Pranburia
Pranburia is a monotypic genus of Southeast Asian ant mimicking corinnid sac spiders containing the single species, Pranburia mahannopi. Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold described the first male in 1993,[2] and the first female in 2001.[3] It has only been found in Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, and Malaysia.[1] The species is named after Narong Mahannop, one of the collectors of the holotype, and the genus is named after the Pranburi Province, where the male holotype was collected.[2]
| Pranburia | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Corinnidae |
| Genus: | Pranburia Deeleman-Reinhold, 1993[1][2] |
| Species: | P. mahannopi |
| Binomial name | |
| Pranburia mahannopi | |
Description
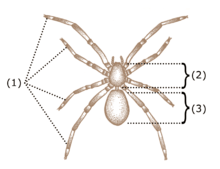
Males have a body length of about 6 millimetres (0.24 in). The carapace is about 3 millimetres (0.12 in) long, is colored dark brown, and has several rows of white feathery setae. The head and back part of the opisthosoma also have several longer bristles. Their eyes span half the width of their head, both rows slightly procurved. The femurs are dark brown, while the other segments and middle legs are a solid shade of lighter brown. They have many of the same characters as members of Castianeira, but can be distinguished by a posterior eye row that is procurved, a labium that is almost two times longer than it is wide, fourth legs that are the same length as the front legs, and trochanters that do not have any notches.[2]
Ant mimicry
These spiders have a unique pair of brushes on the first legs to help them appear like ants if they need to. When alarmed, P. mahannopi joins the femora of its first pair of legs together in front of its head, mimicking a third body segment. At the same time, they wave the tibiae and metatarsi in the air, mimicking ant antennae.[2] Its main mimic model seems to be Diacamma, a queenless ant genus belonging to the subfamily Ponerinae.
References
- "Gen. Pranburia Deeleman-Reinhold, 1993". World Spider Catalog Version 20.0. Natural History Museum Bern. 2019. doi:10.24436/2. Retrieved 2019-05-22.
- Deeleman-Reinhold, C. L. (1993). "A new spider genus from Thailand with a unique ant-mimicking device, with description of some other castianeirine spiders (Araneae: Corinnidae: Castianeirinae)" (PDF). Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society. 40: 167–184.
- Deeleman-Reinhold, C. L. (2001). Forest spiders of South East Asia: with a revision of the sac and ground spiders (Araneae: Clubionidae, Corinnidae, Liocranidae, Gnaphosidae, Prodidomidae and Trochanterriidae [sic]). p. 301.