Petit Luxembourg
The Petit Luxembourg (French pronunciation: [pəti lyksɑ̃buːʁ];"Little Luxembourg") is a French hôtel particulier, currently the residence of the president of the French Senate. It is located at 17–17 bis, rue de Vaugirard, just west of the Luxembourg Palace, which currently serves as the seat of the Senate, in the 6th arrondissement of Paris. Originally built around 1550 to the designs of an unknown architect, it is especially noted for the surviving Rococo interiors designed in 1710–1713 by the French architect Germain Boffrand.[1] Further west, at 19 rue de Vaugirard, is the Musée du Luxembourg.[2]
| Petit Luxembourg | |
|---|---|
 West wing of the Petit Luxembourg | |
 Location within Paris | |
| General information | |
| Type | hôtel particulier |
| Location | Paris, France |
| Address | 17–17 bis, rue de Vaugirard |
| Coordinates | 48.849°N 2.3356°E |
| Current tenants | President of the French Senate |
| Construction started | c. 1550 |
| Renovated | 1710–1713 |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect |
|
Early history
The original sixteenth-century building is of obscure origin,[1] but became known as the Hôtel de Luxembourg after its acquisition in 1570 by François de Luxembourg, who in 1581 became Duc de Piney, Pair de France. Marie de Médicis purchased the hôtel in 1612 when she began acquiring property for the construction of the adjacent Luxembourg Palace. The old hôtel soon became known as the Petit Luxembourg to distinguish it from the larger building.[3]
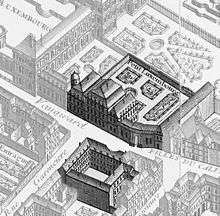
.jpg) Perspective view
Perspective view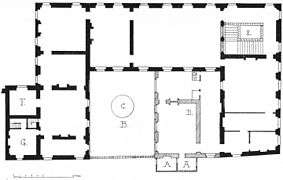 Floor plan with some later modifications made by Marie de Médicis
Floor plan with some later modifications made by Marie de Médicis
In 1627 Marie de Médicis gave the Petit Luxembourg to Cardinal de Richelieu, who occupied it while his own grand palace, the Palais-Cardinal, was constructed on the rue Saint-Honoré. Richelieu left the Petit Luxembourg to his niece, the Duchess of Aiguillon. It was inherited in turn by the Grand Condé, who left it to his son, Henri Jules de Bourbon-Condé.[3] The latter's widow, Anne of Bavaria, Princess Palatine, engaged the architect Germain Boffrand to enlarge and redecorate it between 1710 and 1713.[1][3]
Boffrand's alterations
Boffrand demolished the service buildings to the west of the courtyard, replacing them with a new wing for the Palatine officers. The new wing preserved the style of the old corps de logis to the east and incorporated vestiges of the Couvent des Filles-du-Calvaire, founded by Marie de Médicis in 1622. These can still be seen in the winter garden and the Mannerist interior of the Queen's Chapel. Between the street and the courtyard Boffrand added an entrance screen which connected the old to the new.[1] Its portal is flanked by Tuscan columns on the concave courtyard side and Ionic on the convex street side. The upper floor contains a corridor connecting the east and west wings.
Although Boffrand preserved the façades of the older wing, he completely redesigned the interior. A modest vestibule with Ionic columns leads directly to a grand two-storey stair hall decorated on the upper floor with pilasters of the Composite order, elaborate carvings, and a coffered vault. The staircase, much admired in its day, sweeps up to the piano nobile in a single flight, its grandeur enhanced with balustrades of stone, rather than the more usual wrought iron. The princess's apartments lead directly off the landing. The first room no longer has the original décor, but the next (the Salon des Tapisseries) still has Boffrand's ceiling, cornices, and frieze. The following room, the Grand Salon also retains these elements.[1]
In large rooms, such as the stair hall and the Grand Salon, Boffrand's unit of design was not the wall (as seen with Pierre Lepautre), but rather the entire room. Each wall consisted of a great arcade, which "pulled the space together and subordinated doors, windows, and mirrors to a regular rhythm."[4] The focus of the décor was high in the spandrels between the arches, not in the wall panels as seen with Lepautre. This principle, first employed by J. H. Mansart at the Grand Trianon, kept the main part of the wall surface free for hangings, such as tapestries and paintings. The band of ornate spandrels running around the room achieves a unity, which is further emphasized by the slightly vaulted ceiling. Boffrand's decorative motifs, "the linked C-scrolls entwined with palmettes and festoons," are more similar to those of Jean Bérain than Lepautre.[4]
Boffrand also added another hôtel for the household, with kitchens and stables, on the other side of rue de Vaugirard; an underground passage linked the two residences.
 Boffrand's staircase
Boffrand's staircase- Grand Salon
Later history
During the French Revolution, from 6 October 1789 until their departure into exile on 20 June 1791, the Petit Luxembourg was the assigned residence of the Count of Provence (the future Louis XVIII of France) and his wife.
Under Napoleon, the Conseil d'État (Council of State) was seated at the Petit Luxembourg from 25 December 1799. Since 1958, the Petit Luxembourg has been the official residence of the president of the French Senate.
Images of the Petit Luxembourg
- Courtyard side of the entrance
- Winter garden
 Chapel (1622–1631)
Chapel (1622–1631)- Grand staircase, reflected in a mirror
- Stair hall ceiling with 1894 painting by Hippolyte Berteaux
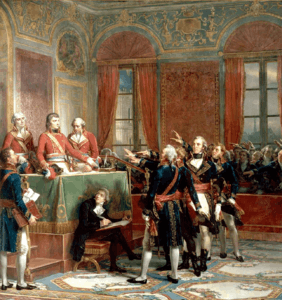 Installation of the Conseil d'Etat at the Petit Luxembourg, 25 December 1799, by Couder, 1856[7]
Installation of the Conseil d'Etat at the Petit Luxembourg, 25 December 1799, by Couder, 1856[7]- Napoleonic marble plaque inserted in 18th-century boiserie
- Office of the Senate President
 Garden fountain, 1905
Garden fountain, 1905- Garden
Notes
- Ayers 2004, p. 132.
- Ochterbeck 2009, p. 202.
- Le « Petit Luxembourg » at the French Senate website.
- Kalnein 1995, p. 61.
- The north service wing (with kitchens and stables) was demolished after 1909, since it is shown on a 1910 map (Hustin 1910, p. XXIV).
- Boffrand 1745, plate XLV.
- "Bicentenaire du Sénat : Conseil d'État" at the French Senate website.
Bibliography
- Ayers, Andrew (2004). The Architecture of Paris. Stuttgart; London: Edition Axel Menges. ISBN 9783930698967.
- Boffrand, Germain (1745). Livre d'architecture. Paris. Copy at INHA
- Hustin, Arthur (1910). Le Luxembourg, son histoire domaniale, architecturale, décorative et anecdotique. Des premiers siècles à l'année 1611. Paris: Imprimérie du Sénat. OCLC 888816591, 563876634. Copy at HathiTrust.
- Kalnein, Wend von (1995). Architecture in France in the Eighteenth Century. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 9780300060133.
- Ochterbeck, Cynthia Clayton, editor (2009). The Green Guide Paris. Greenville, South Carolina: Michelin Maps and Guides. ISBN 9781906261375.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Petit Luxembourg. |
- "The Petit Luxembourg" at the website of the French Senate
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)