Musashimurayama, Tokyo
Musashimurayama (武蔵村山市, Musashi-murayama-shi) is a city located in the western side of Tokyo, Japan. As of 1 February 2016, the city had an estimated population of 70,694, and a population density of 4,610 people per km². The total area of Musashimurayama is 15.32 square kilometres (5.92 sq mi).
Musashimurayama 武蔵村山市 | |
|---|---|
Musashimurayama City Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
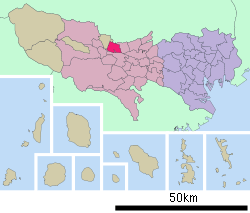 Location of Musashimurayama in Tokyo | |
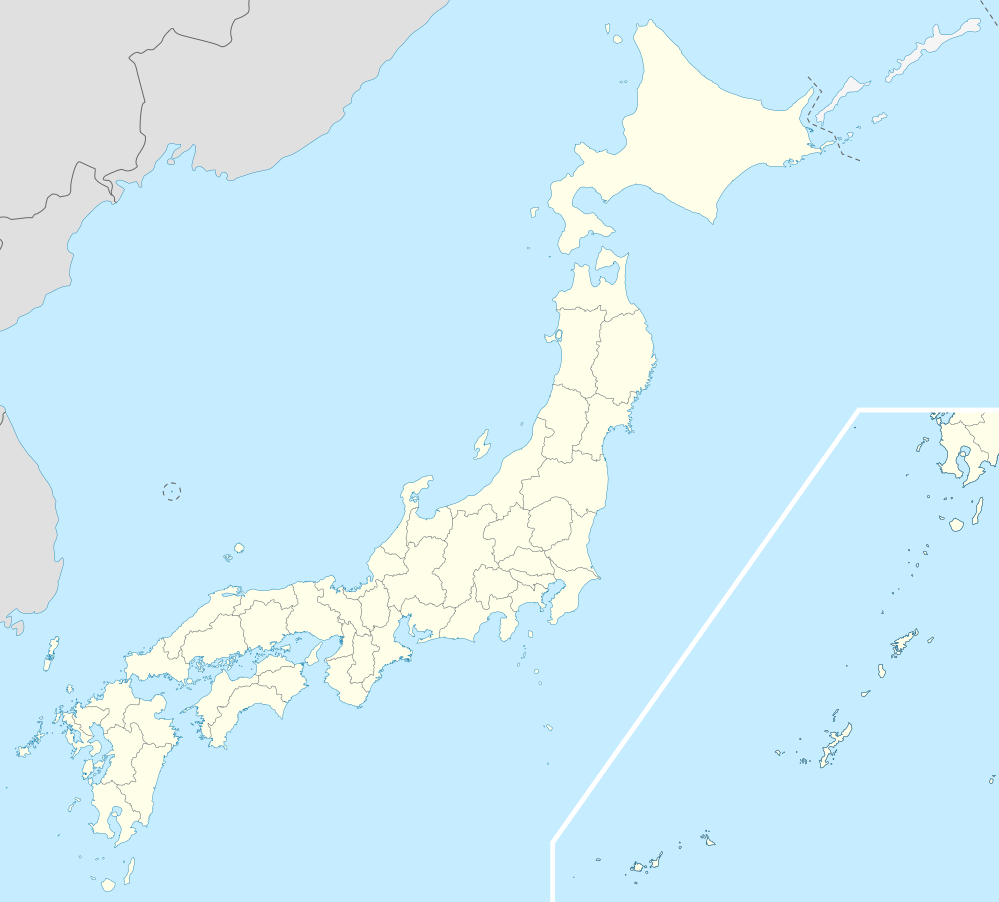 Musashimurayama | |
| Coordinates: 35°45′17.4″N 139°23′14.5″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Tokyo |
| Area | |
| • Total | 15.32 km2 (5.92 sq mi) |
| Population (February 2016) | |
| • Total | 70,649 |
| • Density | 4,610/km2 (11,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| Symbols | |
| • Tree | Celtis sinensis |
| • Flower | Camellia sinensis |
| • Bird | Japanese white-eye |
| Phone number | 042-565-1111 |
| Address | 1-1-1 Honmachi, Musashimurayama-shi, Tokyo 208-8501 |
| Website | www |
Geography
Musashimurayama is located in north-central Tokyo Metropolis, bordered by Saitama Prefecture to the north. Upstream tributaries of the Arakawa River and Tama River flow through the city.
Surrounding municipalities
- Tokyo Metropolis
- Saitama Prefecture
History
The area of present-day Musashimurayama was part of ancient Musashi Province. In Meji era, the area was organized into four villages within Kitatama District in Kanagawa Prefecture.
Kitatama District was transferred to the administrative control of Tokyo Metropolis on April 1, 1893. The village of Murayama was created on April 1, 1917 and was elevated to town status on November 3, 1954. The population of the town grew extremely rapidly in the 1960s with the development of public housing. Murayama was elevated to city status on November 3, 1970 and was named Musashimurayama.
Economy
The area of Musashimurayama was traditionally a center for cotton and textile production. The area remains largely agricultural, although a significant portion of the population commutes to downtown Tokyo.
Musashimurayama was the location of a Nissan automobile assembly plant, originally opened in 1962 by the Prince Motor Company. It closed in March 2001 as part of the Nissan Revival Plan announced in 1999.[1] It is now a museum called Carest Murayama, next to the Aeon Mall Musashi Murayama Megamall occupying a 213,252 square foot facility[2][3]
Education
- Musashimurayama has eight public elementary schools and four public middle schools, and one combined public elementary/middle school, all operated by the city government.
- The Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education operated the three public high schools in the city, as well as one special education school.
- Tokyo Keizai University - Musashimurayama campus
Transportation
Railway
- Musashimurayama is not served by any passenger rail services.
Highway
- Musashimurayama is not served by any expressways or national highways.
Twin towns and sister cities
![]()
References
- 日産村山工場跡地 [Site of former Nissan factory] (in Japanese). Japan: City of Musashimurayama. 2010-04-16. Archived from the original on 2010-04-10. Retrieved 2015-07-22.
- History of old Musashimurayama factory Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- http://www.nissan-global.com/EN/DOCUMENT/PDF/AR/2003/ar2003_12.pdf
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Musashimurayama, Tokyo. |
- Musashimurayama City Official Website (in Japanese)