Operation Desert Rat
Operation Desert Rat (16 February – 3 April 1971) was a diversionary attack by a Laotian irregular regiment upon the crucial communist supply line, the Ho Chi Minh trail. Carried out by the Central Intelligence Agency sponsored Groupement Mobile 33, the Desert Rat offensive struck the rear of the 50,000 North Vietnamese troops combating Operation Lam Son 719 beginning on 16 February 1971. With 16 daily tactical air sorties and airborne forward air controllers available, the Desert Rat guerrillas used their hilltop position near Moung Phine to spot targets for bombing. It also raided, skirmishing 110 times, killing 121 communist soldiers, and sowing 1,500 mines along North Vietnamese lines of communication. On 20 March, it was assaulted by two communist battalions. The major threat of Lam Son 719 ended, leaving the communists free to deal with the minor one of Desert Rat. However, the guerrillas split into three columns and exfiltrated by 3 April 1971. The Royal Lao Government had lost control of the strategic Bolovens Plateau to the communist invaders.
Overview
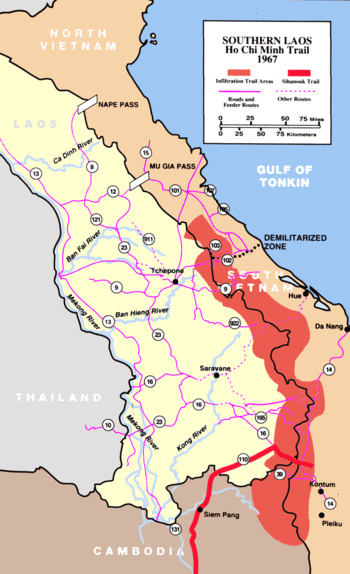
The Ho Chi Minh Trail was the key to the Second Indochina War. North Vietnam's People's Army of Vietnam depended on that logistics route to defeat South Vietnam. As a result, during 1969 and 1970, the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) urged its guerrilla battalions to raid the Trail to disrupt or interdict the supply lines. Eventually, the South Vietnamese launched Operation Lam Son 719 on 8 February 1971 in a failed incursion to cut the Trail. The South Vietnamese failure to sever those lines of communications did not end ground assaults on the Trail. Indeed, Operation Desert Rat would be such.[1][2][3]
Background
Operation Desert Rat was launched on 16 February 1971 as a diversion to Operation Lam Son 719. It followed immediately after Operation Silver Buckle, which ended on 11 February, and was meant to distract communist attention from Operation Lam Son 719.[4] If the operation succeeded in cutting the communist Route 23 supply line, it would starve out their troops on the Bolovens Plateau. Moreover, if the Lao and South Vietnamese linked up their forces, the North Vietnamese forces would be segmented from one another.[5]
Operation
Operation Desert Rat began at Ban Houei Mun, which had also been both the start line and the after action rendezvous for the defeated troops of Operation Silver Buckle. When the regimental-size Groupement Mobile 33 (GM 33) mustered there, it was exposed to accounts of PAVN ferocity in the Silver Buckle fighting before being helilifted into action. As GM 33's troops loaded up at 0730 hours of 16 February 1971 on 14 helicopters of the 21st Special Operations Squadron, they came under communist rocket and mortar fire on the landing zone. However, they succeeded in departing on their mission.[4]
With 16 daily sorties of tactical air power taking advantage of the guerrillas' air superiority, and forward air controllers to direct the strikes, GM 33 had overhead cover. The CIA-sponsored guerrilla regiment landed 15 kilometers southwest of the communist stronghold of Moung Phine. That same day, the Royalist irregular military GM 33 moved to jungled high ground between Routes 23 and 238. From their perch above the two communist lines of communication, the Royalists could fire on any communist traffic. GM 33 settled in to call in air strikes on any targets they espied, and to disrupt the communist rear with forays. Air strikes destroyed 39 PAVN supply trucks and set off 221 fires or secondary explosions while also cratering the road. In 110 skirmishes, the GM 33 irregulars reported killing 121 communists. The Royalists also sowed 1,500 mines along the communist-held roads. The guerrilla regiment would spend over a month in their position in the rear of the 50,000 communists opposing the South Vietnamese invasion, Lam Son 719.[4][6]
On 20 March 1971, GM 33 was slated to move down from its hilltop strongpoint and attack Moung Phine. Half an hour before their scheduled departure, GM 33 was struck by heavy weapons fire followed by an attack by two PAVN battalions. GM 33 held, but its commander lost radio contact with some of the subordinate units. After dark, guerrilla patrols began to infiltrate the Moung Phine Valley.[4]
Operation Lam Son 719 ended on 25 March. With that major distraction gone, the equivalent of a full Army Corps was freed to turn on the irregular regiment. Savannakhet Unit of the CIA, which was controlling the action, radioed in withdrawal plans for GM 33. However, the guerrillas had already split into three columns to return to base. Two of the columns rendezvoused at Moung Phalane on 29 March 1971. The third made it back to Savannakhet.[4]
Results
During the operation, GM 33 troops had recovered a list of 21 communist espionage agents in Moung Phalane from the corpse of a North Vietnamese military intelligence officer. All 21 agents were subsequently arrested by the Royalists while they held that town.[7]
Aftermath
On 3 April 1971, GM 33 moved to the rear at Nong Saphong. They left Moung Phalane defended by two battalions of GM 30.[7]
In the wake of Lam Son 719, Silver Buckle, and Desert Rat, the PAVN extended its territory westward into Laos toward the Kingdom of Thailand to better defend the Trail. They occupied all the usual short takeoff and landing airstrips usually used by the Royalists for their military operations against Moung Phine—Muong Phalane, Attopeu, Ban Houei Sai, Salavan, Paksong, Ban Thateng.[8] The Pathet Lao garrisoned the newly conquered Plateau, backed by three PAVN battalions.[5]
Notes
- Conboy, Morrison, pp. 289–291.
- Castle, pp. 107–110.
- Nalty, pp. 6, 151.
- Conboy, Morrison, p. 290.
- Anthony, Sexton, p. 342.
- Nalty, p. 150.
- Conboy, Morrison, p. 291.
- Nalty, pp. 150–151.
References
- Anthony, Victor B. and Richard R. Sexton (1993). The War in Northern Laos. Command for Air Force History. OCLC 232549943.
- Castle, Timothy N. (1993). At War in the Shadow of Vietnam: U.S. Military Aid to the Royal Lao Government 1955–1975. ISBN 0-231-07977-X.
- Conboy, Kenneth and James Morrison (1995). Shadow War: The CIA's Secret War in Laos. Paladin Press. ISBN 978-1-58160-535-8.
- Nalty, Bernard C. (2005). The War Against Trucks: Aerial Interdiction In Southern Laos 1968–1972. Air Force History and Museums Program. ISBN 978-1-47755-007-6.