Putèr
Puter (also spelled Putèr; pronounced [puˈteːr] (![]()
| Putèr | |
|---|---|
| putèr | |
| Pronunciation | [puˈteːr] ( |
| Native to | Engadin in Switzerland |
| Latin script | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | pute1235[1] |
| IETF | rm-puter[2] |
Classification
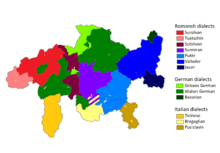
Puter and Vallader are sometimes referred to as one specific variety known as Ladin, as they have retained this word to mean Romansh. However, the term Ladin is primarily associated with the closely related language in Italy's Dolomite mountains also known as Ladin. Puter and Vallader are distinguished from the other Romansh dialects among other things by the retention of the rounded front vowels /y/ and /ø/ (written ü and ö), which have been derounded to /i/ and /e/ in the other dialects. Compare Putèr ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Each village between S-chanf and St. Moritz has a slightly different accent, although the written form remains the same.
Sample
The fable The Fox and the Crow by Jean de La Fontaine in Putèr Romansh, as well as a translation into English, the similar-looking but noticeably different-sounding dialect Vallader, and Rumantsch Grischun.[5]
| Putèr |
Vallader |
Rumantsch Grischun |
Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| La vuolp d’eira darcho üna vouta famanteda. Co ho'la vis sün ün pin ün corv chi tgnaiva ün töch chaschöl in sieu pical. Que am gustess, ho'la penso, ed ho clamo al corv: «Che bel cha tü est! Scha tieu chaunt es uschè bel scu tia apparentscha, alura est tü il pü bel utschè da tuots». | La vuolp d'eira darcheu üna jada fomantada. Qua ha'la vis sün ün pin ün corv chi tgnaiva ün toc chaschöl in seis pical. Quai am gustess, ha'la pensà, ed ha clomà al corv: «Che bel cha tü est! Scha teis chant es uschè bel sco tia apparentscha, lura est tü il plü bel utschè da tuots». | La vulp era puspè ina giada fomentada. Qua ha ella vis sin in pign in corv che tegneva in toc chaschiel en ses pichel. Quai ma gustass, ha ella pensà, ed ha clamà al corv: «Tge bel che ti es! Sche tes chant è uschè bel sco tia parita, lur es ti il pli bel utschè da tuts». | The fox was hungry yet again. There he saw a raven upon a fir holding a piece of cheese in its beak. This I would like, he thought, and shouted at the raven: "You are so beautiful! If your singing is as beautiful as your looks, then you are the most beautiful of all birds.". |
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Putèr pronunciation. |
Sources
- Gross, Manfred (2004), Romanisch – Facts & Figures (in German), Chur, ISBN 3-03900-034-9
- Ricarda, Liver (1999), Rätoromanisch – Eine Einführung in das Bündnerromanische (in German), Tübingen: Gunter Narr, ISBN 3-8233-4973-2
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Puter". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- "Puter idiom of Romansh". IANA language subtag registry. 29 June 2010. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- Gross (2004). p. 31
- Liver 1999; p. 43
- Gross, Manfred (2004), Rumantsch – Facts & Figures Archived 2012-04-18 at the Wayback Machine. (PDF) . Retrieved on 2012-02-28.