Rapper sword
Rapper sword (also known as short sword dance) is a variation of sword dance that emerged from the pit villages of Tyneside in North East England, where miners first performed the tradition.[1]

The dance requires five performers who co-ordinate themselves whilst using "rapper swords" made from flexible steel. Accompanied by traditional folk music, the dancers wear specially-designed shoes that allow for percussive foot movements. Mental alertness, in addition to physical agility, is required in order for dance participants to use the swords effectively without causing harm to themselves or the other performers.[2]
History
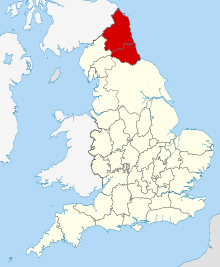
Whilst substantial evidence for the origins of the rapper sword tradition does not exist, as of 2012, since the publication of Rapper; The miner's Dance of North East England by Phil Heaton it is generally accepted that the dance was originally performed in the mining villages of the Northumberland and Durham coalfield in North-East England, with an intensity of activity traced to pits along both the Durham and Northumberland banks of the river Tyne. A hilt-and-point sword dance also existed in South Durham, Cumberland and Yorkshire, where rigid longswords were used. A documented account of the Yorkshire dance has been located in a 1715 article, in which a fairly accurate description can be read. Later references to sword dancing in the northern counties include a dance described in 1787 in the Cumberland Packet newspaper of January 1788, and a description from Teesdale in 1778, referenced by Hutchinson in his View of Northumberland.[3]
At some stage in the nineteenth century, the rigid swords were replaced by flexible rappers in the coalfield. Very little is known about this major development in the tradition because of an absence of sufficient evidence, and it may have been entirely accidental. It used to be commonly thought that the flexible version was used for removing dirt from the backs of pit ponies, but there is no available documentation to verify this theory. It seems that two factors have influenced interpretations of when the rapper sword was introduced: firstly, the relocation of a steel works operation by Ambrose Crowley to the Derwent Valley, before which time it is believed that suitable steel for flexible swords would most likely have been unavailable; and secondly, the prohibitive expense of such instruments before the Bessemer process in 1855 that allowed steel to be made inexpensively.[4]
The dance involves five people, with many including characters, such as Tommy and Betty, who announce the dance, engage the audience and most importantly, collect money from the onlookers.[1] The performers are connected by short swords bearing two handles, with the handle on at least one end being fixed. The other handle is either fixed or swivelling, based on the preference of the rapper side. The flexible rapper swords form an unbroken chain connecting the dancers. The dance is related to the Long Sword dance of Yorkshire, as well as other sword dances in Europe. Some of the earliest teams used hornpipes, rather than the jigs used in the modern era.
Nineteenth century
During the nineteenth century, teams of rapper dancers from the pit villages of Tyneside, and Wearside, would travel annually to the towns of Newcastle upon Tyne, Sunderland and Durham to perform the dance for the crowds, asking for monetary consideration. This was later revived as a source of income during the miners' strikes and lay-offs, especially when the collieries were closed down over winter. Sword dancers of the North East were also active in the political struggles of the coalfield. A team of Tyneside Rovers were part of an early march on parliament in 1890, and another team from Hebburn were part of the famous Jarrow Crusade in 1936. Teams were also reported all over Durham and Northumberland as dancing out and collecting in the 1926 miners' strike and later in the Great Depression.
Twentieth century
By the early twentieth century, the tradition was beginning to die out, but was revived by the interest generated after Cecil Sharp published notations for five of the traditional village dances in his book, The Sword Dances of Northern England. After the First World War, the revival was marked by the fierce competition between pit villages in the rapper classes of the newly instituted North of England Musical Tournament held annually in Newcastle upon Tyne.
After the Second World War, the tradition progressively declined in the original pit villages, partly as a result of social changes in the mining communities. However, another revival was initiated after the war, in 1949 by students at Kings College in Newcastle upon Tyne (now the University of Newcastle upon Tyne), which subsequently spread beyond the traditional area. Revival teams worldwide now perform the rapper tradition, sometimes learned from published notations, sometimes taught by rapper dancers in what is almost a continuation of the earlier oral traditions.
Twenty-first century
The dance has transformed as it moved into the twenty-first century: the pace has quickened and is performed at around 140–160 beats per minute, with different team styles using different rates. It is nonetheless typically performed in a smooth and graceful manner, with one figure flowing seamlessly into the next. A number of acrobatic figures can be employed, including forward and backward somersaults over the swords.
The dance is now almost always performed to jigs (perhaps 90% of the time), with the normal form of rapper stepping being a form of shuffle imported from the local clogging tradition. The jigs used include local tunes and many instruments can, and have been, used to accompany rapper dances (the most popular being fiddles, tin whistles and accordions or melodeons). Many rapper jigs used for the last hundred years are tunes, probably imported by Irish and Scottish immigrants to Tyneside in the nineteenth century. The music is usually performed solo, although it can be performed as a duet; however, rapper is not usually performed to a band. There is much controversy in the rapper community over the use of any form of percussion to accompany rapper beyond the rapper stepping included in the dance.
In modern times, the competitive element of rapper sword dancing has been revived in the form of the Dancing England Rapper Tournament (DERT) competition, and in recent years its American counterpart, Dancing America Rapper Tournament (DART).
Costume

The costume in which the dance is usually performed, referred to as the kit, is a stylised version of the working clothes of the local nineteenth century coal miner (see photograph, left). It consists of shirt; sash; breeks (breeches), hoggers (similar to breeks but shorter), or long trousers; and socks or stockings. Some traditional teams decorated their kit with ribbons or rosettes, and added a tie and/or waistcoat.
Modern teams use a variety of kits, mostly based on the traditional costume, with each team using different combinations of colours to try to have a unique corporate image. Some other modern sides, especially women's sides, use very different kits.
Further information
The Rapper Online website provides information on the origins and history of the dance, team listings, and notations of traditional dances. Current and historical information is also available at "The NUT on the Net", the Internet edition of "The NUT", the journal of the rapper sword dance.
Leading exponents of the tradition in its traditional area include the High Spen Blue Diamonds, the Newcastle Kingsmen, Monkseaton Morris Men, the Sallyport Sword Dancers and Star and Shadow. The Rapper Online website provides a list of rapper sword teams and the Sword Dance Union has produced a map of current UK teams.
The Dancing England Rapper Tournament (DERT) competition, which is open to all rapper sword teams, is held annually in a different UK city or town by a different Rapper side. The tournament is made up of 3 divisions: Premier, Championship, and Open, as well as recently adding a youth competition, DERTy.
| Event | Location | Hosts | Dates | Overall winner | DERTy winner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DERT 2014 | Leeds | Black Swan Rapper | 7–8 March 2014 | Star & Shadow | |
| DERT 2015 | Bristol | Northgate Rapper | 10–12 April 2015 | Newcastle Kingsmen | NYFTE |
| DERT 2016 | Manchester | Medlock Rapper | 11–13 March 2016 | Newcastle Kingsmen | Oakenyouth |
| DERT 2017 | Kendal | Crook Morris | 7–9 April 2017 | Newcastle Kingsmen | NYFTE |
| DERT 2018 | Sheffield | Sheffield Steel | 23–25 March 2018 | Whip the Cat | NFTYE |
| DERT 2019 | Newcastle | Newcastle Kingsmen, Sallyport Sword & Star and Shadow Rapper | 5–7 April 2019 | Newcastle Kingsmen | - |
In 2020, the competition was postoned due to COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom.
Rapper dancing has gained international popularity. Jack The Rapper, based in Norway, attended DERT in 1996, 1999 and 2003. The DERT 2005 and 2006 competitions were attended by three teams from the United States, named Candyrapper (2005), Beside the Point (2006) and Scrambled Six (2007). Red Mum Rapper from Denmark competed in DERTs 2013, 2014 and 2016. The Pocket Flyers (USA) attended DERT 2015 in Bristol. Rapper teams also exist in Australia, Germany and the Basque Country of France.
See also
References
- "Rapper Sword Dancing". Thrales Rapper. Thrales Rapper. Retrieved 14 May 2012.
- John Edwards. "Rapper". Stafford Morris Men. John Edwards. Retrieved 14 May 2012.
- John Asher (2000–2010). "Origins and history of rapper". Rapper Online. John Asher. Retrieved 14 May 2012.
- Tom Besford; Tom Redman (7 May 2011). "The Rapper Sword". Newcastle Kingsmen Sword Dancers. The Newcastle Kingsmen. Retrieved 15 May 2012.