Pexidartinib
Pexidartinib, sold under the brand name Turalio, is a kinase inhibitor drug for the treatment of adults with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) associated with severe morbidity or functional limitations and not amenable to improvement with surgery.[2][3][4][5]
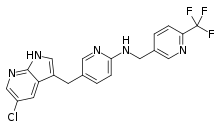 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Turalio |
| Other names | PLX-3397 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a619050 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H15ClF3N5 |
| Molar mass | 417.82 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
On 2 August 2019, it was approved by U.S. FDA for treatment of giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath (GC-TS).[2][6][7]
Common side effects are increased lactate dehydrogenase (proteins that helps produce energy in the body), increased aspartate aminotransferase (enzymes that are mostly in the liver but also in muscles), loss of hair color, increased alanine aminotransferase (enzymes that are primarily in the liver and kidney) and increased cholesterol.[2] Additional side effects include neutropenia (low level of white blood cells that help the immune system defend against disease and infection), increased alkaline phosphatase (enzymes that are mostly in the cells of bone and the liver), decreased lymphocytes (white blood cells that help the immune system defend against disease and infection), eye edema (swelling around the eyes), decreased hemoglobin (protein in red blood cells that carry oxygen), rash, dysgeusia (altered sense of taste) and decreased phosphate (electrolytes that help with energy).[2]
The US prescribing information for pexidartinib includes a boxed warning about the risk of serious and potentially fatal liver injury.[2][3]
Pexidartinib is available in the US only through the Turalio Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program.[2]
History
The approval of pexidartinib was based on the results of a multi-center international clinical trial of 120 subjects, 59 of whom received placebo.[2] The primary efficacy endpoint was the overall response rate (ORR) analyzed after 25 weeks of treatment.[2] The clinical trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in ORR in subjects who received pexidartinib, with an ORR of 38%, compared to no responses in subjects who received placebo.[2] The complete response rate was 15% and the partial response rate was 23%.[2] A total of 22 out of 23 responders who had been followed for a minimum of six months following the initial response maintained their response for six or more months, and a total of 13 out of 13 responders who had been followed for a minimum of 12 months following the initial response maintained their response for 12 or more months.[2]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted the application for pexidartinib breakthrough therapy designation, orphan drug designation, and priority review designation.[2] The FDA granted the approval of Turalio to Daiichi Sankyo.[2]
References
- "Pexidartinib (Turalio) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 28 October 2019. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- "FDA approves first therapy for rare joint tumor". FDA (Press release). 2 August 2019. Retrieved 17 August 2019.

- "Turalio- pexidartinib capsule". DailyMed. 7 August 2019. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- "Pexidartinib Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. 19 August 2019. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- "Microglial Magic: Drug Wipes Them Out, New Set Appears". Alzforum. 18 April 2014. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- "Drug Trials Snapshots: Turalio". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2 August 2019. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "Drug Approval Package: Turalio". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 22 July 2019. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
Further reading
- "Pexidartinib". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Bethesda, MD: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. October 2019. PMID 31869194. NBK551730.
- Lamb YN (November 2019). "Pexidartinib: First Approval". Drugs. 79 (16): 1805–1812. doi:10.1007/s40265-019-01210-0. PMC 7044138. PMID 31602563.
- Roskoski R (February 2020). "Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2020 update". Pharmacol. Res. 152: 104609. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104609. PMID 31862477.
External links
- "Pexidartinib". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- New ATC . WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology