Picoplatin
Picoplatin is a platinum-based antineoplastic agent in clinical development by Poniard Pharmaceuticals (previously NeoRx) for the treatment of patients with solid tumors.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
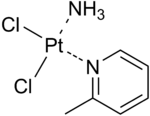
| IUPAC name
azane; 2-methylpyridine; platinum(2+); dichloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.205.233 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10Cl2N2Pt | |
| Molar mass | 376.14 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
In Phase I and Phase II clinical trials, picoplatin demonstrated activity in a variety of solid tumors, including lung, ovarian, colorectal and hormone-refractory prostate cancer.[2] However, in Phase III trials, picoplatin failed to hit its primary endpoint for advanced small cell lung cancer.[3] Hopes are now pinned on its use for metastatic colorectal cancer.[4]
References
- Wheate, Nial J. (2010). "The status of platinum anticancer drugs in the clinic and in clinical trials" (PDF). Dalton Transactions. 39: 8113. doi:10.1039/C0DT00292E. PMID 20593091.
- Picoplatin Clinical Results, Poniard Pharmaceuticals
- Poniard shares crash on Phase III picoplatin failure, fiercebiotech.com, November 16, 2009
- http://www.genengnews.com/specialreports/sritem.aspx?oid=69418732 Nov 2009
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.