Resurrection of Christ Cathedral, Narva
The Resurrection of Christ Cathedral is a Neo-Byzantine style Estonian Orthodox Church of Moscow Patriarchate located in Narva, Estonia. The church was constructed between 1890 and 1896 to cater to the religious needs of the cotton mill workers of the Krenholm Manufacturing Company. The cathedral was the only building standing after the bombing of the city in 1944 during World War II.[1]
| Resurrection Cathedral | |
|---|---|
| Resurrection of Christ Cathedral, Narva | |
| |
| Location | Narva |
| Country | Estonia |
| Denomination | Estonian Orthodox Church of Moscow Patriarchate |
| Website | Cathedral website |
| History | |
| Founded | 1890 |
| Consecrated | 17 November 1896 |
| Architecture | |
| Architect(s) | Pavel Alis |
History
In 1890, the shareholders of the Krenholm Manufacturing Company, under the initiative of director Ivan Prove, decided to construct an Orthodox church for the workers of the company. The shareholders of the company donated 500,000 roubles to construct the church on land donated by Prove. The foundation stone was laid by Bishop Alexander Dmitrievich (Arseny) Bryantsev in the presence of Czar Alexander III and Empress Maria Feodorovna on August 5, 1890. The cathedral also commemorates the meeting between the German Emperor Wilhelm II and Czar Alexander III.[2][3]
While Narva received heavy bombardment during world War II, the cathedral remained standing till the end of the war. On 20 January 1958, it was renamed as the Cathedral of the Resurrection of Jesus Christ. The cathedral underwent extensive renovations as part of its centenary celebrations. The renovated basement church was consecrated in the name of Seraphim of Sarov by Archbishop Cornelius of Tallinn and all of Estonia on November 16, 1996.[2]
Architecture
.jpg)
The architecture is Neo-Byzantine and the architect was Pavel Alis. The church is made in the Greek Cross plan, with a square central mass and four arms of equal length. The walls and dome for the cathedral was made with red bricks sourced locally. The stairways and other aisles were made of Rapakivi granite procured from Finland. The cathedral can hold up to 2000 people during mass and has a bell tower which is 28.8 m high. It also has a three part carved iconostasis made by Afanasjev and a crucifix originally made in the 17th century for the Church of Saint John of Jerusalem outside the walls by Elert Thiele. The icons were painted by Michail Dickarev. The pendentives and the semi-dome space above the main altar were subsequently painted in 1912.[1][2][4][5][6]
Gallery
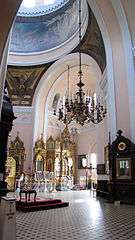 The altar
The altar The dome
The dome- The cathedral's entrance
- The cathedral in winter
.jpg)

See also
References
- "The Resurrection of Christ Orthodox Cathedral". Visit Estonia. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- "Cathedral of the Resurrection of Christ". hramy.ee. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- "METROPOLITAN HILARION OFFICIATES AT CELEBRATION OF 120TH ANNIVERSARY OF CATHEDRAL OF THE RESURRECTION IN NARVA". mospat.ru. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- "Orthodox Resurrection of the Christ Cathedral". spottinghistory.com. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- "Orthodox Cathedral of the Resurrection". Lonely Planet. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- "Orthodox Cathedral of the Resurrection of Christ in Narva". puhkuseestis.ee. Retrieved 12 December 2016.