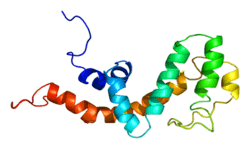
RGS10
Regulator of G-protein signaling 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS10 gene.[5][6]
Function
Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) family members are regulatory molecules that act as GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) for G alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. RGS proteins are able to deactivate G protein subunits of the Gi alpha, Go alpha and Gq alpha subtypes. They drive G proteins into their inactive GDP-bound forms. Regulator of G protein signaling 10 belongs to this family. All RGS proteins share a conserved 120-amino acid sequence termed the RGS domain. This protein associates specifically with the activated forms of the two related G-protein subunits, G-alphai3 and G-alphaz but fails to interact with the structurally and functionally distinct G-alpha subunits. Regulator of G protein signaling 10 protein is localized in the nucleus. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[6]
Interactions
RGS10 has been shown to interact with SAP18[7] and GNAI3.[5]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000148908 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030844 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Hunt TW, Fields TA, Casey PJ, Peralta EG (Sep 1996). "RGS10 is a selective activator of G alpha i GTPase activity". Nature. 383 (6596): 175–7. doi:10.1038/383175a0. PMID 8774883.
- "Entrez Gene: RGS10 regulator of G-protein signalling 10".
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, McBroom-Cerajewski L, Robinson MD, O'Connor L, Li M, Taylor R, Dharsee M, Ho Y, Heilbut A, Moore L, Zhang S, Ornatsky O, Bukhman YV, Ethier M, Sheng Y, Vasilescu J, Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Duewel HS, Stewart II, Kuehl B, Hogue K, Colwill K, Gladwish K, Muskat B, Kinach R, Adams SL, Moran MF, Morin GB, Topaloglou T, Figeys D (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Molecular Systems Biology. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
Further reading
- Popov S, Yu K, Kozasa T, Wilkie TM (Jul 1997). "The regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) domains of RGS4, RGS10, and GAIP retain GTPase activating protein activity in vitro". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 94 (14): 7216–20. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.14.7216. PMC 23796. PMID 9207071.
- Tu Y, Wang J, Ross EM (Nov 1997). "Inhibition of brain Gz GAP and other RGS proteins by palmitoylation of G protein alpha subunits". Science. 278 (5340): 1132–5. doi:10.1126/science.278.5340.1132. PMID 9353196.
- Tu Y, Popov S, Slaughter C, Ross EM (Dec 1999). "Palmitoylation of a conserved cysteine in the regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) domain modulates the GTPase-activating activity of RGS4 and RGS10". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (53): 38260–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.53.38260. PMID 10608901.
- Popov SG, Krishna UM, Falck JR, Wilkie TM (Jun 2000). "Ca2+/Calmodulin reverses phosphatidylinositol 3,4, 5-trisphosphate-dependent inhibition of regulators of G protein-signaling GTPase-activating protein activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (25): 18962–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001128200. PMID 10747990.
- Chatterjee TK, Fisher RA (Aug 2000). "Cytoplasmic, nuclear, and golgi localization of RGS proteins. Evidence for N-terminal and RGS domain sequences as intracellular targeting motifs". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (31): 24013–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002082200. PMID 10791963.
- Burgon PG, Lee WL, Nixon AB, Peralta EG, Casey PJ (Aug 2001). "Phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of a regulator of G protein signaling (RGS10)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (35): 32828–34. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100960200. PMID 11443111.
- Gagnon AW, Murray DL, Leadley RJ (Jul 2002). "Cloning and characterization of a novel regulator of G protein signalling in human platelets". Cellular Signalling. 14 (7): 595–606. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(02)00012-8. PMID 11955952.
- Castro-Fernández C, Conn PM (Jun 2002). "Regulation of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR) by RGS proteins: role of the GnRHR carboxyl-terminus". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 191 (2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0303-7207(02)00082-5. PMID 12062898.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Oh JH, Yang JO, Hahn Y, Kim MR, Byun SS, Jeon YJ, Kim JM, Song KS, Noh SM, Kim S, Yoo HS, Kim YS, Kim NS (Dec 2005). "Transcriptome analysis of human gastric cancer". Mammalian Genome. 16 (12): 942–54. doi:10.1007/s00335-005-0075-2. PMID 16341674.
- Lee HK, Rhee KH, Kim CW, Hwang KY, Kim EE (Sep 2005). "Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of human RGS10 complexed with Galphai3". Acta Crystallographica Section F. 61 (Pt 9): 831–3. doi:10.1107/S1744309105023602. PMC 1978115. PMID 16511171.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, McBroom-Cerajewski L, Robinson MD, O'Connor L, Li M, Taylor R, Dharsee M, Ho Y, Heilbut A, Moore L, Zhang S, Ornatsky O, Bukhman YV, Ethier M, Sheng Y, Vasilescu J, Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Duewel HS, Stewart II, Kuehl B, Hogue K, Colwill K, Gladwish K, Muskat B, Kinach R, Adams SL, Moran MF, Morin GB, Topaloglou T, Figeys D (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Molecular Systems Biology. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.