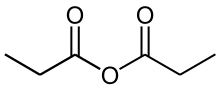
Propionic anhydride
Propanoic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula (CH3CH2CO)2O. This simple acid anhydride is a colourless liquid. It is a widely used reagent in organic synthesis as well as for producing specialty derivatives of cellulose.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propanoic anhydride | |
| Other names
Propionic anhydride Propanoyl propanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.218 |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 130.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear liquid, with a strong smell similar to vinegar |
| Density | 1.015 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −42 °C (−44 °F; 231 K) |
| Boiling point | 167 to 170 °C (333 to 338 °F; 440 to 443 K) |
| Reacts to give propanoic acid | |
| Viscosity | 1.144 cP at ?°C |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R34 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26-45 |
| Flash point | 63 °C (145 °F; 336 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Acetic anhydride
Propanoyl chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
Industrial route to propionic anhydride involves thermal dehydration, driving off the water by distillation:
- 2 CH3CH2CO2H → (CH3CH2CO)2O + H2O
Another routes is the Reppe carbonylation of ethylene with propionic acid and nickel carbonyl as the catalyst:[1]
- CH2=CH2 + CH3CH2CO2H + CO → (CH3CH2CO)2O
Propionic anhydride has also been prepared by dehydration of propionic acid using ketene:[2]
- 2 CH3CH2CO2H + CH2=C=O → (CH3CH2CO)2O + CH3CO2H
Safety
Propanoic anhydride is strong smelling and corrosive, and will cause burns on contact with skin. Vapour can burn eyes and lungs.
Legal Status
Due to its potential use as a precursor in the synthesis of fentanyl and fentanyl analogs, propanoic anhydride is regulated by the United States Drug Enforcement Administration as a List I chemical under the Controlled Substances Act.[3]
References
- Samel, Ulf-Rainer; Kohler, Walter; Gamer, Armin Otto; Keuser,, Ullrich (2005). "Propionic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_223.CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link)
- Williams, J. W. Krynitsky, J. A. (1955). "n-Caproic Anhydride". Organic Syntheses.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collective Volume, 3
- Drugs of Abuse Publication, Chapter 2 Archived 2007-12-20 at the Wayback Machine