Pegna-Bonmartini Rondine
The Pegna-Bonmartini Rondine, or Pegna Rondine, is a single-seat ultralight sport aeroplane designed by Giovanni Pegna and built by Piaggio in Italy during 1923.[1][2]
| Rondine | |
|---|---|
| Role | Single-seat ultralight sport aeroplane |
| National origin | Italy |
| Manufacturer | Piaggio & Co[1][2] |
| Designer | Giovanni Pegna[1][2] |
| First flight | 1923[1][2] |
| Number built | 1[1][2] |
Development
Probably inspired by the success of entrants to the Lympne ultra-light aeroplane trials, Signore Pegna designed the Rondine to take advantage of small low-powered light weight engines available at the time.[1][2]
Design
The Rondine is a mid-winged cantilever monoplane built primarily of wood with fabric-covered wings. The fuselage is noteworthy in being clinker or carvel built similar to boat building techniques. The single piece two-spar wings are of low aspect ratio and relatively thick so external bracing is unnecessary. Control is provided by conventional ailerons and rudder, with a small fixed fin and an all-flying tailplane and elevator mounted above the rear fuselage forward of the fin. The fixed undercarriage consists of braced trousered main legs and a tail-skid.[1][2]
Several powerplants were tested with poor results until the 404 cc (24.65 cu in) ABC 8 hp, used successfully in other contemporary ultra-light aircraft, fitted with a 3:1 reduction gear, was found to be satisfactory.[1][2]
Accommodation for the pilot is in an open cockpit, set at mid chord, with padded edges, protected from the slipstream by a three-piece windscreen.[1][2]
Specifications (Rondine)
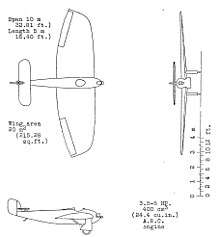
Data from Flight, 23 December 1923[1][2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 6 m (19 ft 8 in)
- Wingspan: 10 m (32 ft 10 in)
- Wing area: 20 m2 (220 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 5
- Empty weight: 131 kg (289 lb)
- Gross weight: 211 kg (465 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × ABC 8hp 2-cyl. air-cooled horizontally opposed piston engine, 6.0 kW (8 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed pitch propeller with 3:1 reduction gearing
Performance
- Maximum speed: 70 km/h (43 mph, 38 kn)
- Landing speed: 40 km/h (25 mph; 22 kn)
- Lift-to-drag: 14
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
References
- "THE PEGNA "RONDINE" LIGHT MONOPLANE 400 c.c A.B.C. Engine" (PDF). Flight: 779. 27 December 1923. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
- "THE PEGNA "RONDINE" LIGHT MONOPLANE 400 c.c A.B.C. Engine" (PDF). Flight: 780. 27 December 1923. Retrieved 17 October 2013.