Paternò–Büchi reaction
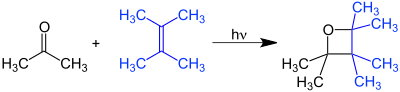
The Paternò–Büchi reaction, named after Emanuele Paternò and George Büchi who established its basic utility and form, is a photochemical reaction that forms four-membered oxetane rings from an excited carbonyl and reacting with an alkene.[1] [2] [3]
| Paternò–Büchi reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Emanuele Paternò George Büchi |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | paterno-buechi-reaction |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000083 |
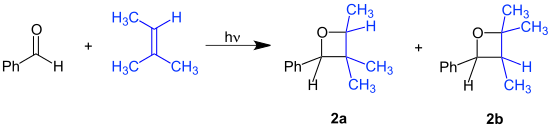
With substrates benzaldehyde and 2-methyl-2-butene the reaction product is a mixture of structural isomers:
Another substrate set is benzaldehyde and furan [4]
The alternative strategy for the above reaction is called the Transposed Paternò−Büchi reaction.
The aza-equivalent of the above reactoin is the Aza Paternò−Büchi reaction.
References
- E. Paterno, G. Chieffi (1909). Gazz. Chim. Ital. 39: 341.
- G. Büchi; Charles G. Inman; E. S. Lipinsky (1954). "Light-catalyzed Organic Reactions. I. The Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds with 2-Methyl-2-butene in the Presence of Ultraviolet Light". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (17): 4327–4331. doi:10.1021/ja01646a024.
- Thorsten Bach (1998). "Stereoselective Intermolecular [2 + 2]-Photocycloaddition Reactions and Their Application in Synthesis". Synthesis. 1998: 683–703. doi:10.1055/s-1998-2054.
- Paternò–Büchi Reaction as a Demonstration of Chemical Kinetics and Synthetic Photochemistry Using a Light Emitting Diode Apparatus Matthew P. Thompson, Jonathan Agger, and Lu Shin Wong Journal of Chemical Education 2015 92 (10), 1716-1720 doi:10.1021/acs.jchemed.5b00129
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.