Potassium amyl xanthate
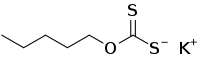
Potassium amyl xanthate is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)4OCS2K. It is a pale yellow powder or pellet with a pungent odor, soluble in water. It is widely used in the mining industry for the separation of ores using the flotation process.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
potassium O-pentylcarbonodithioate | |
| Other names
potassium pentylxanthogenate potassium-O-pentyl dithiocarbonate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11KOS2 | |
| Molar mass | 202.37 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pale yellow or yellow free flowing powder |
| Density | 1.073 g/cm |
| Soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements |
H228, H302, H312, H315, H319, H335, H411 |
| P210, P240, P241, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P370+378, P391, P403+233, P405 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production and properties
Potassium amyl xanthate is prepared by reacting amyl alcohol with carbon disulfide and potassium hydroxide.[1]
- CH3(CH2)4OH + CS2 + KOH → CH3(CH2)4OCS2K + H2O
Potassium amyl xanthate is a pale yellow powder that is relatively stable between pH 8 and 13 with a maximum of stability at pH 10.[2]
Safety
The LD50 is 480 mg/kg (oral, rats) for potassium pentylxanthate.[3]
It is a biodegradable compound.
gollark: https://media.discordapp.net/attachments/461970193728667648/899677663453655050/iu-3.png
gollark: Fascinating.
gollark: Hate crimes are mean and thus impossible.
gollark: Too bad, pyrobot.
gollark: I rescheduled 6 to 8 business weeks to now.
References
- Charles C. Price and Gardner W. Stacy (1948). "p-nitrophenyl) sulfide". Organic Syntheses. 28: 82.; Collective Volume, 3, p. 667
- J. Dyer, L. H. Phifer, Macromolecules 2 (1969) 111. R. J. Millican, C. K. Sauers, J. Org. Chem. 44 (1979) 1964.
- Kathrin-Maria Roy "Xanthates" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.