Misasa, Tottori
Misasa (三朝町, Misasa-chō) is a town located in Tōhaku District, Tottori Prefecture, Japan. It is also home to the official treasure of Sanbutsu-ji, the Misasa Onsen, and Okayama Hospital.
Misasa 三朝町 | |
|---|---|
Town | |
Clockwise from top left: Misasa Spa, Sanbutsu Temple in Mount Mitoku, Mitoku River, Place of Team Hall (Jinsho no Yakata in Japanese), Misasa Art Museum | |
Flag | |
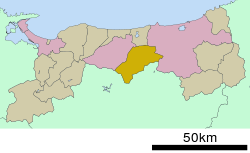 Location of Misasa in Tottori Prefecture | |
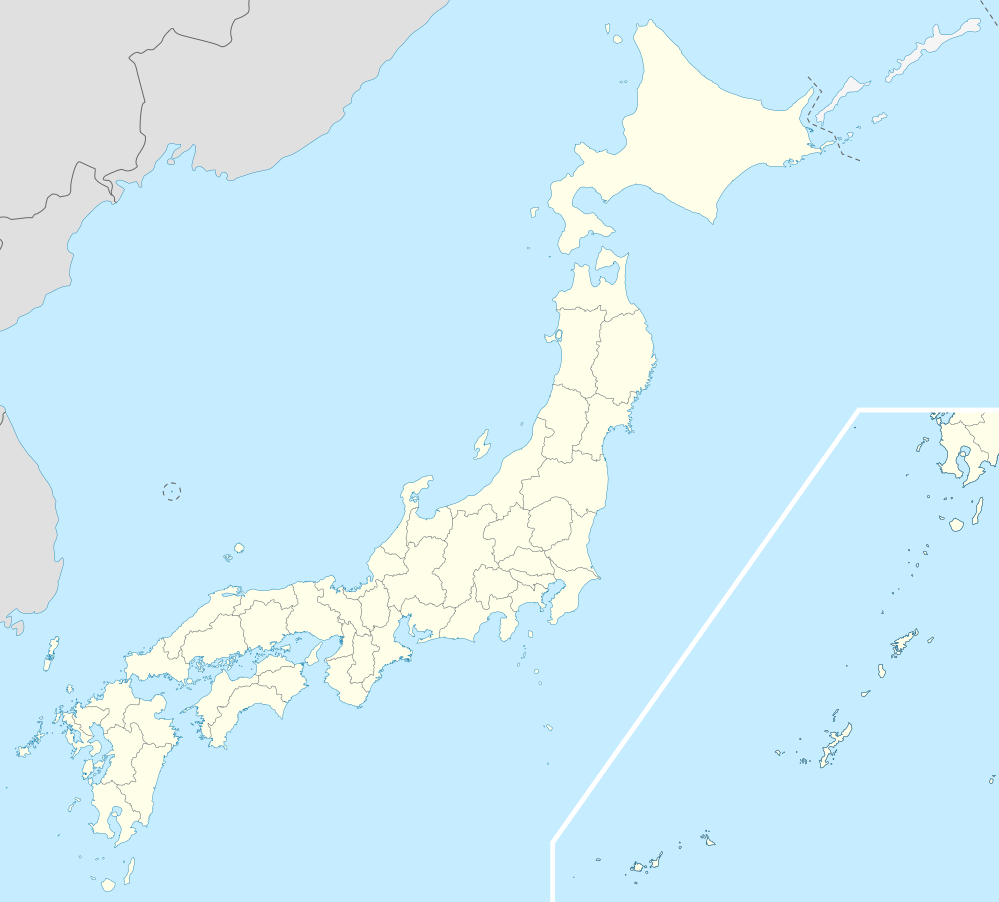 Misasa Location in Japan | |
| Coordinates: 35°25′N 133°52′E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Chūgoku San'in |
| Prefecture | Tottori Prefecture |
| District | Tōhaku |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Hidemitsu Yoshida (since November 1997) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 233.52 km2 (90.16 sq mi) |
| Population (June 1, 2016) | |
| • Total | 6,407 |
| • Density | 27.4/km2 (71/sq mi) |
| Symbols | |
| • Tree | Aesculus |
| • Flower | Rhododendron |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (JST) |
| City hall address | 999-2 Ōaza Ōze, Misasa-chō, Tottori-ken 682-0195 |
| Website | www |
The name "Misasa" (literally "three mornings") originates from the belief that one who stays to enjoy three mornings in the town's famous hot springs will find all of his ailments cured.
As of June 1, 2016, the town has an estimated population of 6,407 and a density of 27.4 persons per km². The total area is 233.46 km².
Misasa is for the most part a spa resort, boasting springs of radium-rich water, exhausting radon, a radioactive gas. It is believed that bathing one in such waters can be good for one's health, although there is no scientific consensus on whether doing so is detrimental or helpful to one's health (see Radiation hormesis). For this reason, the town of Misasa organizes a yearly Marie Curie festival – Marie Curie discovered radium.
The film Koitanibashi was shot in Misasa.[1]
Education
Primary schools
- Nishi Elementary School
- Higashi Elementary School
- Minami Elementary School
Junior high schools
- Misasa Junior High School
Universities
- Institute for Study of the Earth's Interior, Okayama University
Neighboring municipalities
- Tottori Prefecture
- Okayama Prefecture
- Kagamino
- Maniwa
Places of note
- Misasa Onsen
- A radium-rich hot spring.
- Oshika Valley
- It is named a special location, or "meishou" (名所) by the government, and is about 4 km long.
- A temple located on a cliff on the north face of Mount Mitoku, it is designated as one of the National Treasures of Japan.
Twin towns
Misasa is twinned with:
References
- HPriest (2011-11-12). "SPEED's Uehara Takako attends stage greeting for "Koitanibashi"". TokyoHive. Retrieved 2011-11-13.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Misasa, Tottori. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Misasa. |
- Official town website (in English)
- Official town website (in Japanese)

