Papilio aegeus
Papilio aegeus, the orchard swallowtail butterfly or large citrus butterfly is a species of butterfly from the family Papilionidae, that is found in eastern Australia and Papua New Guinea.
| Orchard swallowtail butterfly | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Female, Cairns, Queensland | |
 | |
| Male, Melbourne Zoo | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | P. aegeus |
| Binomial name | |
| Papilio aegeus Donovan, 1805 | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
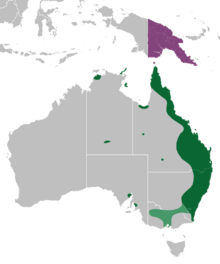 | |
| Range of orchard swallowtail P. a. aegeus; P. a. ormenus P. a. aegeus temporary range | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The larvae of this species are sometimes considered a pest, due to their feeding on citrus leaves in suburban gardens.[1]
Description

Both male and female have black forewings with a white stripe, though there is more white overall on the female forewing. The hindwing is again black, and there is a white swath through the middle. Here the markings differ in that the female has chains of red to orange and blue crescents toward the edge. The markings on the underside are similar to those on top. The body is black.[2] The wingspan is about 140 millimetres (5.5 in) in females and 120 millimetres (4.7 in) in males,[3][4][5] making it rather large overall and the largest butterfly commonly seen in at least part of its range.[3]
Despite being a swallowtail, which group derives its name from the distinctive tails on the hindwing, this characteristic is entirely absent.
Distribution
Papilio aegeus can be found in every state in Australia except Tasmania. Western Australia has well established colonies in the Albany region. There are enthusiasts who are promoting the controlled propagation of eggs and caterpillars in Western Australia, but it is generally found in eastern Australia. It is especially common in Queensland and is the largest butterfly commonly found in Brisbane[3] where there are many citrus trees, on which the larvae feed.[4] During summer, the distribution is temporarily extended to Victoria.
The subspecies P. a. ormenus is found on Papua New Guinea and Thursday Island.
A differentiating feature between males of P. a. aegeus and P. a. ormenus is that P. a. aegeus males have a red spot on the above side of each hindwing, which is absent in the males of P. a. ormenus.
Other subspecies occur on islands in the Banda Sea and the Bismarck Sea.
Variation
Subspecies
- P. a. aegeus — Cape York - East Victoria, South Australia
- P. a. adrastus C. & R. Felder, [1864] — Banda Group
- P. a. aegatinus Rothschild, 1908 — Noemfoor Island
- P. a. goramensis Rothschild, 1908 — Goram Island
- P. a. keianus Rothschild, 1896 — Kai Island
- P. a. kissuanus Rothschild, 1908 — Watubela Island, Goram Island
- P. a. oritas Godman & Salvin, 1879 — New Ireland, New Hanover
- P. a. ormenulus Fruhstorfer, 1902 — Fergusson Island
- P. a. ormenus Guérin-Méneville, [1831] — Aru, Missol, Salawari, Jobi, Waigen, West Irian, Papua, New Guinea, Trobriand, D'Entrecastreaux, Woodlark, Lousiades, Torres Straits Is
- P. a. othello Grose-Smith, 1894 — Biak
- P. a. websteri Grose-Smith, 1894 — New Britain
Forms
Females of both P. a. aegeus and P. a. ormenus have three forms; regular, pale and dark. The pale form has yellow spots on the hindwings, compared to the usual red spots. The forewings are almost completely white. The front wings of the dark form are almost completely black and the hindwings have a smaller white patch.
 P. a. aegeus (male)
P. a. aegeus (male)- P. a. ormenus (male)
- Dark form (female)
Life cycle
Egg
The female lays creamy white, smooth, spherical eggs with an approximate diameter of 0.5 millimetres individually on the upper surface of the leaves and shoots of host plants,[6] primarily tropical to subtropical members of the family Rutaceae,[7] which includes introduced and native citrus. The eggs will hatch about one week later.[7]
Larva
The early instars are brown with three white patches, one the: thorax, above the first pair of prolegs, and one on 8th and 9th segment of the abdomen. It is lined with black and white tubercles.[1] The larva only feed on their food plants, citrus. Feeding usually takes place during the day and resting on the upperside of leaves during the night, resembling fresh bird droppings.[3]
The later instars are green with irregular white, yellow or brown markings that run diagonally up/back from the bottom edge of the thorax to the 4th and 6th segments. After about four weeks, the larva may have reached a length of 60 millimetres (2.4 in) and be ready to pupate.[3]
The larvae are sometimes parasitised by other parasitic insects. Like other swallowtail butterflies, when disturbed, the caterpillar erects its bright red osmeterium from behind the head, releasing the smell of citrus, to drive predators away.[3]
Pupa
The pupa is coloured in cryptic grey, green or brown, depending on the colour of the stem it is attached to. The chrysalis is fastened to a stem of the host plant by means of a cremaster. A thin girdle of silk keeps the head end of the chrysalis uppermost during pupation.[3][6][8] Depending on the season, an imago will emerge from the chrysalis, approximately one to six months later.[1]
Images of life cycle
 An early instar caterpillar
An early instar caterpillar A later instar caterpillar
A later instar caterpillar- Copulating P. a. aegeus in Melbourne Zoo - female above, male below
Larval food plants

Native
The larvae are known to naturally use species the following Australian-native taxa as food plants: Boronia, Citrus, Clausena, Dinosperma, Eriostemon, Flindersia, Geijera, Halfordia, Leionema, Micromelum, Philotheca, Zanthoxylum and Zieria
Introduced
In addition, larvae have also been recorded using introduced species of the following taxa as food plants: Choisya, Citrus, Murraya, Poncirus and Zanthoxylum.
Taxonomy
Papilio aegeus is the nominal member of the aegeus species group. The clade members are:
- Papilio aegeus Donovan, 1805
- Papilio bridgei Mathew, 1886
- ? Papilio erskinei Mathew, 1886
- Papilio gambrisius Cramer, [1777]
- Papilio inopinatus Butler, 1883
- Papilio ptolychus Godman & Salvin, 1888
- Papilio tydeus C. & R. Felder, 1860
- Papilio weymeri Niepelt, 1914
- Papilio woodfordi Godman & Salvin, 1888
References
- http://lepidoptera.butterflyhouse.com.au/papi/aegeus.html
- "Butterflycorner". Retrieved 2009-06-06.
- http://www.brisbaneinsects.com/brisbane_butters/Orch_butt.htm
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-02-28. Retrieved 2014-02-09.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "OzAnimals". Retrieved 2009-06-06.
- "PAPILIONIDAE in Australia". Retrieved 2009-06-06.
- "SOUTH AUSTRALIAN BUTTERFLIES". Archived from the original on 2007-08-27. Retrieved 2009-06-06.
- "Pupa or chrysalis". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2009-06-06.
Cited texts
- Braby, Michael F. The Complete Guide to Butterflies of Australia. Corrected edition. Collingwood, Victoria: CSIRO Publishing
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Papilio aegeus. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Papilio aegeus |
- Brisbane Insects
- PAPILIONIDAE in Australia
- Butterflies and other Invertebrates Club
- Butterflycorner Images from Naturhistorisches Museum Wien