Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
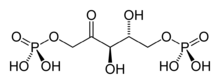
Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) is an organic substance that is involved in photosynthesis. It is a colourless anion, a double phosphate ester of the ketopentose (ketone-containing sugar with five carbon atoms) called ribulose. Salts of RuBP can be isolated, but its crucial biological function happens in solution.[1] To simplify the presentation, the image in the table depicts the acid form of this anion.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,5-Di-O-phosphono-D-ribulose | |
| Other names
Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12O11P2 | |
| Molar mass | 310.088 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Role in photosynthesis
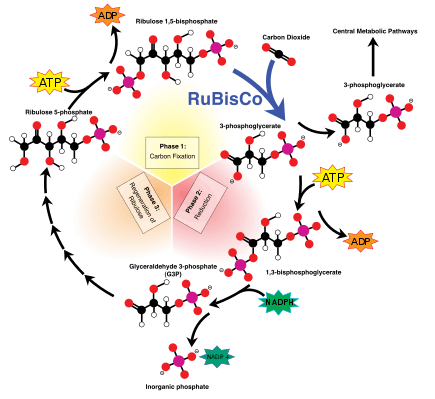
The enzyme ribulose (RuBisCO) catalyzes the reaction between RuBP and carbon dioxide. The product is the highly unstable six-carbon intermediate known as 3-keto-2-carboxyarabinitol 1,5-bisphosphate. This six-carbon intermediate decays virtually instantaneously into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) (see figure). RuBisCO also catalyzes RuBP with oxygen (O
2) in a process called photorespiration, a process that is more prevalent at high temperatures. During photorespiration RuBP combines with O
2 to become 3-PGA + phosphoglycolic acid. In the Calvin cycle, RuBP is a product of the phosphorylation of ribulose-5-phosphate by ATP.
References
- The topic is discussed in all biochemistry textbooks, this one is representative: Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. ISBN 1-57259-153-6.