Oxyclozanide
Oxyclozanide is a salicylanilide anthelmintic. It is used in the treatment and control of fascioliasis in ruminants mainly domestic animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats. It mainly acts by uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in flukes.[1] Along with niclosamide, another tapeworm drug, it has been recently found to display "strong in vivo and in vitro activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)".[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
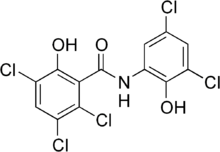
| IUPAC name
2,3,5-Trichloro-N-(3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-6-hydroxybenzamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.186 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H6Cl5NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 401.45 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| QP52AG06 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- CID 16779 from PubChem
- Rajamuthiah, Rajmohan; Fuchs, Beth Burgwyn; Conery, Annie L.; Kim, Wooseong; Jayamani, Elamparithi; Kwon, Bumsup; Ausubel, Frederick M.; Mylonakis, Eleftherios (2015). "Repurposing Salicylanilide Anthelmintic Drugs to Combat Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus". PLoS ONE. 10 (4): e0124595. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0124595. PMC 4405337. PMID 25897961.
- Oxyclozanide MSDS
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.