Posterior cardinal vein
The postcardinal veins or posterior cardinal veins join with the corresponding right and left cardinal veins to form the left common cardinal veins, which empty in the sinus venosus. Most of the posterior cardinal veins regress, what remains of them forms the renal segment of the inferior vena cava and the common iliac veins. Later in the development stages, the posterior cardinal veins are replaced by the subcardinal and supracardinal veins. The subcardinal veins form part of the inferior vena cava, renal veins and gonadal veins. The supracardinal veins form part of the inferior vena cava, the intercostal veins, hemiazygos vein and azygos vein.[1]
| Posterior cardinal vein | |
|---|---|
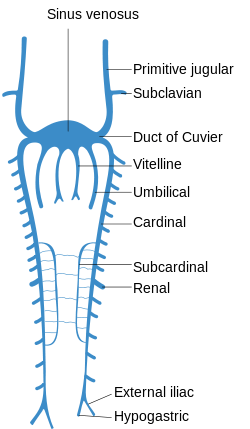 Scheme of arrangement of parietal veins. | |
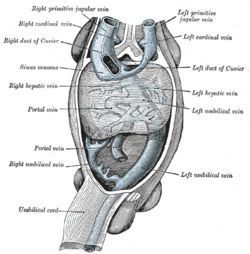 Human embryo with heart and anterior body-wall removed to show the sinus venosus and its tributaries. | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 13 |
| System | Cardiovascular system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Vena postcardinalis |
| TE | E5.11.2.2.2.2.19 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Additional images
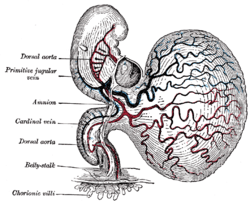 Human embryo of about fourteen days, with yolk-sac.
Human embryo of about fourteen days, with yolk-sac.
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 520 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Henry Gray (1918). Anatomy of the Human Body, page 520.