Mohol bushbaby
The Mohol bushbaby (Galago moholi) is a species of primate in the family Galagidae which is native to mesic woodlands of the southern Afrotropics. It is physically very similar to the Senegal bushbaby, and was formerly considered to be its southern race. The two species differ markedly in their biology however, and no hybrids have been recorded in captivity.[3]
| Mohol bushbaby[1] | |
|---|---|
_(22851755208).jpg) | |
| Mohol bushbaby at Kruger National Park, South Africa | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Strepsirrhini |
| Family: | Galagidae |
| Genus: | Galago |
| Species: | G. moholi |
| Binomial name | |
| Galago moholi A. Smith, 1836 | |
 | |
Description
The Mohol bushbaby is a medium size species with a head-and-body length of 15 cm (6 in) and a tail of 23 cm (9 in).The head is broad, with a short muzzle, orange eyes and diamond-shaped black eye-rings. The nose-stripe is whitish and the ears are large and grey. The dorsal surface of the body has a greyish-brown pelage, and the underparts are white, sometimes with a yellowish tinge. The flanks, inside of the limbs, hands and feet are yellowish. The fingers and toes have spatulate tips. The tail is darker than the rest of the fur but is not very bushy.[4]
Range
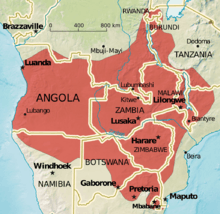
It is found in Angola, Botswana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe.[5] Perhaps also present in Rwanda and Burundi.[2]
Habitat
Surprisingly, breeding populations of this species are to be found in the suburbs of Johannesburg and Pretoria. Some of these were originally escaped or released pets, while others have migrated from warmer regions.[6]
Ecology
The Mohol bushbaby feeds predominantly on insects and gum. The gum is an exudate from Acacia trees that oozes out of punctures made by insects. The most favoured gum-trees are sweet thorn (Acacia karroo) and umbrella thorn (Vachellia tortilis). In the winter, the bushbaby moves between gum trees across the ground, but in the wet summer season, it usually travels arboreally, and consumes a much higher percentage of invertebrates. Feeding takes place soon after sunset, and then again throughout the night spasmodically.[4]
Races
Several authors recognize two races:[3][5]
- G. m. moholi – Moholi lesser bushbaby
- Range: eastern part of range, westwards to western Zambia, where it intergrades with bradfieldi
- G. m. bradfieldi Roberts, 1931 – Namibia bushbaby
- Range: Waterberg in Namibia northwards to southern Angola, and eastwards to northern Botswana including Makgadikgadi Pan, and the Western Province of Zambia[7]
References
- Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 125. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- Bearder, S.; Svensson, M.; Butynski, T.M. (2019). "Galago moholi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T8788A17963285. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- Kingdon, Jonathan; Happold, David; Butynski, Thomas; Hoffmann, Michael; Happold, Meredith; Kalina, Jan (2013). Mammals of Africa. London: Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 430–433. ISBN 9781408189962.
- Jonathan Kingdon; David Happold; Thomas Butynski; Michael Hoffmann; Meredith Happold; Jan Kalina (2013). Mammals of Africa. A&C Black. pp. 430–434. ISBN 978-1-4081-8996-2.
- Grubb, P.; Butynski, T. M.; Oates, J. F.; Bearder, S. K.; Disotell, T. R.; Groves, C. P.; Struhsaker, T. T. (2003). "Assessment of the diversity of African primates". International Journal of Primatology. 24 (6): 1301–1357. doi:10.1023/B:IJOP.0000005994.86792.b9.
- "Bushbaby SOS". Fairly Wild. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- Meester, J. A. J.; Rautenbach, I. L.; Dippenaar, N. J.; Baker, C. M. (1986). Classification of southern African mammals. Pretoria: Transvaal Museum Monograph # 5. ISBN 0907990061.
