Rheum nobile
Rheum nobile, the Sikkim rhubarb[1] or noble rhubarb or पदमचाल, is a giant herbaceous plant native to the Himalaya, from northeastern Afghanistan, east through northern Pakistan and India, Nepal, Sikkim (in India), Bhutan, and Tibet to Myanmar, occurring in the alpine zone at 4000–4800 m altitude.[2]
| Noble rhubarb | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Polygonaceae |
| Genus: | Rheum |
| Species: | R. nobile |
| Binomial name | |
| Rheum nobile Hook.f. & Thomson | |
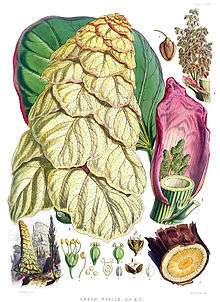
It is an extraordinary species of rhubarb (genus Rheum). At 1–2 m tall, the monocarpic inflorescences of R. nobile tower above the other shrubs and low herbs in its habitat, and it is visible across valleys a mile away.[3]
R. nobile is often called a glasshouse plant because of its outer curtain of translucent bracts which pass visible light, creating a greenhouse effect, while blocking ultraviolet radiation. These are likely defenses against the increased UV-B exposure and extreme cold in its high altitude range.[4]
Description
An individual R. nobile is a conical tower of delicate, straw-coloured, shining, translucent, regularly overlapping bracts; the higher ones have pink edges. Large, glossy, green radicle leaves, with red petioles and nerves, form a broad base to the plant. Turning up the bracts reveals membranous, fragile, pink stipules. Within these are short branched panicles of diminutive green flowers.[5]
The root is often 1–2 m (3.3–6.6 ft) long and as thick as an arm, and bright yellow inside. After flowering, the stem lengthens and the bracts separate one from another, turning a coarse red-brown. As the fruit ripens, the bracts fall away, leaving a ragged-looking stem covered with panicles of deep brown pendulous fruits. As Hooker put their appearance: "In the winter, these naked black stems, projecting from the beetling cliffs, or towering above the snow, are in dismal keeping with the surrounding desolation of that season."[5]
Karyotypy
R. nobile has a chromosome count of 2n=22.[6]
Bracts

The bracts of R. nobile are 110-170 µm thick and do not differentiate into palisade and spongy layers.[7] They selectively block ultraviolet radiation while letting almost all visible light through; thus the developing flowers and the apical meristem are protected from the intense radiation found in high altitudes. The major UV blockers found in the bracts are all quercetin flavonoids:[8]
- Rutin, quercetin 3-O-rutinoside: widespread in higher plants and previously reported in leaves and petioles of other Rheum species
- Guaijaverin, quercetin 3-O-arabinoside: first report in Rheum
- Hyperin, quercetin 3-O-galactoside: widespread in plants and previously reported in leaves and petioles of R. rhaponticum
- Isoquercitrin, quercetin 3-O-glucoside: widespread in plants and previously reported in leaves and petioles of R. rhaponticum
- Quercetin 3-O-[6″-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroyl)-glucoside]: first finding in nature
Minor UV blockers include quercetin 7-O-glycoside, quercetin itself, kaempferol glycoside, and feruloyl ester.
Edibility
The stems are pleasantly acidic, and they are consumed by the local people, who call the plant Chuka. The hollow of the stem contains a good deal of limpid water.[5]
History

A description of R. nobile was first published by Joseph Dalton Hooker and Thomas Thomson in 1855. Hooker wrote:
- "The present is certainly the most striking of the many fine alpine plants of Sikkim; and though in every botanical character, as also in the acid juice of the stem, a genuine Rhubarb, it differs so remarkably in habit and general appearance from any of its congeners, that at first sight it could not be recognized as one of them. I first saw it from a distance of fully a mile, dotting the black cliffs of the Lachen valley at 14,000 feet [4,300 m] elevation, in inaccessible situations, and was quite at a loss to conceive what it could be; not was it till I had turned back the curious bracteal leaves and examined the flowers that I was persuaded of its being a true Rhubarb."[5]
References
- Hooker, Joseph Dalton; J. F. Cathcart; W. H. Fitch (1855). Illustrations of Himalayan plants. London: L. Reeve. pp. 93–95. LCCN 05024640.
- T. Iwashina; et al. (April 2004). "Flavonoids in translucent bracts of the Himalayan Rheum nobile (Polygonaceae) as ultraviolet shields". Journal of Plant Research. 117 (2): 101–107. doi:10.1007/s10265-003-0134-2. PMID 14749969.
- Tsukaya, Hirokazu (February 2002). "Optical and anatomical characteristics of bracts from the Chinese "glasshouse" plant, Rheum alexandrae Batalin (Polygonaceae), in Yunnan, China". Journal of Plant Research. 115 (1): 59–63. doi:10.1007/s102650200009.
Notes
- Eisenreich, Dan (1996–2010). "Rhubarb Botanical Information". The Rhubarb Compendium. Retrieved 2 April 2019.CS1 maint: date format (link)
- "Rheum nobile". Flora of China. eFloras.org. Retrieved 2006-06-11.
- "Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- Iwashina et al. p.101
- Hooker p.94
- Ruirui, Liu; Wang, Ailan; Tian, Xinmin; Wang, Dongshi; Liu, Jianquan (2010). "Uniformity of karyotypes in Rheum (Polygonaceae), a species-rich genus in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and adjacent regions". Caryologia Firenze. 63 (1): 82–90. doi:10.1080/00087114.2010.10589711. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- Tsukaya pp.60-61
- Iwashina et al. 104-106
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rheum nobile. |