Pirehill Hundred
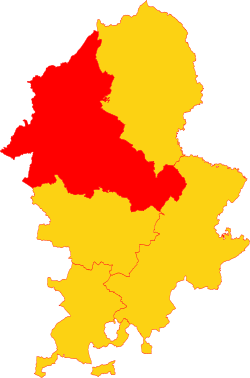
Pirehill is a hundred in the county of Staffordshire, England. The Hundred is located in the north-west and toward the upper centre of Staffordshire. It is about 28 miles in length, north to south, and around 8 to 20 miles in breadth. It is bounded on the north-east by Totmonslow (Totmanslow) Hundred, on the east by Offlow Hundred, on the south by Cuttleston Hundred and on the west and north-west by Shropshire and Cheshire.[1]
| Pirehill | |
|---|---|
| Former subdivision of England | |
 | |
| History | |
| • Origin | Anglo-Saxon period |
| • Created | 10th century |
| • Abolished | 1894 |
| • Succeeded by | various |
| Status | Obsolete |
| Government | Hundred |
| Subdivisions | |
| • Type | Parishes (see text) |
| • Units | Parishes |
The River Trent rises at its northern extremity and flows through it in a south-easterly direction, passing the noble seats of Trentham, where it becomes somewhat navigable, then Ingestre, Shugborough and Wolseley; and nearly parallel with that river now runs the Trent and Mersey Canal. It contains the boroughs of Stafford, the county town, the town of Newcastle-under-Lyme and the city of Stoke-on-Trent, which latter includes the Potteries. Besides these, Pirehill has six market towns: Burslem, Hanley, Lane-End, Stone, Eccleshall and Abbots Bromley.
.jpg)

Name
A large number of Hundred names refer to hills or mounds which were gathering sites. Some of these at least are very conspicuous hills, which afford a commanding view of the countryside for miles around. It seems likely that such moot and mustering sites were chosen as being remote and bare, from which approaching forces would be easily spotted.[2] In this case the Pirehill Hundred was named after Pire Hill (height 462 ft), a hill two miles south of Stone.[3] The hill was a meeting place for the Hundred Moot and also a mustering point in case of invasion. It is noteworthy that the meeting-places of the two northern hundreds (Pirehill and Totmonslow) are in the extreme south of the respective hundreds.[4] Presumably this was to unify Staffordshire's forces with those of the neighbouring hundreds, and thus to meet invaders in force, invaders who might either: i) be travelling as war-bands up the River Trent, navigable to Stone; or ii) renegades invading from Wales and seeking the vital upper Trent crossing at Stone; or iii) pressing down in larger numbers from Northumbria, in which case there would be an urgent local need to fall back south to Stone.
The first element of the Pire Hill name may be connected with Middle English piren 'to peer', in modern English peer, meaning 'to look narrowly'. The meaning of the name would be 'look-out hill'. Alternatively a possible corruption from an earlier Anglo-Saxon derivation of spyre would give a similar meaning, a spyre-mann meaning 'one who tracks and sees'. Pire Hill is the highest point for some distance; there is nothing higher between it and the river Trent, and it seems to have a good view down the Trent valley. On topographical grounds there is nothing against such derivations. Old English pirige, pyrige 'pear-tree' may be possible phonologically, but seems less likely for other reasons [5] A later authority, David Horovitz, suggests in his PhD thesis A survey and analysis of the place-names of Staffordshire (2003) that it "not inconceivable" that name might also have come from the Latin pyra, meaning bonfire, and "that the name could record the early use of the hill as a beacon".
History
Pirehill is one of the largest of the five hundreds of Staffordshire, having an area of 201,493 acres (314 sq. miles). The origin of the hundred dates from the division of his kingdom by King Alfred the Great into counties, hundreds and tithings. From the beginning, Staffordshire was divided into the hundreds of Pirehill, Totmonslow, Offlow, Cuttleston and Seisdon.[6]. The importance of the hundreds declined from the 17th century.
By the early 19th century the Hundred comprised 42 parishes, 14 chapelries and 5 extra-parochial places, which were subdivided into 126 townships and containing several hundred villages and hamlets. It was separated into the north and south divisions, under the control of two chief constables. The north and south divisions were of very unequal extent and population. The large parishes of Adbaston, Eccleshall and Seighford, had townships in both divisions, an inconvenience which divided many of their parochial affairs between the two chief constables.
Most of the functions of the Hundreds were extinguished with the establishment of county courts in 1867. Yet use of these division continued for much of the 19th Century, by which time Pirehill was the most populous Hundred in Staffordshire, with a population in 1861 of 149,734.[7] By that time there had been centuries of improvements to the land, and the hundred was deemed remarkable for the fertility of its soil, for the beauty and variety of its scenery and the number and magnificence of its stately halls (the seats of the nobility and gentry), as also for the extent and importance of its growing manufactures such as the distinctive pottery making district - the long chain of towns and villages called the Potteries, a renowned place of china and pottery manufacturing. The number of the inhabitants nearly doubled during 1801-1831, as a vast population growth occurred in the Potteries and at Newcastle-under-Lyme, Stone and Stafford. The Hundred also contains Stafford and Stone, which were renowned for shoe manufacturing, thought these industries attracted less workers from the countryside than did the bustling Potteries with its leisure-time attractions.
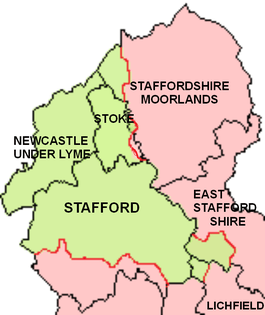
Abandoned although never abolished by legal statute, in 1894 the Hundred was made functionally obsolete with the establishment of urban districts and rural districts in Staffordshire.[8] Of the local government districts created in the 1974 re-organisation, Newcastle-Under-Lyme and Stoke-on-Trent (now a city and unitary authority) fall within Pirehill Hundred, as does the district (or borough) of Stafford except for its southern-most parishes. The districts of Staffordshire Moorlands, East Staffordshire and Lichfield only have one or two parishes each in the old Hundred.[9]
Population statistics

The population of the Hundred, its two divisions and its various parochial units is shown below:[10]
Pirehill North Division
| Parish | Pop. 1831 | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Adbaston | 601 | |
| Ashley | 825 | |
| Audley | 3,617 | |
| Balterley | 305 | Part of Barthomley parish, mostly Cheshire |
| Betley | 870 | |
| Biddulph | 1,987 | |
| Burslem | 12,714 | |
| Drayton in Hales | 737 | Part of parish, mostly in Shropshire |
| Eccleshall | 4,471 | Including Chapel and Hill Chorlton |
| High Offley | 759 | |
| Keele | 1,130 | |
| Madeley | 1,190 | |
| Maer | 505 | |
| Mucklestone | 964 | |
| Newcastle-under-Lyme | 8,192 | |
| Norton-in-the-Moors | 2,407 | |
| Standon | 420 | |
| Stoke-on-Trent | 37,220 | |
| Swynnerton | 791 | |
| Tentham | 2,344 | |
| Whitmore | 281 | |
| Wolstanton | 10,853 | |
| Total | 93,183 | |
Pirehill South Division
| Parish | Population in 1831 | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Abbots Bromley | 1621 | |
| Barlaston | 514 | |
| Blithfield | 468 | |
| Chartley Holme | 9 | Extra-parochial area |
| Chebsey | 414 | Including Chebsey: 377 and Cold Borton: 37 |
| Colton | 675 | |
| Colwich | 874 | |
| Cresswell | 11 | Extra-parochial area |
| Ellenhall | 286 | |
| Gayton | 296 | |
| Ingestre | 116 | |
| Milwich | 551 | |
| (Newcastle-under-Lyme) | - | Included under North Division |
| Ranton | 273 | |
| Ranton Abbey | 17 | Extra-parochial area |
| Sandon | 558 | |
| Seighford | 898 | |
| Stafford | 8,512 | See breakdown below |
| Stone | 7,808 | |
| Stowe | 1,283 | |
| Tixall | 176 | |
| Weston under Trent | 498 | |
| Yarlet | 21 | Extra-parochial area |
| Total | 25,879 | |
Parochial areas in the parliamentary borough of Stafford (as from 1832)
| Parish | Population in 1831 | Hundred |
|---|---|---|
| Parishes within the municipal borough | ||
| St Mary (part) and St Chad | 6,956 | Pirehill |
| Castle Church | 1,374 | Cuttleston |
| Townships of St. Mary's parish outside the municipal borough | ||
| Tillington | 42 | Pirehill |
| Hopton & Coton | 642 | Pirehill |
| Worston | 25 | Pirehill |
| Marston | 119 | Pirehill |
| Salt & Enson | 533 | Pirehill |
| Whitgreave | 195 | Pirehill |
| Total | 9,886 | |
| Total within Pirehill Hundred | 8,512 | |
| Total within Cuttleston Hundred | 1,374 | |
The Northern Division (91,148 acres) and Southern Division (110,345 acres) were roughly similar in area, but as indicated above, the Northern Division had the vast majority of the population. The Southern Division encompassed an area around Stafford and Stone, now within Stafford District (but not its western-most parishes), with the remainder falling in the Northern Division.[11]
Notes
- See History, Gazetteer and Directory of Staffordshire by William White (1834)
- The English Hundred Names, by Olof Anderson, Lund (Sweden), 1934. Page xxxiii
- See Ordnance Survey map at 52°52'42"N 2°9'30"W. The hill is just west of Pirehill Lane, near the farm and fire station of the same name
- The English Hundred Names, by Olof Anderson, Lund (Sweden), 1934. Page 144
- The English Hundred Names, by Olof Anderson, Lund (Sweden), 1934. Page 147
- A topographical history of Staffordshire, by William Pitt, pub J. Smith (Newcastle -under-Lyme), 1817; page 13
- Imperial Gazetteer of England and Wales, by John Marius Wilson, 1872
- See Staffordshire in http://www.visionofbritain.org.uk
- See www.staffordshire.gov.uk
- See History, Gazetteer and Directory of Staffordshire by William White (1834)
- Imperial Gazetteer of England and Wales, by John Marius Wilson, 1872 and www.staffordshire.gov.uk