley of the Lavant and the district of Völkermarkt in Carinthia fell to the Diocese of Gurk; in consequence of which the District of Marburg was transferred from Seckau to Lavant; since then the diocese comprises the whole of southern Styria. By the decree of the Congregation of the Consistory of 20 May 1857, the see of the bishop was removed from St. Andrä to Marburg; the parish church of St. John the Baptist in that place being elevated into a cathedral, and the title "of Lavant" being preserved. On 4 September 1859, Bishop Anton Martin Slomšek (1846–62) made his solemn entry into Marburg. His successors, Jakob Maximilian Stepischnegg (1862–89), and Michael Napotnik (since 1889) have shown great zeal for the promotion of the spiritual life by introducing religious orders and founding educational and charitable institutions and clubs. But the most beneficial work done for the religious life of the diocese was that of the diocesan synods, held by Stepischnegg (1883), and by Napotnik, who followed his example (1896, 1900, 1903, and 1906).
The old cathedral chapter, which was composed of the canons of the Augustinian order, was dissolved in 1808, and its property was assigned to the "Religionsfond" founded by Joseph II; in 1825 a new cathedral chapter was provisionally erected, and definitively so in 1847.
The most prominent ecclesiastical buildings in the diocese are: the cathedral and parish church of St. John the Baptist, at Marburg, which was begun in the middle of the twelfth century as a Romanesque basilica, rebuilt after 1520 in the Gothic style, again restored after the fire in 1601, and once more in 1885; the provostship and parish church of St. Georg, at Pettau, erected in the Gothic style about 1314; the abbey and parish church of St. Daniel, at Cilli, dates from the middle of the sixteenth century; and the shrine of St. Maria der Wüste, in the neighbourhood of Marburg (built 1628), in the baroque style.
Present statistics
In 2004, the diocese of Maribor had 704,384 Catholics of 826,229 people (= 85.3% of inhabitants), 311 diocesan and 93 regular priests, 4 permanent deacons, 109 male 134? and 290 female members of religious orders. On April 7, 2006 Pope Benedict XVI elevated the diocese to an archdiocese with the new suffragan dioceses of Celje and Murska Sobota.
List of (prince-)bishops
Suffragan Bishops of Lavant
- Ulrich von Haus (1228–1257)
- Karl von Friesach (1257–1260)
- Otto von Mörnstein (1260–1264)
- Almerich Grafendorfer (1265–1267)
- Herbord (1267–1275)
- Gerhard von Ennstal (1275–1285)
- Konrad I (1285–1291)
- Heinrich von Helfenberg (1291–1299)
- Wulfing von Stubenberg (1299–1304)
- Werner (1304–1316)
- Dietrich Wolfhauer (1317–1332)
- Heinrich I Krafft (1332–1338)
- Heinrich II von Leis (1338–1342)
- Heinrich III (1342–1356)
- Peter Kröll von Reichenhall (1357–1363)
- Heinrich IV Krapff (1363–1387)
- Ortolf von Offenstetten (1387–1391)
- Augustin (1389–1391)
- Nikolaus von Unhorst (1391–1397)
- Konrad II Torer von Törlein (1397–1408)
- Ulrich II (1408–1411)
- Wolfhard von Ehrenfels (1411–1421)
- Friedrich Deys (1421–1423)
- Lorenz von Lichtenberg (1424–1432)
- Hermann von Gnas (1433–1436)
- Lorenz von Lichtenberg (1436–1446)
Suffragan Prince-Bishops of Lavant
- Theobald Schweinpeck (1446–1463)
- Rudolf von Rüdesheim (1463–1468)
- Johann I von Roth (1468–1483)
- Georg I (1483–1486)
- Erhard Paumgartner (1487–1508)
- Leonhard Peurl (1508–1536)
- Philipp I Renner (1536–1555)
- Martin Herkules Rettinger von Wiespach (1556–1570)
- Georg II Agricola (1570–1584)
- Georg III Stobäus von Palmburg (1584–1618)
- Leonhard II von Götz (1619–1640)
- Albert von Priamis (1640.12.29 – death 1654.09.08)
- Max Gandolf von Kuenburg (1654.12.08 – 1665.02.07), later Bishop of Seckau (Austria) (1665.02.07 – 1668.07.30), Metropolitan Archbishop of Salzburg (Austria) ([1668.07.30] 1668.11.12 – 1687.05.03) and Apostolic Administrator of above Seckau (1668.11.12 – 1687.05.03), created Cardinal-Priest but with no Title assigned (1686.09.02 – death 1687.05.03)
- Sebastian von Pötting-Persing (1665.04.03 – 1673.09.25), later Bishop of Passau (Bavaria, Germany) ([1673.03.11] 1673.09.25 – death 1689.03.16)
- Franz I Kaspar Freiherr von Stadion (1673.10.21 – death 1704.02.13)
- Johann II Sigmund (1704.02.22 – 1708.04.01), later Bishop of Chiemsee (1708.04.01 – death 1711.11.18)
- Philipp II (1708.04.11 – death 1718.02.14)
- Leopold Anton von Firmian (1718.03.11 – 1724.01.17), later Bishop of Seckau (Austria) (1724.01.17 – 1727.12.22), Metropolitan Archbishop of Salzburg (Austria) ([1727.10.04] 1727.12.22 – death 1744.10.22)
- Joseph I Oswald von Attems (1724.02.20 – death 1744.05.04)
- Virgilius Augustin Maria von Firmian (1744.05.26 – retired 1753.07.15), died 1788
- Johann (Baptist) III von Thun-Valsassina, Reichsgraf von Thurn und Taxis (1754.02.04 – death 1762.06.03)
- Joseph II Franz Anton von Auersperg (1763.05.08 – 1764.01.04), later Bishop of Gurk (Austria) ([1772.10.18] 1773.01.31 – 1783.05.19), Bishop of Passau (Bavaria, Germany) ([1783.05.19] 1784.06.25 – death 1795.08.21), created Cardinal-Priest but with no Title assigned (1789.03.30 – death 1795.08.21)
- Peter II von Thun (? 1772)
- Franz II de Paula Xaver Ludwig Jakob, Fürst von Breuner (1773.09.30 – 1777.05.01), later Bishop of Chiemsee (1786.06.15 – death 1797.03.01)
- Vinzenz Joseph von Schrattenbach (1777.05.31 – resigned? 1790.01.29 see below)
- Gandolf Ernst Graf von Kuenberg (1790.02.20 – death 1793.12.12)
- Vinzenz Joseph von Schrattenbach (see above 1795.06.26 – 1800.08.11), later Bishop of Brno (Brünn, Bohemia) ([1800.06.04] 1800.08.11 – death 1816.05.25)
- Leopold II Maximilian von Firmian (1800.11.23 – 1822.04.19); previously Titular Bishop of Tiberias (1797.07.24 – 1800.11.23) as Auxiliary Bishop of Passau (Germany) (1797.07.24 – 1800.11.23); later Metropolitan Archbishop of Wien (Vienna, Austria) ([1822.01.25] 1822.04.19 – death 1831.11.29)
- Ignaz Franz Zimmermann (1824.05.19 – death 1843.09.28)
- Franz Xaver Kuttnar (1843.11.23 – death 1846.03.08)
- Anton Martin Slomšek (1846.05.30 – death 1862.09.24)
Suffragan Bishops of (Lavant-)Maribor
- TO CHECK
- Suffragan Bishops of Lavant
- Blessed Anton Martin Slomšek, Prince-Bishop of Lavant (1846.05.30 – death 1862.09.24)
- Jakob Ignaz Maximilian Stepischnegg, Prince-Bishop of Lavant (1862.12.21 – 1889.06.28)
- Mihael Napotnik, Prince-Bishop of Lavant (1889.09.27 – death 1922.03.28)
- Andrej Karlin, Bishop of Lavant (1923.06.06 – death 1933.03.06), previously Bishop of Koper (Slovenia) (1911.02.06 – 1919.12.15), Bishop of Trieste (Italy) (1911.02.06 – 1919.12.15), Titular Bishop of Themiscyra (1919.12.15 – 1923.06.06)
- Ivan Jožef Tomažič, Bishop of Lavant (1933.06.27 – death 1949.02.27), succeeded as previous Auxiliary Bishop of Lavant (1928.06.08 – 1933.06.27) and Titular Bishop of Bargala (1928.06.08 – 1933.06.27)
- Maksimilijan Držečnik, Bishop of Lavant (1960.06.15 – 1962.03.05), previously Titular Bishop of Abrittum (1946.09.15 – 1960.06.15) as Auxiliary Bishop of Lavant (1946.09.15 – 1960.06.15) and Apostolic Administrator of Lavant (1949 – 1960.06.15); from 1962 Bishop of Maribor (Slovenia) (1962.03.05 – death 1978.05.13)
- from 1962.03.05: United with (as title of) Diocese of Maribor)
- Suffragan Bishops of Maribor and Bishops of Lavant
- BIOs to ELABORATE
- Franc Kramberger, Bishop of Maribor (1980–2011), from 2006 Archbishop of Maribor
- Archbishops of Maribor and Bishops of Lavant
- Marjan Turnšek, Archbishop of Maribor (2011–2013)
- Alojzij Cvikl, Archbishop of Maribor (2013–)
See also
Sources and external links
- Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- GCatholic, with incumbent bios
- Catholic Hierarchy
![]()